os/unix/ngx_writev_chain.c源代码分析
本节我们主要介绍一下nginx中的分散发送实现。
1. os/unix/ngx_writev_chain.c源代码
在介绍函数的具体实现之前,我们这里再次给出ngx_chain_t数据结构示意图:
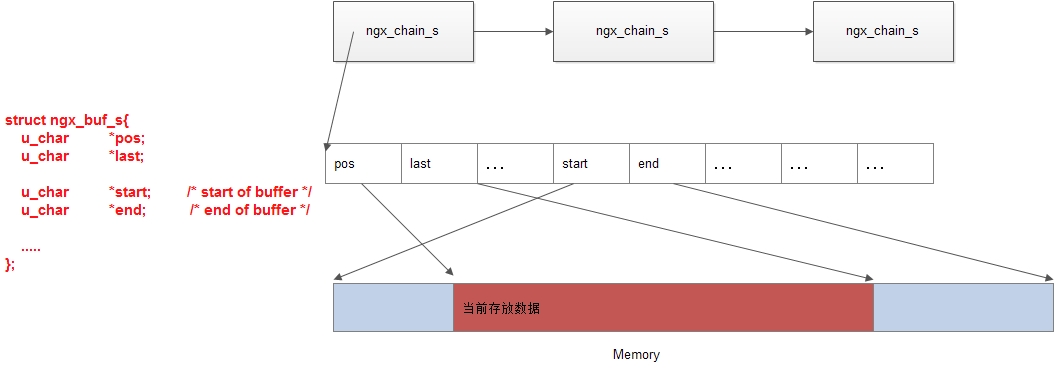
1.1 函数ngx_writev_chain()
/*
* Copyright (C) Igor Sysoev
* Copyright (C) Nginx, Inc.
*/
#include <ngx_config.h>
#include <ngx_core.h>
#include <ngx_event.h>
ngx_chain_t *
ngx_writev_chain(ngx_connection_t *c, ngx_chain_t *in, off_t limit)
{
ssize_t n, sent;
off_t send, prev_send;
ngx_chain_t *cl;
ngx_event_t *wev;
ngx_iovec_t vec;
struct iovec iovs[NGX_IOVS_PREALLOCATE];
wev = c->write;
if (!wev->ready) {
return in;
}
#if (NGX_HAVE_KQUEUE)
if ((ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_KQUEUE_EVENT) && wev->pending_eof) {
(void) ngx_connection_error(c, wev->kq_errno,
"kevent() reported about an closed connection");
wev->error = 1;
return NGX_CHAIN_ERROR;
}
#endif
/* the maximum limit size is the maximum size_t value - the page size */
if (limit == 0 || limit > (off_t) (NGX_MAX_SIZE_T_VALUE - ngx_pagesize)) {
limit = NGX_MAX_SIZE_T_VALUE - ngx_pagesize;
}
send = 0;
vec.iovs = iovs;
vec.nalloc = NGX_IOVS_PREALLOCATE;
for ( ;; ) {
prev_send = send;
/* create the iovec and coalesce the neighbouring bufs */
cl = ngx_output_chain_to_iovec(&vec, in, limit - send, c->log);
if (cl == NGX_CHAIN_ERROR) {
return NGX_CHAIN_ERROR;
}
if (cl && cl->buf->in_file) {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_ALERT, c->log, 0,
"file buf in writev "
"t:%d r:%d f:%d %p %p-%p %p %O-%O",
cl->buf->temporary,
cl->buf->recycled,
cl->buf->in_file,
cl->buf->start,
cl->buf->pos,
cl->buf->last,
cl->buf->file,
cl->buf->file_pos,
cl->buf->file_last);
ngx_debug_point();
return NGX_CHAIN_ERROR;
}
send += vec.size;
n = ngx_writev(c, &vec);
if (n == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_CHAIN_ERROR;
}
sent = (n == NGX_AGAIN) ? 0 : n;
c->sent += sent;
in = ngx_chain_update_sent(in, sent);
if (send - prev_send != sent) {
wev->ready = 0;
return in;
}
if (send >= limit || in == NULL) {
return in;
}
}
}下面我们来简单分析一下这个函数:
1) 处理!wev->ready情况
wev = c->write;
if (!wev->ready) {
return in;
}wev->ready为0时,表示当前socket尚未准备好发送数据,一般情况是当前发送缓冲区已满。
2) 对kqueue情形下pending_eof的处理
#if (NGX_HAVE_KQUEUE)
if ((ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_KQUEUE_EVENT) && wev->pending_eof) {
(void) ngx_connection_error(c, wev->kq_errno,
"kevent() reported about an closed connection");
wev->error = 1;
return NGX_CHAIN_ERROR;
}
#endif我们当前不支持NGX_HAVE_KQUEUE。在kqueue模型下,wev->pending_eof表示当前socket 连接已经关闭,但是当前还未被处理。
3) 设置一次发送的最大发送数量
/* the maximum limit size is the maximum size_t value - the page size */
if (limit == 0 || limit > (off_t) (NGX_MAX_SIZE_T_VALUE - ngx_pagesize)) {
limit = NGX_MAX_SIZE_T_VALUE - ngx_pagesize;
}在ngx_auto_config.h头文件中,我们有如下定义:
#ifndef NGX_MAX_SIZE_T_VALUE #define NGX_MAX_SIZE_T_VALUE 2147483647 #endif
因为这里size_t表示数据的最大值为NGX_MAX_SIZE_T_VALUE,另外可能还需要留有一些其他的空间,因此这里限定一次发送数据的最大大小为:
limit = NGX_MAX_SIZE_T_VALUE - ngx_pagesize;
这里ngx_pagesize大小为4096.
4) 发送数据
ngx_chain_t *
ngx_writev_chain(ngx_connection_t *c, ngx_chain_t *in, off_t limit)
{
ssize_t n, sent;
//send用于记录截止到本次发送为止,预计发送的总字节数; prev_send用于记录截止到上一次为止,已经成功发送的数据
off_t send, prev_send;
send = 0;
for ( ;; ) {
prev_send = send;
//1) 创建iovec并合并相邻的buf, c1这里表示当前ngx_chain_t的哪一个节点(这里只作为判断使用,并不不作为下一次发送的起点
// 使用,因为数据的实际发送大小可能不等于这里合并的大小)
cl = ngx_output_chain_to_iovec(&vec, in, limit - send, c->log);
//2) 判断c1出错的相应状况
if (cl == NGX_CHAIN_ERROR) {
return NGX_CHAIN_ERROR;
}
if (cl && cl->buf->in_file) {
return NGX_CHAIN_ERROR;
}
//3) 发送数据
send += vec.size;
n = ngx_writev(c, &vec);
if (n == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_CHAIN_ERROR;
}
//4) 根据当前实际的发送数据量sent,计算下一次发送的起始地址
sent = (n == NGX_AGAIN) ? 0 : n;
c->sent += sent;
in = ngx_chain_update_sent(in, sent);
//5) 期望发送字节数与实际发送字节数不同,则一般表示当前发送缓存区已满,将wev->ready置为0
if (send - prev_send != sent) {
wev->ready = 0;
return in;
}
//6) 发送结束,退出
if (send >= limit || in == NULL) {
return in;
}
}
}1.2 函数ngx_output_chain_to_iovec()
ngx_chain_t *
ngx_output_chain_to_iovec(ngx_iovec_t *vec, ngx_chain_t *in, size_t limit,
ngx_log_t *log)
{
size_t total, size;
u_char *prev;
ngx_uint_t n;
struct iovec *iov;
iov = NULL;
prev = NULL;
total = 0;
n = 0;
for ( /* void */ ; in && total < limit; in = in->next) {
if (ngx_buf_special(in->buf)) {
continue;
}
if (in->buf->in_file) {
break;
}
if (!ngx_buf_in_memory(in->buf)) {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_ALERT, log, 0,
"bad buf in output chain "
"t:%d r:%d f:%d %p %p-%p %p %O-%O",
in->buf->temporary,
in->buf->recycled,
in->buf->in_file,
in->buf->start,
in->buf->pos,
in->buf->last,
in->buf->file,
in->buf->file_pos,
in->buf->file_last);
ngx_debug_point();
return NGX_CHAIN_ERROR;
}
size = in->buf->last - in->buf->pos;
if (size > limit - total) {
size = limit - total;
}
if (prev == in->buf->pos) {
iov->iov_len += size;
} else {
if (n == vec->nalloc) {
break;
}
iov = &vec->iovs[n++];
iov->iov_base = (void *) in->buf->pos;
iov->iov_len = size;
}
prev = in->buf->pos + size;
total += size;
}
vec->count = n;
vec->size = total;
return in;
}下面简单分析一下合并流程:
ngx_chain_t *
ngx_output_chain_to_iovec(ngx_iovec_t *vec, ngx_chain_t *in, size_t limit,
ngx_log_t *log)
{
//用于记录上一次合并后的末尾位置
u_char *prev;
for ( /* void */ ; in && total < limit; in = in->next) {
{
//1) 剔除无效的buf
//2) 合并相邻buf
}
}1.3 函数ngx_writev()
ssize_t
ngx_writev(ngx_connection_t *c, ngx_iovec_t *vec)
{
ssize_t n;
ngx_err_t err;
eintr:
n = writev(c->fd, vec->iovs, vec->count);
ngx_log_debug2(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, c->log, 0,
"writev: %z of %uz", n, vec->size);
if (n == -1) {
err = ngx_errno;
switch (err) {
case NGX_EAGAIN:
ngx_log_debug0(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, c->log, err,
"writev() not ready");
return NGX_AGAIN;
case NGX_EINTR:
ngx_log_debug0(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, c->log, err,
"writev() was interrupted");
goto eintr;
default:
c->write->error = 1;
ngx_connection_error(c, err, "writev() failed");
return NGX_ERROR;
}
}
return n;
}这里调用writev()函数将数据通过socket发送出去。这里主要是对发送出错情况下,的处理:
-
NGX_EAGAIN: 表示当前socket并未准备好发送数据,一般是在发送缓冲区已经满的情况下出现
-
NGX_EINTR: 此种情况是受中断影响,直接继续尝试发送即可
-
default: socket连接出现问题,报错退出

