数据结构之Trie
本文主要介绍Trie树的一些基本概念,转载自《数据结构之Trie》。
1. Trie树的基本概念
In computer science, a trie, also called digital tree and sometimes radix tree or prefix tree (as they can be searched by prefixes), is an ordered tree data structure that is used to store a dynamic set or associative array where the keys are usually strings.
在计算机科学中,一个Trie树,又称为数字树,有时候也被称为基数树(radix tree)或者前缀树(prefix tree,这是因为它们可以按前缀来进行查找)。它是一种有序的树形数据结构,通常用于存储动态集(dynamic set)或者关联数组(associative array),动态集与关联数组的键通常都是string类型。
Unlike a binary search tree, no node in the tree stores the key associated with that node; instead, its position in the tree defines the key with which it is associated.All the descendants of a node have a common prefix of the string associated with that node, and the root is associated with the empty string. Values are not necessarily associated with every node. Rather, values tend only to be associated with leaves, and with some inner nodes that correspond to keys of interest. For the space-optimized presentation of prefix tree, see compact prefix tree.
和二叉搜索树不一样,树中没有节点来存储与该节点所关联的键(key);相反,它在树中的位置定义了它与该节点关联的键。节点的所有后代与该节点所关联的字符串都有共同的前缀,并且根与空字符串关联。相反,值往往只与叶和一些内部节点关联。
下面是来自百度百科的介绍:
字典树,又称单词查找树,Trie树,是一种树形结构,是一种哈希树的变种。典型应用是用于统计,排序和保存大量的字符串(但不仅限于字符串),所以经常被搜索引擎系统用于文本词频统计。它的优点是:利用字符串的公共前缀来减少查询时间,最大限度地减少无谓的字符串比较,查询效率比哈希树高。
1.1 性质
它有3个基本性质:
-
根节点不包含字符,除根节点外每一个节点都只包含一个字符;
-
从根节点到某一节点,路径上经过的字符连接起来,为该节点对应的字符串;
-
每个节点的所有子节点包含的字符都不相同。
1.2 基本操作
其基本操作有:查找、插入和删除,当然删除操作比较少见。
1.3 实现方法
数据结构定义:
struct TrieNode{
char c;
struct TrieNode children[256];
};搜索字典项目的方法为:
(1) 从根结点开始一次搜索;
(2) 取得要查找关键词的第一个字母,并根据该字母选择对应的子树并转到该子树继续进行检索;
(3) 在相应的子树上,取得要查找关键词的第二个字母,并进一步选择对应的子树进行检索。
(4) 迭代过程……
(5) 在某个结点处,关键词的所有字母已被取出,则读取附在该结点上的信息,即完成查找。
其他操作类似处理。下面给出一个C语言版本的实现:
#define MAX 26 //字符集大小
typedef struct TrieNode
{
int nCount; //记录该字符出现次数
struct TrieNode* next[MAX];
}TrieNode;
TrieNode Memory[1000000];
int allocp=0;
/*初始化*/
void InitTrieRoot(TrieNode **pRoot)
{
*pRoot=NULL;
}
/*创建新结点*/
TrieNode* CreateTrieNode()
{
int i;
TrieNode *p;
p=&Memory[allocp++];
p->nCount=1;
for(i=0;i<MAX;i++)
{
p->next[i]=NULL;
}
return p;
}
/*插入*/
void InsertTrie(TrieNode **pRoot,char *s)
{
int i,k;
TrieNode *p;
if(!(p=*pRoot))
{
p=*pRoot=CreateTrieNode();
}
i=0;
while(s[i])
{
k=s[i++]-'a'; //确定branch
if(!p->next[k])
p->next[k]=CreateTrieNode();
else
p->next[k]->nCount++;
p=p->next[k];
}
}
//查找
int SearchTrie(TrieNode** pRoot,char *s)
{
TrieNode *p;
int i,k;
if(!(p=*pRoot))
{
return 0;
}
i=0;
while(s[i])
{
k=s[i++]-'a';
if(p->next[k]==NULL) return 0;
p=p->next[k];
}
return p->nCount;
}此外,我们也可以按如下方式来定义Trie树的结点结构:
typedef struct TrieNode{
int bTerminated; //本节点是否也作为一个终节点
int nCount; //本节点的所有非空孩子的个数
struct TrieNode *next[MAX];
}TrieNode;
void Print(char *result, int start, int end)
{
for(i=start;i<end;i++)
printf("%c", result[i]);
printf("\n");
}
void TraverseTrie(TrieNode *pRoot, char *result, int curPos)
{
if (!pRoot)
return;
if(pRoot->bTerminated == 1)
Print(result, 0, curPos);
for(i = 0; i<MAX;i++){
if (pRoot->next[i]){
result[curPos++] = i + 'a';
TraverseTrie(pRoot->next[i], result, curPos);
curPos--;
}
}
}1.4 应用
串的快速检索
给出N个单词组成的熟词表,以及一篇全用小写英文书写的文章,请你按最早出现的顺序写出所有不在熟词表中的生词。 在这道题中,我们可以用数组枚举,用哈希,用字典树,先把熟词建一棵树,然后读入文章进行比较,这种方法效率是比较高的。
“串”排序
给定N个互不相同的仅由一个单词构成的英文名,让你将他们按字典序从小到大输出用字典树进行排序,采用数组的方式创建字典树,这棵树的每个结点的所有儿子很显然地按照其字母大小排序。对这棵树进行先序遍历即可。
最长公共前缀
对所有串建立字典树,对于两个串的最长公共前缀的长度即他们所在的结点的公共祖先个数,于是,问题就转化为当时公共祖先问题。
2. Trie/Radix/Suffix Tree
这三种树有点类似,这里简单做一个比较:
2.1 Trie Tree
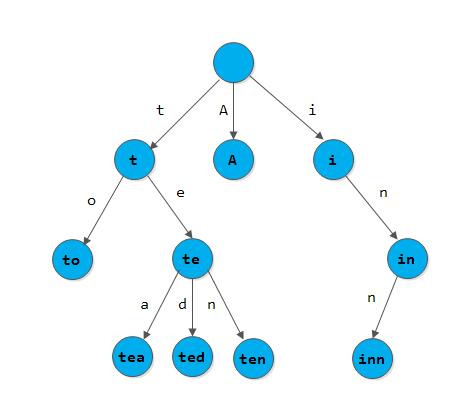
Trie Tree又称为字典树。下面是A, to, tea, ted, ten, i, in, inn这些单词组成的字典树:
2.2 Radix Tree
Radix Tree又称为基数树。基数树与字典树的区别在于基数树将单词压缩了, 节点变得更少:
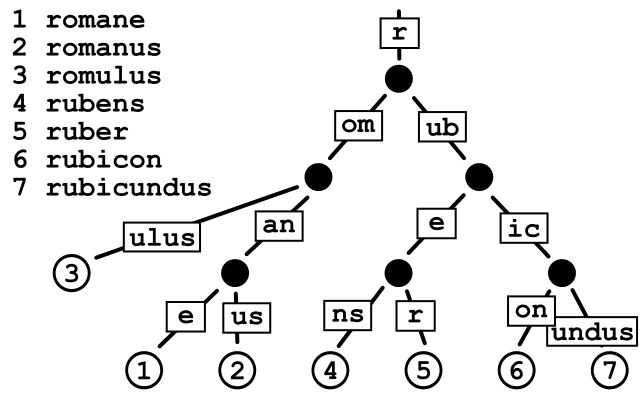
可以按如下方式来定义Radix Tree的结构:
typedef struct radix_tree_s{
char value[STR_MAXLEN + 1]; //压缩的单词存放于value中
int bTerminate;
struct radix_tree_s *next[26]; //按压缩单词的首字母排序
}radix_tree_t;2.3 Suffix Tree
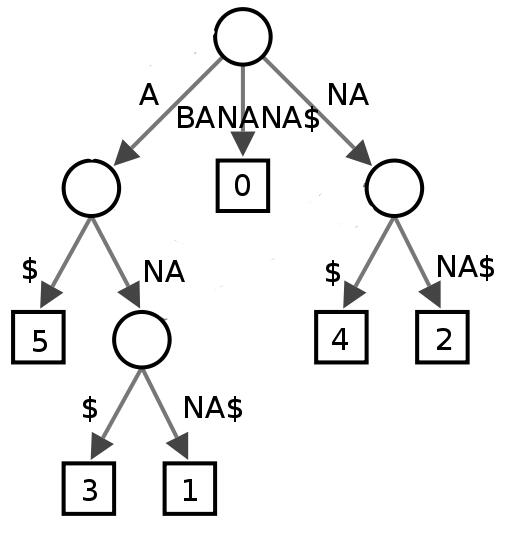
Suffix Tree又称为后缀树。单词 “BANANA” 的后缀树. 每个后缀以$结尾。所有的后缀为A$、NA$、 ANA$、NANA$、ANANA$ and BANANA$。 叶子节点表示后缀的起始坐标. 实际上后缀树就是一个单词的所有后缀组成的字典树, 并且把字典树单词进行了压缩。
[参看]:

