gperftools的使用
本文介绍一下gperftools工具的使用,在此做个记录以便后续查阅。
1. gperftools介绍
gperftools由一个支持高性能(high-performance)、多线程(multi-threaded)的malloc()实现,以及若干实用的性能分析工具所组成。
gperftools来源于Google Performance Tools,是目前我所见过的最快的malloc,能够搭配threads以及STL进行良好的工作。gperftools主要支持如下5个功能:
1.1 gperftools的安装
当前最新版本的gperftools为gperftools-2.9.1,我们下载此版本进行安装。
1) 下载gperftools-2.9.1
执行如下命令下载gperftools-2.9.1,并解压:
# mkdir gperftools-inst # cd gperftools-inst/ # wget https://github.com/gperftools/gperftools/releases/download/gperftools-2.9.1/gperftools-2.9.1.tar.gz # ls gperftools-2.9.1.tar.gz # tar -zxvf gperftools-2.9.1.tar.gz # cd gperftools-2.9.1/ # ls aclocal.m4 ChangeLog config.guess configure.ac docs install-sh m4 missing pprof-symbolize src vsprojects AUTHORS ChangeLog.old config.sub COPYING gperftools.sln libtool Makefile.am NEWS README test-driver benchmark compile configure depcomp INSTALL ltmain.sh Makefile.in packages README_windows.txt TODO
2)下载libunwind
gperftools依赖于libunwind,官方建议我们安装新版的libunwind,因此这里我们可以到libunwind download下载libunwind-1.5.0版本:
# mkdir libunwind-inst # cd libunwind-inst/ # wget --no-check-certificate https://download.savannah.gnu.org/releases/libunwind/libunwind-1.5.0.tar.gz # ls libunwind-1.5.0.tar.gz # tar -zxvf libunwind-1.5.0.tar.gz # cd libunwind-1.5.0/ # ls acinclude.m4 AUTHORS config configure.ac doc INSTALL Makefile.in README tests aclocal.m4 ChangeLog configure COPYING include Makefile.am NEWS src TODO
我们将libunwind-1.5.0安装到/usr/local/libunwind-1.5.0目录:
# mkdir /usr/local/libunwind-1.5.0 # ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/libunwind-1.5.0 # make # make install # ls /usr/local/libunwind-1.5.0/ include lib
2) 安装gperftools-2.9.1
上面解压完成后,我们查看其README以及INSTALL文件,以了解相关安装步骤。
根据INSTALL文档说明,安装gperftools-2.9.1需要依赖于autoconf、automake以及libtool工具,但目前新版本不用安装这些似乎也可以。
执行如下命令:
# mkdir -p /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1 # ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1 --enable-frame-pointers --enable-libunwind \ CPPFLAGS=-I/usr/local/libunwind-1.5.0/include LDFLAGS=-L/usr/local/libunwind-1.5.0/lib # make # make install # ls /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/ bin include lib share
安装成功之后,执行如下命令验证:
# ls /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/bin -al total 360 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 28 02:07 . drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 4096 Nov 28 02:07 .. -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 178256 Nov 28 02:07 pprof -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 178256 Nov 28 02:07 pprof-symbolize # /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/bin/pprof --version pprof (part of gperftools 2.0) Copyright 1998-2007 Google Inc. This is BSD licensed software; see the source for copying conditions and license information. There is NO warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
其实/usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/bin/pprof是一个perf脚本文件,我们来看一下:
# file /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/bin/pprof /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/bin/pprof: Perl script, ASCII text executable
3) 将相应的目录添加到ld查找路径中
在/etc/ld.so.conf.d/目录下创建gperftools-x86_64.conf:
/usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/lib在/etc/ld.so.conf.d/目录下创建libunwind-x86_64.conf:
/usr/local/libunwind-1.5.0/lib然后再执行如下命令:
# ldconfig
# ldconfig -p | grep gperftools
libtcmalloc_minimal_debug.so.4 (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/lib/libtcmalloc_minimal_debug.so.4
libtcmalloc_minimal_debug.so (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/lib/libtcmalloc_minimal_debug.so
libtcmalloc_minimal.so.4 (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/lib/libtcmalloc_minimal.so.4
libtcmalloc_minimal.so (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/lib/libtcmalloc_minimal.so
libtcmalloc_debug.so.4 (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/lib/libtcmalloc_debug.so.4
libtcmalloc_debug.so (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/lib/libtcmalloc_debug.so
libtcmalloc_and_profiler.so.4 (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/lib/libtcmalloc_and_profiler.so.4
libtcmalloc_and_profiler.so (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/lib/libtcmalloc_and_profiler.so
libtcmalloc.so.4 (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/lib/libtcmalloc.so.4
libtcmalloc.so (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/lib/libtcmalloc.so
libprofiler.so.0 (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/lib/libprofiler.so.0
libprofiler.so (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/lib/libprofiler.so
# ldconfig -p | grep libunwind
libunwind.so.8 (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/libunwind-1.5.0/lib/libunwind.so.8
libunwind.so (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/libunwind-1.5.0/lib/libunwind.so
libunwind-x86_64.so.8 (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/libunwind-1.5.0/lib/libunwind-x86_64.so.8
libunwind-x86_64.so (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/libunwind-1.5.0/lib/libunwind-x86_64.so
libunwind-setjmp.so.0 (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/libunwind-1.5.0/lib/libunwind-setjmp.so.0
libunwind-setjmp.so (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/libunwind-1.5.0/lib/libunwind-setjmp.so
libunwind-ptrace.so.0 (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/libunwind-1.5.0/lib/libunwind-ptrace.so.0
libunwind-ptrace.so (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/libunwind-1.5.0/lib/libunwind-ptrace.so
libunwind-coredump.so.0 (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/libunwind-1.5.0/lib/libunwind-coredump.so.0
libunwind-coredump.so (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/libunwind-1.5.0/lib/libunwind-coredump.so2. TCMalloc: Thread-Caching Malloc
tcmalloc是Thread Cache malloc的缩写,号称比ptmalloc2(glibc 2.3内部所使用)更快的内存管理库。在一台2.8GHZ P4主机上,ptmalloc2大约要花费300ns来执行一对malloc/free操作,而tcmalloc执行同样的操作只需花费大约50ns。内存分配速率是malloc()实现时的一个重要方面,因为假如malloc()内存分配速率不够快,那么应用程序本身就得在malloc()的基础上构建自己的内存管理链。
对于多线程程序,tcmalloc也可以降低锁的竞争。对于小对象(small objects),可以实现无锁分配;针对大对象(large objects),tcmalloc使用更高效的spinlocks来实现。ptmalloc2也会通过per-thread arenas来降低锁竞争,但是这存在一个巨大的问题,ptmalloc2所分配的内存不能在arenas之间移动,这可能会造成巨大的空间浪费。
2.1 Usage
要使用tcmalloc,我们只需要通过-ltcmallc链接符号将TCMalloc链接进应用程序即可;或者在不重新编译应用程序的情况下,直接使用LD_PRELOAD:
# LD_PRELOAD="/usr/lib/libtcmalloc.so"
TCMalloc同时也包含heap checker和heap profiler功能。
假如在某些情况下(比如为了降低编译出的bin文件大小),你只想链接一个不含heap profiler和heap checker功能的TCMalloc的话,那么你可以选择链接libtcmalloc_minimal即可。
2.2 Overview
TCMalloc会为每个线程指定一个thread-local cache。针对小对象的分配,直接使用thread-local cache即可满足。在必要的情况下,对象(objects)会从Central Heap移动到thread-local cache中,并且具有垃圾回收机制周期性的将thread-local cache所占用的内存归还给centrol heap。如下图所示:
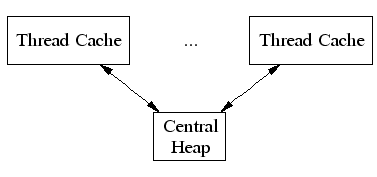
TCMalloc会将<=256KB大小的对象作为small objects,其他作为large objects来处理。针对large objects,tcmalloc会使用page-level allocator直接从central heap中分配内存。
注:一个page是一块8K对其的内存,因此针对large object其总是页对齐的,并且会占用整数页大小的空间。
2.3 使用示例
如下我们写一个内存分配程序来测试一下tcmalloc的内存分配性能:
2.3.1 运行一段时间就会正常退出的程序的性能分析
这种情况下,我们可以直接在代码中插入性能分析函数。编写如下示例代码(not_run_always.c):
#include <gperftools/profiler.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void f()
{
int i;
for (i=0; i<1024*1024; ++i)
{
char *p = (char*)malloc(1024*1024*120);
free(p);
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
ProfilerStart("test.prof"); //开启性能分析
f();
ProfilerStop(); //停止性能分析
return 0;
}1)编译
执行如下命令进行编译:
# gcc -o not_run_always not_run_always.c -I /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/include/ -L /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/lib/ -ltcmalloc -lprofiler # ls not_run_always not_run_always.c
注:编译时需要连接tcmalloc和profiler库。
2) 运行not_run_always程序
执行如下命令not_run_always:
# ldd ./not_run_always
linux-vdso.so.1 => (0x00007ffe743fe000)
libtcmalloc.so.4 => not found
libprofiler.so.0 => not found
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007f38726fe000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007f3872acc000)
# ./not_run_always
PROFILE: interrupts/evictions/bytes = 15/0/1104
# ls
not_run_always not_run_always.c test.prof注:此处用export LD_LIBRARY_PATH似乎一直出现问题。
我们看到生成了test.prof文件。
3) 使用pprof命令进行分析
下面我们使用pprof命令对test.prof进行分析:
# /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/bin/pprof --text ./not_run_always ./test.prof
Using local file ./not_run_always.
Using local file ./test.prof.
Total: 15 samples
2 13.3% 13.3% 12 80.0% ::do_free_pages [clone .isra.15]
2 13.3% 26.7% 2 13.3% SpinLock::Lock (inline)
2 13.3% 40.0% 2 13.3% __GI_madvise
2 13.3% 53.3% 5 33.3% tcmalloc::PageHeap::ReleaseAtLeastNPages
1 6.7% 60.0% 1 6.7% SpinLock::Unlock (inline)
1 6.7% 66.7% 3 20.0% TCMalloc_SystemRelease
1 6.7% 73.3% 1 6.7% std::_Rb_tree_insert_and_rebalance
1 6.7% 80.0% 1 6.7% std::_Rb_tree_rebalance_for_erase
1 6.7% 86.7% 2 13.3% tcmalloc::PageHeap::AllocLarge
1 6.7% 93.3% 1 6.7% tcmalloc::PageHeap::MergeIntoFreeList
1 6.7% 100.0% 2 13.3% tcmalloc::PageHeap::PrependToFreeList
0 0.0% 100.0% 2 13.3% ::do_malloc_pages
0 0.0% 100.0% 2 13.3% SpinLockHolder (inline)
0 0.0% 100.0% 1 6.7% _M_insert_ (inline)
0 0.0% 100.0% 1 6.7% _M_insert_unique (inline)
0 0.0% 100.0% 15 100.0% __libc_start_main
0 0.0% 100.0% 15 100.0% _start
0 0.0% 100.0% 3 20.0% do_allocate_full (inline)
0 0.0% 100.0% 3 20.0% do_malloc (inline)
0 0.0% 100.0% 1 6.7% do_malloc_pages
0 0.0% 100.0% 15 100.0% f
0 0.0% 100.0% 15 100.0% main
0 0.0% 100.0% 1 6.7% std::_Rb_tree::_M_erase_aux (inline)
0 0.0% 100.0% 1 6.7% std::_Rb_tree::erase[abi:cxx11] (inline)
0 0.0% 100.0% 1 6.7% std::set::erase[abi:cxx11] (inline)
0 0.0% 100.0% 1 6.7% std::set::insert (inline)
0 0.0% 100.0% 1 6.7% tcmalloc::PageHeap::Carve
0 0.0% 100.0% 3 20.0% tcmalloc::PageHeap::DecommitSpan
0 0.0% 100.0% 3 20.0% tcmalloc::PageHeap::Delete
0 0.0% 100.0% 5 33.3% tcmalloc::PageHeap::IncrementalScavenge
0 0.0% 100.0% 2 13.3% tcmalloc::PageHeap::New
0 0.0% 100.0% 3 20.0% tcmalloc::PageHeap::ReleaseSpan
0 0.0% 100.0% 1 6.7% tcmalloc::PageHeap::RemoveFromFreeList
0 0.0% 100.0% 3 20.0% tcmalloc::allocate_full_malloc_oom
0 0.0% 100.0% 1 6.7% ~SpinLockHolder (inline)
下面我们介绍一下输出结果中每一列的含义,参考cpu profile。每行包含6列数据,依次为:
-
Number of profiling samples in this function
-
Percentage of profiling samples in this function
-
Percentage of profiling samples in the functions printed so far
-
Number of profiling samples in this function and its callees
-
Percentage of profiling samples in this function and its callees
-
Function name
4) 函数调用树形式的pdf分析报告
运行如下命令生成函数调用树形式的pdf分析报告:
# /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/bin/pprof --pdf ./not_run_always ./test.prof > test.pdf
Using local file ./not_run_always.
Using local file ./test.prof.
sh: dot: command not found
sh: ps2pdf: command not found这里需要安装ps2pdf,比较麻烦,这里不做介绍。
5) 更多输出格式
pprof还支持输出更多格式,请参看pprof cpuprofile
2.3.2 一直运行的程序的性能分析
一直运行的程序由于不能正常退出,所以不能采用上面的方法。我们可以用信号量来开启/关闭性能分析,具体代码如下:
#include <gperftools/profiler.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <signal.h>
void signal_handler(int signo)
{
static int profile_started = 0;
signal(signo, signal_handler);
printf("recv signal[%d]", signo);
switch(signo)
{
case SIGUSR1:
if (!profile_started) {
ProfilerStart("test.prof"); //开启性能分析
}else{
ProfilerStop(); //停止性能分析
}
printf("Process recieve SIGUSR1");
break;
}
exit(0);
}
void f()
{
int i;
for (i=0; i<1024*1024; ++i)
{
char *p = (char*)malloc(1024*1024*120);
free(p);
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
signal(SIGUSR1, signal_handler);
while(1){
f();
sleep(1000);
}
return 0;
}通过kill命令发送信号给进程来开启/关闭性能分析:
# kill -s SIGUSR1 PID //第一次运行命令启动性能分析 # kill -s SIGUSR1 PID //再次运行命令关闭性能分析,产生test.prof
3. 内存泄露检测
gperftools的heap checker组件可以用于检测C++ 程序中的内存泄露问题。要使用heap checker,总共分3步:
-
链接 tcmalloc 库到应用程序中
-
运行程序
-
分析输出
1) 链接tcmalloc库
heapchecker是tcmalloc的一部分,所以为了在可执行程序中使用heap checker,在应用程序的链接阶段使用-ltcmalloc链接 tcmalloc库。
2) 运行代码
使用heap checker的推荐方式是完整程序运行模式,此时heap checker可以在程序的main()函数开始前跟踪内存分配,然后在程序退出时再次检查。如果它发现来了任何内存泄露,heap checker会直接终止程序(通过 exit(1)),并打印一条消息,告诉你接下来如何使用 pprof 来继续跟踪该内存泄露问题。
完整程序运行的 heap checker支持4种模式:
-
minimal:在程序初始化期间(即 main 函数运行前)不进行内存泄露检查
-
normal:正常模式,通过跟踪某块内存是否可以被 live object 来访问,来判断是否出现内存泄露
-
strict:类似于 normal 模式,但是对全局对象的内存泄露有一些额外的检查
-
draconian:在该模式下,只有所有申请的内存都被释放,才认为没有出现内存泄露
一般使用normal模式就可以满足日常要求了。
heap checker的另一种使用方法是检测指定代码块是否出现了内存泄露。为了实现这一点,需要在代码片段的开始部分创建一个 HeapLeakChecker结构体,并在结束部分调用NoLeaks()。例如:
HeapLeakChecker heap_checker("test_foo");
{
code that exercises some foo functionality;
this code should not leak memory;
}
if (!heap_checker.NoLeaks()) assert(NULL == "heap memory leak");需要注意,添加HeapLeakChecker只是在程序中添加了内存泄露检测代码,为了真实地检测程序是否出现了内存泄露,仍然需要运行程序,并打开 heap-checker。
env HEAPCHECK=local your_program除了指定为local模式外,之前的normal等模式也是可以的,此时除了运行local检查外,还将进行完整程序运行检查。
当然,运行heap checker是有代价的。heap checker需要记录每次内存申请时的调用栈信息,这就导致了使用heap checke 时,程序需要消耗更多的内存,同时程序运行速度也更慢。另外,需要注意,由于heap checker内部使用了heap profile框架,所以不能同时运行heap checker和heap profile。
3) 忽略已知的内存泄露
对于已知的内存泄露,如果想让 heap checker 忽略这些内存泄露信息,可以在应用程序代码中添加中如下代码:
{
HeapLeakChecker::Disabler disabler;
<leaky code>
}另一种方式是使用 IgnoreObject,它接收一个指针参数,对该参数所指向的对象将不再进行内存泄露检查.
4) 使用pprof查看内存泄露结果
heap checker 运行结束时会打印基本的泄露信息,包括调用栈和泄露对象的地址。除此之外,还可以使用 pprof 命令行工具来可视化地查看调用栈。
3.1 示例
接下来通过一个示例讲述如何使用 gperftools 的 heap checker 来发现程序的内存泄露问题。
1) 编写测试程序
编写如下测试程序(memory_leak.cpp)
// Copyright (C) fuchencong.com
#include <iostream>
int func() {
int *p = new int(10);
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
std::cout << "memory leak test" << std::endl;
return func();
}2) 编译
执行如下命令编译程序:
# g++ -std=c++0x -g -o memory_leak memory_leak.cpp -L /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/lib/ -ltcmalloc # ls memory_leak memory_leak.cpp
3) 运行程序
# env HEAPCHECK=normal ./memory_leak
WARNING: Perftools heap leak checker is active -- Performance may suffer
memory leak test
Have memory regions w/o callers: might report false leaks
Leak check _main_ detected leaks of 4 bytes in 1 objects
The 1 largest leaks:
*** WARNING: Cannot convert addresses to symbols in output below.
*** Reason: Cannot find 'pprof' (is PPROF_PATH set correctly?)
*** If you cannot fix this, try running pprof directly.
Leak of 4 bytes in 1 objects allocated from:
@ 4008ff
@ 400940
@ 7f5b859d2555
@ 400829
If the preceding stack traces are not enough to find the leaks, try running THIS shell command:
pprof ./memory_leak "/tmp/memory_leak.28948._main_-end.heap" --inuse_objects --lines --heapcheck --edgefraction=1e-10 --nodefraction=1e-10 --gv
If you are still puzzled about why the leaks are there, try rerunning this program with HEAP_CHECK_TEST_POINTER_ALIGNMENT=1 and/or with HEAP_CHECK_MAX_POINTER_OFFSET=-1
If the leak report occurs in a small fraction of runs, try running with TCMALLOC_MAX_FREE_QUEUE_SIZE of few hundred MB or with TCMALLOC_RECLAIM_MEMORY=false, it might help find leaks m
Exiting with error code (instead of crashing) because of whole-program memory leaks这里虽然检测出了内存泄露,但是并没有打印出调用栈的符号信息,根据提示,可能是PPROF_PATH环境变量没有正确设置。按照如下方式设置环境变量:
# echo $PPROF_PATH # ls /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/bin/pprof /usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/bin/pprof # export PPROF_PATH=/usr/local/gperftools-2.9.1/bin/pprof
再次运行,可以看到已经打印出了内存泄露的栈信息:
# env HEAPCHECK=normal ./memory_leak
WARNING: Perftools heap leak checker is active -- Performance may suffer
memory leak test
Have memory regions w/o callers: might report false leaks
Leak check _main_ detected leaks of 4 bytes in 1 objects
The 1 largest leaks:
Using local file ./memory_leak.
Leak of 4 bytes in 1 objects allocated from:
@ 4008ff func
@ 400940 main
@ 7f3275673555 __libc_start_main
@ 400829 _start
If the preceding stack traces are not enough to find the leaks, try running THIS shell command:
pprof ./memory_leak "/tmp/memory_leak.29850._main_-end.heap" --inuse_objects --lines --heapcheck --edgefraction=1e-10 --nodefraction=1e-10 --gv
If you are still puzzled about why the leaks are there, try rerunning this program with HEAP_CHECK_TEST_POINTER_ALIGNMENT=1 and/or with HEAP_CHECK_MAX_POINTER_OFFSET=-1
If the leak report occurs in a small fraction of runs, try running with TCMALLOC_MAX_FREE_QUEUE_SIZE of few hundred MB or with TCMALLOC_RECLAIM_MEMORY=false, it might help find leaks m
Exiting with error code (instead of crashing) because of whole-program memory leaks
[参看]:

