core/ngx_conf_file.c源代码分析
本节我们讲述nginx配置文件相关的一些内容。
1. 相关静态函数声明
/*
* Copyright (C) Igor Sysoev
* Copyright (C) Nginx, Inc.
*/
#include <ngx_config.h>
#include <ngx_core.h>
#define NGX_CONF_BUFFER 4096
// 对指令的解析校验等方面的处理
static ngx_int_t ngx_conf_handler(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_int_t last);
// 读取配置文件并进行词法分析
static ngx_int_t ngx_conf_read_token(ngx_conf_t *cf);
// 主要用于nginx配置模块在退出时刷新相应的打开文件
static void ngx_conf_flush_files(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);2. 相关变量定义
1) nginx配置模块支持的指令
static ngx_command_t ngx_conf_commands[] = {
{ ngx_string("include"),
NGX_ANY_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_conf_include,
0,
0,
NULL },
ngx_null_command
};这里nginx配置模块(conf module)当前只支持一个include指令。其携带一个参数,可以放置于nginx配置文件的任意位置。在解析include指令时,通过调用ngx_conf_include()来完成。include指令语法如下:
include file | mask通过include指令将file文件,或者满足mask匹配的文件包含到配置文件中来。所包含进来的文件必须满足nginx定义的相关语法。例如:
include mime.types; include vhosts/*.conf
2) nginx配置模块
ngx_module_t ngx_conf_module = {
NGX_MODULE_V1,
NULL, /* module context */
ngx_conf_commands, /* module directives */
NGX_CONF_MODULE, /* module type */
NULL, /* init master */
NULL, /* init module */
NULL, /* init process */
NULL, /* init thread */
NULL, /* exit thread */
ngx_conf_flush_files, /* exit process */
NULL, /* exit master */
NGX_MODULE_V1_PADDING
};这里ngx_conf_module并不需要任何模块上下文module context,所支持的模块指令为ngx_conf_commands,模块类型为NGX_CONF_MODULE,在进程退出时的回调函数为ngx_conf_flush_files。
3) 配置指令参数数组
/* The eight fixed arguments */
static ngx_uint_t argument_number[] = {
NGX_CONF_NOARGS,
NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
NGX_CONF_TAKE2,
NGX_CONF_TAKE3,
NGX_CONF_TAKE4,
NGX_CONF_TAKE5,
NGX_CONF_TAKE6,
NGX_CONF_TAKE7
};3. 配置解析相关函数实现
3.1 函数ngx_conf_param()
本函数主要用于处理通过nginx命令行的-g选项传递进来的参数。-g directives是用于设置全局配置指令的,例如:
# nginx -g "pid /var/run/nginx.pid; worker_processes `sysctl -n hw.ncpu`;"
char *
ngx_conf_param(ngx_conf_t *cf)
{
char *rv;
ngx_str_t *param;
ngx_buf_t b;
ngx_conf_file_t conf_file;
param = &cf->cycle->conf_param;
if (param->len == 0) {
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}
ngx_memzero(&conf_file, sizeof(ngx_conf_file_t));
ngx_memzero(&b, sizeof(ngx_buf_t));
b.start = param->data;
b.pos = param->data;
b.last = param->data + param->len;
b.end = b.last;
b.temporary = 1;
conf_file.file.fd = NGX_INVALID_FILE;
conf_file.file.name.data = NULL;
conf_file.line = 0;
cf->conf_file = &conf_file;
cf->conf_file->buffer = &b;
rv = ngx_conf_parse(cf, NULL);
cf->conf_file = NULL;
return rv;
}通过nginx命令行-g选项传递进来的参数保存在cf->cycle->conf_param中。函数首先构造一个conf_file对象,用于表示当前的一个配置文件:
typedef struct {
ngx_file_t file; // 当前数据存在于内存,因此此字段暂时不用
ngx_buf_t *buffer; // 指向一个临时的内存
ngx_buf_t *dump; // NULL
ngx_uint_t line; // 0
} ngx_conf_file_t;再接着调用ngx_conf_parse()当前的配置对象.
3.2 函数ngx_conf_parse()
char *
ngx_conf_parse(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_str_t *filename)
{
char *rv;
u_char *p;
off_t size;
ngx_fd_t fd;
ngx_int_t rc;
ngx_buf_t buf, *tbuf;
ngx_conf_file_t *prev, conf_file;
ngx_conf_dump_t *cd;
enum {
parse_file = 0,
parse_block,
parse_param
} type;
#if (NGX_SUPPRESS_WARN)
fd = NGX_INVALID_FILE;
prev = NULL;
#endif
if (filename) {
/* open configuration file */
fd = ngx_open_file(filename->data, NGX_FILE_RDONLY, NGX_FILE_OPEN, 0);
if (fd == NGX_INVALID_FILE) {
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, ngx_errno,
ngx_open_file_n " \"%s\" failed",
filename->data);
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
prev = cf->conf_file;
cf->conf_file = &conf_file;
if (ngx_fd_info(fd, &cf->conf_file->file.info) == NGX_FILE_ERROR) {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf->log, ngx_errno,
ngx_fd_info_n " \"%s\" failed", filename->data);
}
cf->conf_file->buffer = &buf;
buf.start = ngx_alloc(NGX_CONF_BUFFER, cf->log);
if (buf.start == NULL) {
goto failed;
}
buf.pos = buf.start;
buf.last = buf.start;
buf.end = buf.last + NGX_CONF_BUFFER;
buf.temporary = 1;
cf->conf_file->file.fd = fd;
cf->conf_file->file.name.len = filename->len;
cf->conf_file->file.name.data = filename->data;
cf->conf_file->file.offset = 0;
cf->conf_file->file.log = cf->log;
cf->conf_file->line = 1;
type = parse_file;
if (ngx_dump_config
#if (NGX_DEBUG)
|| 1
#endif
)
{
p = ngx_pstrdup(cf->cycle->pool, filename);
if (p == NULL) {
goto failed;
}
size = ngx_file_size(&cf->conf_file->file.info);
tbuf = ngx_create_temp_buf(cf->cycle->pool, (size_t) size);
if (tbuf == NULL) {
goto failed;
}
cd = ngx_array_push(&cf->cycle->config_dump);
if (cd == NULL) {
goto failed;
}
cd->name.len = filename->len;
cd->name.data = p;
cd->buffer = tbuf;
cf->conf_file->dump = tbuf;
} else {
cf->conf_file->dump = NULL;
}
} else if (cf->conf_file->file.fd != NGX_INVALID_FILE) {
type = parse_block;
} else {
type = parse_param;
}
for ( ;; ) {
rc = ngx_conf_read_token(cf);
/*
* ngx_conf_read_token() may return
*
* NGX_ERROR there is error
* NGX_OK the token terminated by ";" was found
* NGX_CONF_BLOCK_START the token terminated by "{" was found
* NGX_CONF_BLOCK_DONE the "}" was found
* NGX_CONF_FILE_DONE the configuration file is done
*/
if (rc == NGX_ERROR) {
goto done;
}
if (rc == NGX_CONF_BLOCK_DONE) {
if (type != parse_block) {
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0, "unexpected \"}\"");
goto failed;
}
goto done;
}
if (rc == NGX_CONF_FILE_DONE) {
if (type == parse_block) {
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0,
"unexpected end of file, expecting \"}\"");
goto failed;
}
goto done;
}
if (rc == NGX_CONF_BLOCK_START) {
if (type == parse_param) {
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0,
"block directives are not supported "
"in -g option");
goto failed;
}
}
/* rc == NGX_OK || rc == NGX_CONF_BLOCK_START */
if (cf->handler) {
/*
* the custom handler, i.e., that is used in the http's
* "types { ... }" directive
*/
if (rc == NGX_CONF_BLOCK_START) {
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0, "unexpected \"{\"");
goto failed;
}
rv = (*cf->handler)(cf, NULL, cf->handler_conf);
if (rv == NGX_CONF_OK) {
continue;
}
if (rv == NGX_CONF_ERROR) {
goto failed;
}
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0, rv);
goto failed;
}
rc = ngx_conf_handler(cf, rc);
if (rc == NGX_ERROR) {
goto failed;
}
}
failed:
rc = NGX_ERROR;
done:
if (filename) {
if (cf->conf_file->buffer->start) {
ngx_free(cf->conf_file->buffer->start);
}
if (ngx_close_file(fd) == NGX_FILE_ERROR) {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_ALERT, cf->log, ngx_errno,
ngx_close_file_n " %s failed",
filename->data);
rc = NGX_ERROR;
}
cf->conf_file = prev;
}
if (rc == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}在nginx_auto_config.h头文件中,我们有如下定义:
#ifndef NGX_SUPPRESS_WARN #define NGX_SUPPRESS_WARN 1 #endif
接下来我们分几个部分来对ngx_conf_parse()进行讲解:
1) 判断解析类型
ngx_conf_parse()函数支持解析三种类型的配置: parse_file、parse_block、parse_param。
- parse_file类型: 当
filename不为NULL时,表示要解析的是一个配置文件。此时需要进行一些相应的前期处理:
char *
ngx_conf_parse(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_str_t *filename)
{
....
if(filename)
{
// 1: 打开filename文件
fd = ngx_open_file(filename->data, NGX_FILE_RDONLY, NGX_FILE_OPEN, 0);
// 2: 保留cf中原来的conf_file,以便后续恢复
prev = cf->conf_file;
//3: 构造一个新的conf_file
cf->conf_file = &conf_file;
cf->conf_file->buffer = &buf; //此处构造一个4096字节的空间(注意这里并不是在内存池中分配的),主要是用于在指令解析时用到
//4: 如果nginx启动时携带-T选项,以检查并dump出配置的话,则执行如下:
if (ngx_dump_config
#if (NGX_DEBUG)
|| 1
#endif
)
{
//1) 创建一个名称为filename,大小为filename文件大小的dump缓存
size = ngx_file_size(&cf->conf_file->file.info);
tbuf = ngx_create_temp_buf(cf->cycle->pool, (size_t) size);
//2) 将该缓存配置为conf_file->dump
cf->conf_file->dump = tbuf;
}
}
}-
parse_block类型: 当
conf_file->file.fd != NGX_INVALID_FILE时,则为parse_block类型 -
parse_param类型
2) 解析配置指令
char *
ngx_conf_parse(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_str_t *filename)
{
for(;;)
{
//1) 从cf中读取到相应的token
rc = ngx_conf_read_token(cf);
/* 上述rc可能的返回值有:
*
* NGX_ERROR: 表明解析出现错误
* NGX_OK: 表明成功解析到一个以";"结尾的token
* NGX_CONF_BLOCK_START: 表明成功解析到一个token,并且该token是一个块配置指令,后面跟随"{"
* NGX_CONF_BLOCK_DONE: 成功解析到"}"
* NGX_CONF_FILE_DONE: 成功解析完配置文件
*/
//2) 根据返回值,对解析结果进行处理
if(rc == NGX_ERROR)
goto done;
if(rc == NGX_CONF_BLOCK_DONE)
{
//如若当前解析类型不是parse_block,则goto failed,否则goto done
if(type != parse_block)
{
goto failed;
}
goto done;
}
if(rc == NGX_CONF_FILE_DONE)
{
//如若当前解析类型为parse_block,则goto failed,否则goto done
if(type == parse_block)
{
goto failed;
}
goto done;
}
if(rc == NGX_CONF_BLOCK_START)
{
//如果当前解析类型为parse_param,则goto failed,否则goto done
// 这里不支持通过-g选项传递“块指令”
if(type == parse_param)
{
goto failed;
}
}
//3) 针对rc返回值为NGX_OK或者NGX_CONF_BLOCK_START情况,调用cf->handler进行处理
// 是一个定制的handler,例如: http的"types {...}"指令
if(cf->handler)
{
//调用cf->handler()进行处理
}
//4) 调用ngx_conf_handler()对上述获取到的token进行处理
rc = ngx_conf_handler();
if(rc == NGX_ERROR)
goto failed;
}
failed:
rc = NGX_ERROR;
done:
//5) 如果filename不为NULL,需要进行相应的关闭文件操作
if(filename)
{
//恢复现场
}
if(rc == NGX_ERROR)
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}3.3 函数ngx_conf_handler()
static ngx_int_t
ngx_conf_handler(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_int_t last)
{
char *rv;
void *conf, **confp;
ngx_uint_t i, found;
ngx_str_t *name;
ngx_command_t *cmd;
name = cf->args->elts;
found = 0;
for (i = 0; cf->cycle->modules[i]; i++) {
cmd = cf->cycle->modules[i]->commands;
if (cmd == NULL) {
continue;
}
for ( /* void */ ; cmd->name.len; cmd++) {
if (name->len != cmd->name.len) {
continue;
}
if (ngx_strcmp(name->data, cmd->name.data) != 0) {
continue;
}
found = 1;
if (cf->cycle->modules[i]->type != NGX_CONF_MODULE
&& cf->cycle->modules[i]->type != cf->module_type)
{
continue;
}
/* is the directive's location right ? */
if (!(cmd->type & cf->cmd_type)) {
continue;
}
if (!(cmd->type & NGX_CONF_BLOCK) && last != NGX_OK) {
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0,
"directive \"%s\" is not terminated by \";\"",
name->data);
return NGX_ERROR;
}
if ((cmd->type & NGX_CONF_BLOCK) && last != NGX_CONF_BLOCK_START) {
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0,
"directive \"%s\" has no opening \"{\"",
name->data);
return NGX_ERROR;
}
/* is the directive's argument count right ? */
if (!(cmd->type & NGX_CONF_ANY)) {
if (cmd->type & NGX_CONF_FLAG) {
if (cf->args->nelts != 2) {
goto invalid;
}
} else if (cmd->type & NGX_CONF_1MORE) {
if (cf->args->nelts < 2) {
goto invalid;
}
} else if (cmd->type & NGX_CONF_2MORE) {
if (cf->args->nelts < 3) {
goto invalid;
}
} else if (cf->args->nelts > NGX_CONF_MAX_ARGS) {
goto invalid;
} else if (!(cmd->type & argument_number[cf->args->nelts - 1]))
{
goto invalid;
}
}
/* set up the directive's configuration context */
conf = NULL;
if (cmd->type & NGX_DIRECT_CONF) {
conf = ((void **) cf->ctx)[cf->cycle->modules[i]->index];
} else if (cmd->type & NGX_MAIN_CONF) {
conf = &(((void **) cf->ctx)[cf->cycle->modules[i]->index]);
} else if (cf->ctx) {
confp = *(void **) ((char *) cf->ctx + cmd->conf);
if (confp) {
conf = confp[cf->cycle->modules[i]->ctx_index];
}
}
rv = cmd->set(cf, cmd, conf);
if (rv == NGX_CONF_OK) {
return NGX_OK;
}
if (rv == NGX_CONF_ERROR) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0,
"\"%s\" directive %s", name->data, rv);
return NGX_ERROR;
}
}
if (found) {
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0,
"\"%s\" directive is not allowed here", name->data);
return NGX_ERROR;
}
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0,
"unknown directive \"%s\"", name->data);
return NGX_ERROR;
invalid:
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0,
"invalid number of arguments in \"%s\" directive",
name->data);
return NGX_ERROR;
}1) 函数流程分析
下面我们简要分析一下该函数(这里注意cf->args包含了指令及参数部分):
static ngx_int_t
ngx_conf_handler(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_int_t last)
{
//1) 循环遍历ngx_modules数组,在modules数组中找出与当前指令相同的command配置,然后进行检查
for(i=0; cf->cycle->modulesi];i++)
{
cmd = cf->cycle->modules[i]->commands;
//2) 循环遍历该模块下的所有commands
for(; cmd->name.len;cmd++)
{
//3) 找到对应的command
//4) 判断当前配置指令是否在正确的配置模块中(判断模块类型)
// 注意NGX_CONF_MODULE可以出现在任意位置
//5) 判断实际命令类型与当前配置命令类型是否一致
//6) 如果当前配置指令不是一个“块配置”指令,则必须以";"结尾
if (!(cmd->type & NGX_CONF_BLOCK) && last != NGX_OK) {
}
//7) 如果当前配置指令是一个“块配置”指令,则后续必须跟一个"{"
if ((cmd->type & NGX_CONF_BLOCK) && last != NGX_CONF_BLOCK_START) {
}
//8) 判断指令的参数个数是否合法
if(!(cmd->type & NGX_CONF_ANY))
{
if(cmd->type & NGX_CONF_FLAG)
{
//后续只能跟on/off一个参数
}
else if(cmd->type & NGX_CONF_1MORE)
{
//至少携带一个参数
}
else if(cmd->type & NGX_CONF_2MORE)
{
//至少携带2个参数
}
else if(cf->args->nelts > NGX_CONF_MAX_ARGS)
{
//指令+参数部分不能超过NGX_CONF_MAX_ARGS
}
else if (!(cmd->type & argument_number[cf->args->nelts - 1]))
{
//判断当前携带参数个数是否合法
}
}
//9) 建立指令的配置上下文(关于配置指令上下文的问题,我们后面会继续进行详细讲解)
/* set up the directive's configuration context */
conf = NULL;
if (cmd->type & NGX_DIRECT_CONF)
{
conf = ((void **) cf->ctx)[cf->cycle->modules[i]->index];
}
else if (cmd->type & NGX_MAIN_CONF)
{
conf = &(((void **) cf->ctx)[cf->cycle->modules[i]->index]);
}
else if (cf->ctx)
{
confp = *(void **) ((char *) cf->ctx + cmd->conf);
if (confp) {
conf = confp[cf->cycle->modules[i]->ctx_index];
}
}
//注意此处调用相应模块钩子函数,然后进入对应的配置块解析,调用完成后恢复cf对象
//例如,解析到ngx_events_module模块的event指令,调用ngx_events_block()函数
//注意: ngx_events_block()函数中的上下文恢复:*cf = pcf;
rv = cmd->set(cf, cmd, conf);
if(rv == NGX_CONF_OK)
return NGX_OK;
return NGX_ERROR;
}
}
//10) 返回错误
return NGX_ERROR;
}2) 指令的配置上下文
上面说道建立指令的配置上下文,下面我们来看一下cf->ctx这个数据结构是如何建立的,这个ctx大概是一个怎样的数据结构。主要参考代码位置src/core/ngx_cycle.c源文件的ngx_init_cycle()函数:
//头文件:src/core/ngx/cycle.h
struct ngx_cycle_s {
void ****conf_ctx;
....
}
ngx_cycle_t *
ngx_init_cycle(ngx_cycle_t *old_cycle)
{
....
cycle->conf_ctx = ngx_pcalloc(pool, ngx_max_module * sizeof(void *));
if (cycle->conf_ctx == NULL) {
ngx_destroy_pool(pool);
return NULL;
}
....
for (i = 0; cycle->modules[i]; i++) {
if (cycle->modules[i]->type != NGX_CORE_MODULE) {
continue;
}
module = cycle->modules[i]->ctx;
if (module->create_conf) {
rv = module->create_conf(cycle);
if (rv == NULL) {
ngx_destroy_pool(pool);
return NULL;
}
cycle->conf_ctx[cycle->modules[i]->index] = rv;
}
}
....
}
//源文件: objs/ngx_modules.c
ngx_module_t *ngx_modules[] = {
&ngx_core_module,
&ngx_errlog_module,
&ngx_conf_module,
&ngx_openssl_module,
&ngx_regex_module,
&ngx_events_module,
&ngx_event_core_module,
&ngx_epoll_module,
&ngx_http_module,
&ngx_http_core_module,
&ngx_http_log_module,
&ngx_http_upstream_module,
&ngx_http_static_module,
&ngx_http_autoindex_module,
&ngx_http_index_module,
&ngx_http_auth_basic_module,
&ngx_http_access_module,
&ngx_http_limit_conn_module,
&ngx_http_limit_req_module,
&ngx_http_geo_module,
&ngx_http_map_module,
&ngx_http_split_clients_module,
&ngx_http_referer_module,
&ngx_http_rewrite_module,
&ngx_http_ssl_module,
&ngx_http_proxy_module,
&ngx_http_fastcgi_module,
&ngx_http_uwsgi_module,
&ngx_http_scgi_module,
&ngx_http_memcached_module,
&ngx_http_empty_gif_module,
&ngx_http_browser_module,
&ngx_http_upstream_hash_module,
&ngx_http_upstream_ip_hash_module,
&ngx_http_upstream_least_conn_module,
&ngx_http_upstream_keepalive_module,
&ngx_http_upstream_zone_module,
&ngx_http_write_filter_module,
&ngx_http_header_filter_module,
&ngx_http_chunked_filter_module,
&ngx_http_range_header_filter_module,
&ngx_http_gzip_filter_module,
&ngx_http_postpone_filter_module,
&ngx_http_ssi_filter_module,
&ngx_http_charset_filter_module,
&ngx_http_userid_filter_module,
&ngx_http_headers_filter_module,
&ngx_http_copy_filter_module,
&ngx_http_range_body_filter_module,
&ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module,
NULL
};从上面我们可以看到,首先建立了一个ngx_max_module大小的指针数组,然后再针对NGX_CORE_MODULE类型的模块调用:
rv = module->create_conf(cycle);来创建相应的上下文存放在该模块对应的索引处。属于NGX_CORE_MODULE的主要有以下几个:
-
ngx_core_module -
ngx_events_module -
ngx_openssl_module -
ngx_google_perftools_module -
ngx_http_module -
ngx_errlog_module -
ngx_mail_module -
ngx_regex_module -
ngx_stream_module -
ngx_thread_pool_module
下面我们就来简单的分析ngx_core_module、ngx_events_module、ngx_http_module这三个比较有代表性的模块,看其create_conf()到底是怎么创建起配置上下文的。
3) ngx_core_module模块
static ngx_core_module_t ngx_core_module_ctx = {
ngx_string("core"),
ngx_core_module_create_conf,
ngx_core_module_init_conf
};
ngx_module_t ngx_core_module = {
NGX_MODULE_V1,
&ngx_core_module_ctx, /* module context */
ngx_core_commands, /* module directives */
NGX_CORE_MODULE, /* module type */
NULL, /* init master */
NULL, /* init module */
NULL, /* init process */
NULL, /* init thread */
NULL, /* exit thread */
NULL, /* exit process */
NULL, /* exit master */
NGX_MODULE_V1_PADDING
};通过查看源代码,我们可以看到其实是创建了一个ngx_core_conf_t数据结构,以此作为该模块配置指令上下文的。
4) ngx_events_module模块
static ngx_core_module_t ngx_events_module_ctx = {
ngx_string("events"),
NULL,
ngx_event_init_conf
};
ngx_module_t ngx_events_module = {
NGX_MODULE_V1,
&ngx_events_module_ctx, /* module context */
ngx_events_commands, /* module directives */
NGX_CORE_MODULE, /* module type */
NULL, /* init master */
NULL, /* init module */
NULL, /* init process */
NULL, /* init thread */
NULL, /* exit thread */
NULL, /* exit process */
NULL, /* exit master */
NGX_MODULE_V1_PADDING
};这里我们可以看到,并没有通过module->create_conf创建其配置指令上下文的,但是我们可以看到:
static char *
ngx_events_block(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
{
...
//这里构建了一个无名指针,主要是为了与http类型的模块兼容
ctx = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(void *));
if (ctx == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
*ctx = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, ngx_event_max_module * sizeof(void *));
if (*ctx == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
*(void **) conf = ctx;
...
cf->ctx = ctx; //注意这里,后面关系到event模块地址的计算
}这里创建了一个二级指针数组,来存放上下文。
5) ngx_http_module模块
static ngx_core_module_t ngx_http_module_ctx = {
ngx_string("http"),
NULL,
NULL
};
ngx_module_t ngx_http_module = {
NGX_MODULE_V1,
&ngx_http_module_ctx, /* module context */
ngx_http_commands, /* module directives */
NGX_CORE_MODULE, /* module type */
NULL, /* init master */
NULL, /* init module */
NULL, /* init process */
NULL, /* init thread */
NULL, /* exit thread */
NULL, /* exit process */
NULL, /* exit master */
NGX_MODULE_V1_PADDING
};这里我们可以看到,并没有通过module->create_conf创建其配置指令上下文,但是我们可以看到:
typedef struct {
void **main_conf;
void **srv_conf;
void **loc_conf;
} ngx_http_conf_ctx_t;
static char *
ngx_http_block(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
{
...
/* the main http context */
ctx = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_conf_ctx_t));
if (ctx == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
*(ngx_http_conf_ctx_t **) conf = ctx;
....
ctx->main_conf = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool,
sizeof(void *) * ngx_http_max_module);
ctx->srv_conf = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(void *) * ngx_http_max_module);
ctx->loc_conf = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(void *) * ngx_http_max_module);
}这里创建了一个ngx_http_conf_ctx_t作为其上下文,其中main_conf、srv_conf、loc_conf又是指向一个指针数组,最后再指向相应的上下文。
5) ngx_cycle_s.conf_ctx结构示意图
通过上面的分析,我们可以刻画出4级指针的一个整体结构:
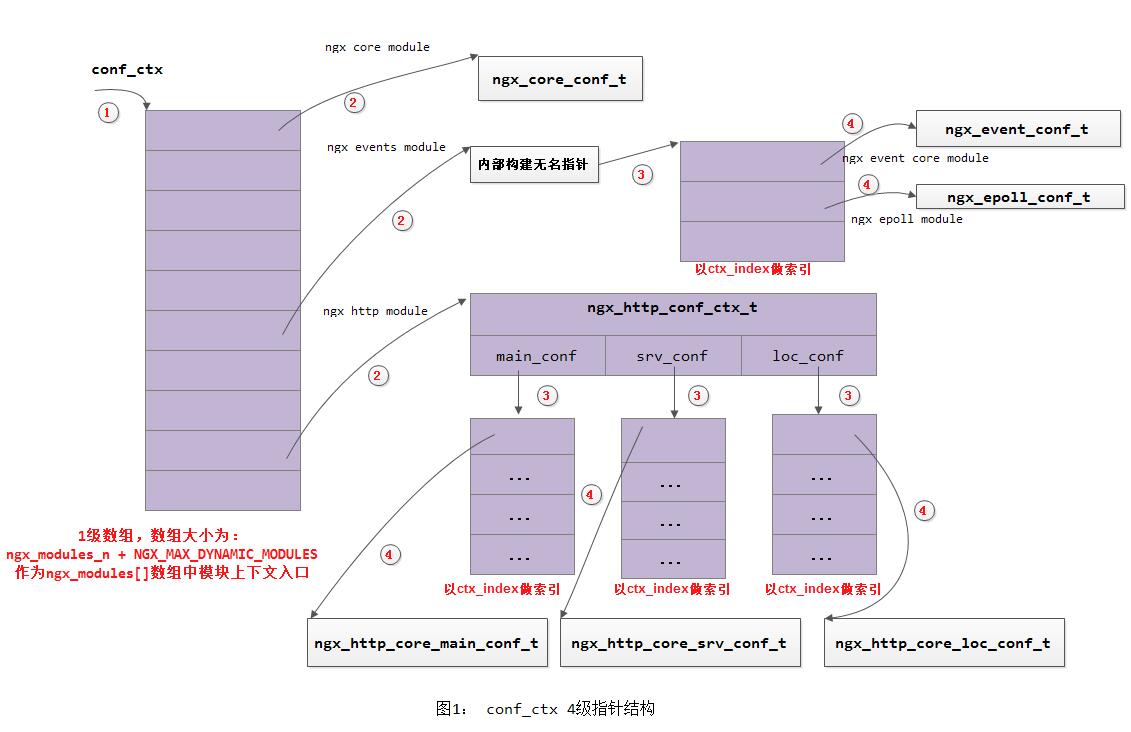
注意: 1) 上述ctx_index的初始化是在src/core/ngx_module.c的ngx_count_modules()中完成 2) 只有属于NGX_CORE_MODULE类型的模块才在cycle->conf_ctx数组中有相应的入口。
这里我们以解析http模块的server指令为例:
http{
server{
listen 80;
}
server{
listen 81;
}
}
在解析到http指令时,调用ngx_conf_handler(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_int_t last), 此时cf->ctx值为cycle->conf_ctx;而到了解析server指令时,再调用到ngx_conf_handler()函数时,cf->ctx的值为ngx_http_conf_ctx_t。
6) 建立指令上下文部分代码分析
static ngx_int_t
ngx_conf_handler(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_int_t last)
{
/* set up the directive's configuration context */
conf = NULL;
if (cmd->type & NGX_DIRECT_CONF) {
conf = ((void **) cf->ctx)[cf->cycle->modules[i]->index];
} else if (cmd->type & NGX_MAIN_CONF) {
conf = &(((void **) cf->ctx)[cf->cycle->modules[i]->index]);
} else if (cf->ctx) {
confp = *(void **) ((char *) cf->ctx + cmd->conf);
if (confp) {
conf = confp[cf->cycle->modules[i]->ctx_index];
}
}
rv = cmd->set(cf, cmd, conf);
}对于NGX_DIRECT_CONF类型,例如上图中的ngx_core_conf_t,直接将4级指针强制转换成2级指针即可;
对于NGX_MAIN_CONF类型,例如上图中的ngx_events_module以及ngx_http_module,则直接保存的地址是&conf_ctx[module_index];
对于其他类型,则保存对应数组在ctx_index索引处的地址, 例如对于ngx_event_core_module,由于cf->ctx当前指向的就是上面所构建的这个无名指针,因此这里confp就是这个无名指针指向的地址。
7) nginx module的启动流程
首先在ngx_init_cycle()中为cycle->conf_ctx分配空间,然后针对ngx_modules[]数组中的每一个NGX_CORE_MODULE类型的元素,调用其cycle->modules[i]->ctx的create_conf()来创建context; 再接着完成nginx -g选项传递进来的全局指令的解析,然后完成nginx配置文件的解析; 最后再针对ngx_modules[]数组中每一个NGX_CORE_MODULE类型的元素调用cycle->modules[i]->ctx的init_conf()来完成最后配置的一个初始化。
针对非NGX_CORE_MODULE类型的module,则在解析到对应配置块时调用该模块的ngx_module_s.ctx结构来完成上下文的建立。
struct ngx_cycle_s {
void ****conf_ctx;
...
};
struct ngx_module_s {
ngx_uint_t ctx_index;
ngx_uint_t index;
char *name;
....
void *ctx; //用户基于此来创建对应module上下文
ngx_command_t *commands;
ngx_uint_t type;
...
};
//针对核心模块,上述ngx_module_s.ctx指向的就是如下这样一个上下文
typedef struct {
ngx_str_t name;
void *(*create_conf)(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);
char *(*init_conf)(ngx_cycle_t *cycle, void *conf);
} ngx_core_module_t;
//针对配置文件解析,生成相应的ngx_conf_s对象,该对象关联着ngx_conf_file_t对象
struct ngx_conf_s {
char *name;
ngx_array_t *args;
ngx_cycle_t *cycle;
ngx_pool_t *pool;
ngx_pool_t *temp_pool;
ngx_conf_file_t *conf_file;
ngx_log_t *log;
void *ctx; //指向cycle->conf_ctx
ngx_uint_t module_type; //解析到的当前指令属于哪一个module
ngx_uint_t cmd_type; //当前解析到哪一个配置块的配置(NGX_MAIN_CONF/NGX_HTTP_MAIN_CONF等)
ngx_conf_handler_pt handler; //指令解析钩子函数
char *handler_conf;
};
[参看]

