event/ngx_event.c源文件分析
本章我们讲述一下nginx中event的实现。Nginx中的event对象ngx_event_t提供了一种机制,能够通知程序发生了某个事件。这里的event主要包括两大种类:
-
IO事件
-
定时器事件
1. 相关事件模块变量的声明
/*
* Copyright (C) Igor Sysoev
* Copyright (C) Nginx, Inc.
*/
#include <ngx_config.h>
#include <ngx_core.h>
#include <ngx_event.h>
#define DEFAULT_CONNECTIONS 512
extern ngx_module_t ngx_kqueue_module;
extern ngx_module_t ngx_eventport_module;
extern ngx_module_t ngx_devpoll_module;
extern ngx_module_t ngx_epoll_module;
extern ngx_module_t ngx_select_module;通常情况下,我们Linux操作系统支持select、poll、epoll这三种事件驱动机制。这里nginx启动时会根据当前event模块的配置选择恰当的事件驱动。
注: 这里似乎没有ngx_poll_module,但是在ngx_event_core_init_conf()函数中,通过cycle->modules[i]仍能够选择到。2. 相关静态函数声明
//初始化event模块 上下文 时的一个回调函数
static char *ngx_event_init_conf(ngx_cycle_t *cycle, void *conf);
//初始化event core模块的回调函数
static ngx_int_t ngx_event_module_init(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);
//初始化进程时候针对event core模块的回调函数,其会在ngx_event_module_init()函数之后才会调用
static ngx_int_t ngx_event_process_init(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);
//配置文件解析到events命令时候的回调函数
static char *ngx_events_block(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf);
//配置文件解析到worker_connections指令时的回调函数
static char *ngx_event_connections(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd,
void *conf);
//配置文件解析到use指令时的回调函数
static char *ngx_event_use(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf);
//配置文件解析到debug_connection指令时的回调函数
static char *ngx_event_debug_connection(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd,
void *conf);
//创建event core模块上下文的回调函数
static void *ngx_event_core_create_conf(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);
//初始化event core模块上下文的回调函数
static char *ngx_event_core_init_conf(ngx_cycle_t *cycle, void *conf);3. 相关变量定义
static ngx_uint_t ngx_timer_resolution;
sig_atomic_t ngx_event_timer_alarm;
static ngx_uint_t ngx_event_max_module;
ngx_uint_t ngx_event_flags;
ngx_event_actions_t ngx_event_actions;
static ngx_atomic_t connection_counter = 1;
ngx_atomic_t *ngx_connection_counter = &connection_counter;
ngx_atomic_t *ngx_accept_mutex_ptr;
ngx_shmtx_t ngx_accept_mutex;
ngx_uint_t ngx_use_accept_mutex;
ngx_uint_t ngx_accept_events;
ngx_uint_t ngx_accept_mutex_held;
ngx_msec_t ngx_accept_mutex_delay;
ngx_int_t ngx_accept_disabled;
#if (NGX_STAT_STUB)
ngx_atomic_t ngx_stat_accepted0;
ngx_atomic_t *ngx_stat_accepted = &ngx_stat_accepted0;
ngx_atomic_t ngx_stat_handled0;
ngx_atomic_t *ngx_stat_handled = &ngx_stat_handled0;
ngx_atomic_t ngx_stat_requests0;
ngx_atomic_t *ngx_stat_requests = &ngx_stat_requests0;
ngx_atomic_t ngx_stat_active0;
ngx_atomic_t *ngx_stat_active = &ngx_stat_active0;
ngx_atomic_t ngx_stat_reading0;
ngx_atomic_t *ngx_stat_reading = &ngx_stat_reading0;
ngx_atomic_t ngx_stat_writing0;
ngx_atomic_t *ngx_stat_writing = &ngx_stat_writing0;
ngx_atomic_t ngx_stat_waiting0;
ngx_atomic_t *ngx_stat_waiting = &ngx_stat_waiting0;
#endif下面我们简要介绍一下这些字段:
- ngx_timer_resolution: 可以通过nginx配置文件主配置段中的
timer_resolution指令来降低worker进程的定时器分辨率(timer resolution),这样就可以降低gettimeofday()系统调用的次数。默认情况下,gettimeofday()会在每一次收到kernel事件时被调用。我们可以通过降低timer resolution的值,这样gettimeofday()函数就会每隔interval时间被调用一次。例如:
timer_resolution 100ms;
内部interval的实现依赖于所使用的方法:
假如所采用的事件驱动机制是```kqueue```的话,使用EVFILT_TIMER filter来实现 假如所采用的事件驱动机制是```eventport```的话,使用timer_create()来实现 否则,采用setitimer()来实现
-
ngx_event_timer_alarm: 当收到
SIGALARM信号时,会将此变量置为1,以指示更新Nginx缓存时间 -
ngx_event_max_module: 当前属于NGX_EVENT_MODULE模块的个数
-
ngx_event_flags: 用于保存当前
事件驱动机制所支持的事件掩码 -
ngx_event_actions: 用于保存当前事件驱动机制下的actions函数
-
connection_counter/ngx_connection_counter: 用于统计当前的连接数
-
ngx_accept_mutex_ptr: 存放互斥量内存地址的指针
-
ngx_accept_mutex: accept互斥锁
-
ngx_use_accept_mutex: 表示是否需要通过对accept加锁来解决惊群问题。当nginx worker进程数
大于1时,且配置文件中开启了accept_mutex时,这个标志置为1 -
ngx_accept_events: 表示在获取accept互斥锁的时候,是否还需要调用ngx_enable_accept_events()来使能accept events。通常采用
eventport这一事件驱动机制时才需要。 -
ngx_accept_mutex_held: 用于指示当前是否拿到了锁
-
ngx_accept_mutex_delay: 当
accept_mutex被启用的话,如果当前有另一个worker进程正在accept新连接(connections),则当前worker进程最长会等待多长时间尝试重新开始accept新连接。其实就是获取互斥锁的最大延迟时间 -
ngx_accept_disabled: 用于控制当前worker进程是否参与获取
ngx_accept_mutex。一般在当前worker进程连接数过多时,就不会参与竞争,这样可以起到负载均衡的目的。
我们当前并不支持NGX_STAT_STUB,该宏定义需要在启用HTTP_STUB_STATUS编译选项时才会定义。请参看Module ngx_http_stub_status_module但是这里我们还是简单介绍一下各字段的含义。
-
ngx_stat_accepted0/ngx_stat_accepted: 用于统计当前nginx一共accept多少连接
-
ngx_stat_handled0/ngx_stat_handled: 用于统计当前所处理的总的连接数。通常情况下,本字段的值与
ngx_stat_accepted字段的值相同,除非达到了一些资源的限制(例如,worker_connections的限制) -
ngx_stat_requests0/ngx_stat_requests: 用于统计客户端总的请求数
-
ngx_stat_active0/ngx_stat_active: 用于统计当前处于active状态的客户端连接数,这也包括
Waiting状态的连接 -
ngx_stat_reading0/ngx_stat_reading: 当前Nginx正在读取
请求头(request header)的连接数 -
ngx_stat_writing0/ngx_stat_writing: 当前nginx正在向客户端
回写应答(write the response back)的连接数 -
ngx_stat_waiting0/ngx_stat_waiting: 当前正处于空闲状态的客户端连接数。
4. event module相关变量
static ngx_command_t ngx_events_commands[] = {
{ ngx_string("events"),
NGX_MAIN_CONF|NGX_CONF_BLOCK|NGX_CONF_NOARGS,
ngx_events_block,
0,
0,
NULL },
ngx_null_command
};
static ngx_core_module_t ngx_events_module_ctx = {
ngx_string("events"),
NULL,
ngx_event_init_conf
};
ngx_module_t ngx_events_module = {
NGX_MODULE_V1,
&ngx_events_module_ctx, /* module context */
ngx_events_commands, /* module directives */
NGX_CORE_MODULE, /* module type */
NULL, /* init master */
NULL, /* init module */
NULL, /* init process */
NULL, /* init thread */
NULL, /* exit thread */
NULL, /* exit process */
NULL, /* exit master */
NGX_MODULE_V1_PADDING
};
static ngx_str_t event_core_name = ngx_string("event_core");
static ngx_command_t ngx_event_core_commands[] = {
{ ngx_string("worker_connections"),
NGX_EVENT_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_event_connections,
0,
0,
NULL },
{ ngx_string("use"),
NGX_EVENT_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_event_use,
0,
0,
NULL },
{ ngx_string("multi_accept"),
NGX_EVENT_CONF|NGX_CONF_FLAG,
ngx_conf_set_flag_slot,
0,
offsetof(ngx_event_conf_t, multi_accept),
NULL },
{ ngx_string("accept_mutex"),
NGX_EVENT_CONF|NGX_CONF_FLAG,
ngx_conf_set_flag_slot,
0,
offsetof(ngx_event_conf_t, accept_mutex),
NULL },
{ ngx_string("accept_mutex_delay"),
NGX_EVENT_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_conf_set_msec_slot,
0,
offsetof(ngx_event_conf_t, accept_mutex_delay),
NULL },
{ ngx_string("debug_connection"),
NGX_EVENT_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_event_debug_connection,
0,
0,
NULL },
ngx_null_command
};
ngx_event_module_t ngx_event_core_module_ctx = {
&event_core_name,
ngx_event_core_create_conf, /* create configuration */
ngx_event_core_init_conf, /* init configuration */
{ NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL }
};
ngx_module_t ngx_event_core_module = {
NGX_MODULE_V1,
&ngx_event_core_module_ctx, /* module context */
ngx_event_core_commands, /* module directives */
NGX_EVENT_MODULE, /* module type */
NULL, /* init master */
ngx_event_module_init, /* init module */
ngx_event_process_init, /* init process */
NULL, /* init thread */
NULL, /* exit thread */
NULL, /* exit process */
NULL, /* exit master */
NGX_MODULE_V1_PADDING
};下面简单介绍一下这些变量:
-
ngx_events_commands: nginx的
events命令 -
ngx_events_module_ctx: events模块上下文
-
ngx_events_module: nginx events模块
-
event_core_name: nginx 事件核心模块名称为
event_core -
ngx_event_core_commands: nginx事件核心模块命令
-
ngx_event_core_module_ctx: nginx事件核心模块上下文
-
ngx_event_core_module: nginx事件核心模块
5. 函数ngx_process_events_and_timers()
void
ngx_process_events_and_timers(ngx_cycle_t *cycle)
{
ngx_uint_t flags;
ngx_msec_t timer, delta;
if (ngx_timer_resolution) {
timer = NGX_TIMER_INFINITE;
flags = 0;
} else {
timer = ngx_event_find_timer();
flags = NGX_UPDATE_TIME;
#if (NGX_WIN32)
/* handle signals from master in case of network inactivity */
if (timer == NGX_TIMER_INFINITE || timer > 500) {
timer = 500;
}
#endif
}
if (ngx_use_accept_mutex) {
if (ngx_accept_disabled > 0) {
ngx_accept_disabled--;
} else {
if (ngx_trylock_accept_mutex(cycle) == NGX_ERROR) {
return;
}
if (ngx_accept_mutex_held) {
flags |= NGX_POST_EVENTS;
} else {
if (timer == NGX_TIMER_INFINITE
|| timer > ngx_accept_mutex_delay)
{
timer = ngx_accept_mutex_delay;
}
}
}
}
delta = ngx_current_msec;
(void) ngx_process_events(cycle, timer, flags);
delta = ngx_current_msec - delta;
ngx_log_debug1(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, cycle->log, 0,
"timer delta: %M", delta);
ngx_event_process_posted(cycle, &ngx_posted_accept_events);
if (ngx_accept_mutex_held) {
ngx_shmtx_unlock(&ngx_accept_mutex);
}
if (delta) {
ngx_event_expire_timers();
}
ngx_event_process_posted(cycle, &ngx_posted_events);
}本函数作为nginx处理IO事件以及定时器事件的主入口函数。下面我们简要分析一下函数的实现:
void
ngx_process_events_and_timers(ngx_cycle_t *cycle)
{
//1) 获得下一次事件处理的超时时间。这里如果配置了ngx_timer_resolution的话,那么将timer设置为NGX_TIMER_INFINITE,
// flag设置为0; 否则,将从红黑树中查找最近超时时间,并将flag设置为NGX_UPDATE_TIME。这里注意将timer设置为
// NGX_TIMER_INFINITE也并不会造成在IO空闲时无限等待,导致定时器事件永不执行,因为在ngx_event_process_init()函数中
// 我们会设置通过setitimer()或eventport或kqueue独有的超时机制来确保定时器会得到触发
//2) 当nginx worker进程数大于1,并且配置文件中开启了accept_mutex时,ngx_use_accept_mutex字段会置为1,此时会尝试
// 获取accept_mutex互斥锁。如果ngx_accept_disabled大于0,表示当前worker进程连接数较多负载较重,此时会放弃获取
//accept_mutex; 否则调用ngx_trylock_accept_mutex()尝试获取,如果获取到了的话,则flags |= NGX_POST_EVENTS;
//否则,会在ngx_accept_mutex_delay时间之后再尝试获取accept_mutex锁,以接受客户端的连接
//3) 记录当前的时间(单位: 毫秒)
delta = ngx_current_msec;
//4) 等待IO事件的到来,timer时间到了超时返回,或者收到中断信号返回
(void) ngx_process_events(cycle, timer, flags);
//5) 计算上述等待耗费的时间
delta = ngx_current_msec - delta;
//6) 处理ngx_posted_accept_events这一post队列中的事件(这是因为accept事件优先级较高,所以放到前面来处理)
ngx_event_process_posted(cycle, &ngx_posted_accept_events);
//7) 如果当前获得了accept_mutex锁,还需要释放锁,否则别的进程获取不到accept_mutex锁,将永远得不到机会
// 来accept客户端连接
if (ngx_accept_mutex_held) {
ngx_shmtx_unlock(&ngx_accept_mutex);
}
//8) 处理定时器集合中的超时事件
if (delta) {
ngx_event_expire_timers();
}
//9) 处理ngx_posted_events这一post队列只能够的事件(这种事件优先级较低,放到最后来进行处理)
ngx_event_process_posted(cycle, &ngx_posted_events);
}6. 函数ngx_handle_read_event()
ngx_int_t
ngx_handle_read_event(ngx_event_t *rev, ngx_uint_t flags)
{
if (ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_CLEAR_EVENT) {
/* kqueue, epoll */
if (!rev->active && !rev->ready) {
if (ngx_add_event(rev, NGX_READ_EVENT, NGX_CLEAR_EVENT)
== NGX_ERROR)
{
return NGX_ERROR;
}
}
return NGX_OK;
} else if (ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_LEVEL_EVENT) {
/* select, poll, /dev/poll */
if (!rev->active && !rev->ready) {
if (ngx_add_event(rev, NGX_READ_EVENT, NGX_LEVEL_EVENT)
== NGX_ERROR)
{
return NGX_ERROR;
}
return NGX_OK;
}
if (rev->active && (rev->ready || (flags & NGX_CLOSE_EVENT))) {
if (ngx_del_event(rev, NGX_READ_EVENT, NGX_LEVEL_EVENT | flags)
== NGX_ERROR)
{
return NGX_ERROR;
}
return NGX_OK;
}
} else if (ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_EVENTPORT_EVENT) {
/* event ports */
if (!rev->active && !rev->ready) {
if (ngx_add_event(rev, NGX_READ_EVENT, 0) == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
return NGX_OK;
}
if (rev->oneshot && !rev->ready) {
if (ngx_del_event(rev, NGX_READ_EVENT, 0) == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
return NGX_OK;
}
}
/* iocp */
return NGX_OK;
}本函数用于向nginx事件驱动机制登记为读事件。通常在连接建立或者读取完一次数据之后,需要再调用一次本函数。下面简要介绍一下函数的实现:
ngx_int_t
ngx_handle_read_event(ngx_event_t *rev, ngx_uint_t flags)
{
if (ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_CLEAR_EVENT) {
//1) 表示当前nginx事件驱动机制采用的是边沿触发方式。一般epoll、kqueue支持
//此种触发方式。调用ngx_add_event()添加读事件
if (!rev->active && !rev->ready){
}
}else if(ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_LEVEL_EVENT){
//2) 表示当前nginx事件驱动机制采用的是水平触发方式。一般select、poll、dev/poll只
//支持此种触发方式。调用ngx_add_event()添加读事件
if (!rev->active && !rev->ready) {
ngx_add_event();
return NGX_OK;
}
if (rev->active && (rev->ready || (flags & NGX_CLOSE_EVENT))) {
//此种情况下要删除事件。这是因为底层nginx事件驱动机制采用的水平触发,而我们nginx对于上层
//统一采用的都是边沿触发。这里如果不移除,那么底层会不断的进行通知,导致系统性能较差
ngx_del_event();
}
}else if (ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_EVENTPORT_EVENT) {
//3) 处理eventport读事件
if (!rev->active && !rev->ready){
//添加读事件
return NGX_OK;
}
if (rev->oneshot && !rev->ready) {
//如果是oneshot事件,并且现在没有数据可读了,那么要移除该一次性事件
ngx_del_event();
return NGX_OK;
}
}
}注意: Nginx中事件驱动机制底层有些支持边沿触发,有些只支持水平触发。但是在Nginx上层统一都采用边沿触发。以降低事件的通知频率,提高整体系统性能。
7. 函数ngx_handle_write_event()
ngx_int_t
ngx_handle_write_event(ngx_event_t *wev, size_t lowat)
{
ngx_connection_t *c;
if (lowat) {
c = wev->data;
if (ngx_send_lowat(c, lowat) == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
}
if (ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_CLEAR_EVENT) {
/* kqueue, epoll */
if (!wev->active && !wev->ready) {
if (ngx_add_event(wev, NGX_WRITE_EVENT,
NGX_CLEAR_EVENT | (lowat ? NGX_LOWAT_EVENT : 0))
== NGX_ERROR)
{
return NGX_ERROR;
}
}
return NGX_OK;
} else if (ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_LEVEL_EVENT) {
/* select, poll, /dev/poll */
if (!wev->active && !wev->ready) {
if (ngx_add_event(wev, NGX_WRITE_EVENT, NGX_LEVEL_EVENT)
== NGX_ERROR)
{
return NGX_ERROR;
}
return NGX_OK;
}
if (wev->active && wev->ready) {
if (ngx_del_event(wev, NGX_WRITE_EVENT, NGX_LEVEL_EVENT)
== NGX_ERROR)
{
return NGX_ERROR;
}
return NGX_OK;
}
} else if (ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_EVENTPORT_EVENT) {
/* event ports */
if (!wev->active && !wev->ready) {
if (ngx_add_event(wev, NGX_WRITE_EVENT, 0) == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
return NGX_OK;
}
if (wev->oneshot && wev->ready) {
if (ngx_del_event(wev, NGX_WRITE_EVENT, 0) == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
return NGX_OK;
}
}
/* iocp */
return NGX_OK;
}本函数用于向nginx事件驱动机制登记为写事件。通常在连接建立或者连接当前不处于写状态时,需要再调用一次本函数。下面简要介绍一下函数的实现:
ngx_int_t
ngx_handle_write_event(ngx_event_t *wev, size_t lowat)
{
//1) 如果lowat值不为0,那么调用ngx_send_lowat()函数设置socket的SO_SNDLOWAT选项,表示
//若该socket发送缓冲区中的数据低于lowat时,那么epoll、select等事件驱动机制就能检测到
//当前socket可写
if (ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_CLEAR_EVENT) {
//2) 表示当前nginx事件驱动机制采用的是边沿触发方式。一般epoll、kqueue支持
//此种触发方式。调用ngx_add_event()添加读事件
if (!wev->active && !wev->ready) {
//这里判断条件要求当前event本身不处于写ready状态,才需要进行设置
}
}else if (ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_LEVEL_EVENT) {
//3) 表示当前nginx事件驱动机制采用的是水平触发方式。一般select、poll、dev/poll只
//支持此种触发方式。调用ngx_add_event()添加写事件
if (!wev->active && !wev->ready) {
ngx_add_event();
return NGX_OK;
}
if (wev->active && wev->ready) {
//此种情况下要删除事件。这是因为底层nginx事件驱动机制采用的水平触发,而我们nginx对于上层
//统一采用的都是边沿触发。这里如果不移除,那么底层会不断的进行通知,导致系统性能较差
ngx_del_event();
}
}else if (ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_EVENTPORT_EVENT) {
//3) 处理eventport写事件
if (!wev->active && !wev->ready){
//添加读事件
return NGX_OK;
}
if (wev->oneshot && wev->ready) {
//如果是oneshot事件,并且现在处于写就绪状态,那么要移除该一次性事件
ngx_del_event();
return NGX_OK;
}
}
}8. 函数ngx_event_init_conf()
static char *
ngx_event_init_conf(ngx_cycle_t *cycle, void *conf)
{
if (ngx_get_conf(cycle->conf_ctx, ngx_events_module) == NULL) {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cycle->log, 0,
"no \"events\" section in configuration");
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}此函数会在nginx event模块初始化时被调用。下面简要介绍一下本函数的调用流程:
ngx_init_cycle(){
ngx_conf_param();
//当解析到events{}块时,就会调用到ngx_events_block()函数,并在其中创建
//event的上下文
ngx_conf_parse();
//初始化核心模块NGX_CORE_MODULE,即回调核心模块的init_conf()函数。
//对于events模块,其本身属于核心模块,因此会在这里调用到ngx_event_init_conf()函数
//如果配置文件中没有配置event{}块,那么此处就会出错
}9. 函数ngx_event_module_init()
static ngx_int_t
ngx_event_module_init(ngx_cycle_t *cycle)
{
void ***cf;
u_char *shared;
size_t size, cl;
ngx_shm_t shm;
ngx_time_t *tp;
ngx_core_conf_t *ccf;
ngx_event_conf_t *ecf;
cf = ngx_get_conf(cycle->conf_ctx, ngx_events_module);
ecf = (*cf)[ngx_event_core_module.ctx_index];
if (!ngx_test_config && ngx_process <= NGX_PROCESS_MASTER) {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_NOTICE, cycle->log, 0,
"using the \"%s\" event method", ecf->name);
}
ccf = (ngx_core_conf_t *) ngx_get_conf(cycle->conf_ctx, ngx_core_module);
ngx_timer_resolution = ccf->timer_resolution;
#if !(NGX_WIN32)
{
ngx_int_t limit;
struct rlimit rlmt;
if (getrlimit(RLIMIT_NOFILE, &rlmt) == -1) {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_ALERT, cycle->log, ngx_errno,
"getrlimit(RLIMIT_NOFILE) failed, ignored");
} else {
if (ecf->connections > (ngx_uint_t) rlmt.rlim_cur
&& (ccf->rlimit_nofile == NGX_CONF_UNSET
|| ecf->connections > (ngx_uint_t) ccf->rlimit_nofile))
{
limit = (ccf->rlimit_nofile == NGX_CONF_UNSET) ?
(ngx_int_t) rlmt.rlim_cur : ccf->rlimit_nofile;
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_WARN, cycle->log, 0,
"%ui worker_connections exceed "
"open file resource limit: %i",
ecf->connections, limit);
}
}
}
#endif /* !(NGX_WIN32) */
if (ccf->master == 0) {
return NGX_OK;
}
if (ngx_accept_mutex_ptr) {
return NGX_OK;
}
/* cl should be equal to or greater than cache line size */
cl = 128;
size = cl /* ngx_accept_mutex */
+ cl /* ngx_connection_counter */
+ cl; /* ngx_temp_number */
#if (NGX_STAT_STUB)
size += cl /* ngx_stat_accepted */
+ cl /* ngx_stat_handled */
+ cl /* ngx_stat_requests */
+ cl /* ngx_stat_active */
+ cl /* ngx_stat_reading */
+ cl /* ngx_stat_writing */
+ cl; /* ngx_stat_waiting */
#endif
shm.size = size;
shm.name.len = sizeof("nginx_shared_zone") - 1;
shm.name.data = (u_char *) "nginx_shared_zone";
shm.log = cycle->log;
if (ngx_shm_alloc(&shm) != NGX_OK) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
shared = shm.addr;
ngx_accept_mutex_ptr = (ngx_atomic_t *) shared;
ngx_accept_mutex.spin = (ngx_uint_t) -1;
if (ngx_shmtx_create(&ngx_accept_mutex, (ngx_shmtx_sh_t *) shared,
cycle->lock_file.data)
!= NGX_OK)
{
return NGX_ERROR;
}
ngx_connection_counter = (ngx_atomic_t *) (shared + 1 * cl);
(void) ngx_atomic_cmp_set(ngx_connection_counter, 0, 1);
ngx_log_debug2(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, cycle->log, 0,
"counter: %p, %uA",
ngx_connection_counter, *ngx_connection_counter);
ngx_temp_number = (ngx_atomic_t *) (shared + 2 * cl);
tp = ngx_timeofday();
ngx_random_number = (tp->msec << 16) + ngx_pid;
#if (NGX_STAT_STUB)
ngx_stat_accepted = (ngx_atomic_t *) (shared + 3 * cl);
ngx_stat_handled = (ngx_atomic_t *) (shared + 4 * cl);
ngx_stat_requests = (ngx_atomic_t *) (shared + 5 * cl);
ngx_stat_active = (ngx_atomic_t *) (shared + 6 * cl);
ngx_stat_reading = (ngx_atomic_t *) (shared + 7 * cl);
ngx_stat_writing = (ngx_atomic_t *) (shared + 8 * cl);
ngx_stat_waiting = (ngx_atomic_t *) (shared + 9 * cl);
#endif
return NGX_OK;
}此函数作为nginx event核心模块的初始化函数,会在nginx中所有模块(nginx core模块、http模块、event模块、upstream模块等)都完成之后,在ngx_init_cycle()中被调用:
ngx_init_cycle(){
ngx_init_modules();
}
下面我们就简要介绍一下本函数的实现:
static ngx_int_t
ngx_event_module_init(ngx_cycle_t *cycle)
{
//1) 获取nginx event模块的配置以及event core模块的配置
void ***cf;
ngx_core_conf_t *ccf;
ngx_event_conf_t *ecf;
cf = ngx_get_conf(cycle->conf_ctx, ngx_events_module);
ecf = (*cf)[ngx_event_core_module.ctx_index];
//2) 日志中打印当前nginx所使用的事件驱动机制
if (!ngx_test_config && ngx_process <= NGX_PROCESS_MASTER) {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_NOTICE, cycle->log, 0,
"using the \"%s\" event method", ecf->name);
}
//3) 获取nginx core模块配置以当前时间分辨率
ccf = (ngx_core_conf_t *) ngx_get_conf(cycle->conf_ctx, ngx_core_module);
ngx_timer_resolution = ccf->timer_resolution;
//4) 获得可以打开连接的限制数。该限制数首先不能超过操作系统所设置的资源限制数,也不能
//操作nginx配置文件中worker_rlimit_nofile配置指令设置的值
//5) 因为下面都是初始化互斥锁相关操作,因此如果nginx不是以master/worker方式工作的话,那么初始化到
//这里就会结束
if (ccf->master == 0) {
return NGX_OK;
}
//6) 这里确保accept_mutex只会初始化一次。即使在nginx进行restart的情况下
if (ngx_accept_mutex_ptr) {
return NGX_OK;
}
//7) 计算存放如下这些所有nginx进程都能访问到的全局变量所需要的空间。这里注意到
// c1的大小应该大于等于cache line size,这样就能确保下面所分配的共享内存块
// 被真正映射到物理内存之中
/* cl should be equal to or greater than cache line size */
cl = 128;
size = cl /* ngx_accept_mutex */
+ cl /* ngx_connection_counter */
+ cl; /* ngx_temp_number */
#if (NGX_STAT_STUB)
size += cl /* ngx_stat_accepted */
+ cl /* ngx_stat_handled */
+ cl /* ngx_stat_requests */
+ cl /* ngx_stat_active */
+ cl /* ngx_stat_reading */
+ cl /* ngx_stat_writing */
+ cl; /* ngx_stat_waiting */
#endif
//8) 为各全局共享内存变量指定首地址
}如下是各全局共享内存变量在内存中的示意图:

10. 函数ngx_timer_signal_handler()
#if !(NGX_WIN32)
static void
ngx_timer_signal_handler(int signo)
{
ngx_event_timer_alarm = 1;
#if 1
ngx_log_debug0(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, ngx_cycle->log, 0, "timer signal");
#endif
}
#endif此函数作为SIGALRM信号的处理函数。
11. 函数ngx_event_process_init()
static ngx_int_t
ngx_event_process_init(ngx_cycle_t *cycle)
{
ngx_uint_t m, i;
ngx_event_t *rev, *wev;
ngx_listening_t *ls;
ngx_connection_t *c, *next, *old;
ngx_core_conf_t *ccf;
ngx_event_conf_t *ecf;
ngx_event_module_t *module;
ccf = (ngx_core_conf_t *) ngx_get_conf(cycle->conf_ctx, ngx_core_module);
ecf = ngx_event_get_conf(cycle->conf_ctx, ngx_event_core_module);
if (ccf->master && ccf->worker_processes > 1 && ecf->accept_mutex) {
ngx_use_accept_mutex = 1;
ngx_accept_mutex_held = 0;
ngx_accept_mutex_delay = ecf->accept_mutex_delay;
} else {
ngx_use_accept_mutex = 0;
}
#if (NGX_WIN32)
/*
* disable accept mutex on win32 as it may cause deadlock if
* grabbed by a process which can't accept connections
*/
ngx_use_accept_mutex = 0;
#endif
ngx_queue_init(&ngx_posted_accept_events);
ngx_queue_init(&ngx_posted_events);
if (ngx_event_timer_init(cycle->log) == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
for (m = 0; cycle->modules[m]; m++) {
if (cycle->modules[m]->type != NGX_EVENT_MODULE) {
continue;
}
if (cycle->modules[m]->ctx_index != ecf->use) {
continue;
}
module = cycle->modules[m]->ctx;
if (module->actions.init(cycle, ngx_timer_resolution) != NGX_OK) {
/* fatal */
exit(2);
}
break;
}
#if !(NGX_WIN32)
if (ngx_timer_resolution && !(ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_TIMER_EVENT)) {
struct sigaction sa;
struct itimerval itv;
ngx_memzero(&sa, sizeof(struct sigaction));
sa.sa_handler = ngx_timer_signal_handler;
sigemptyset(&sa.sa_mask);
if (sigaction(SIGALRM, &sa, NULL) == -1) {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_ALERT, cycle->log, ngx_errno,
"sigaction(SIGALRM) failed");
return NGX_ERROR;
}
itv.it_interval.tv_sec = ngx_timer_resolution / 1000;
itv.it_interval.tv_usec = (ngx_timer_resolution % 1000) * 1000;
itv.it_value.tv_sec = ngx_timer_resolution / 1000;
itv.it_value.tv_usec = (ngx_timer_resolution % 1000 ) * 1000;
if (setitimer(ITIMER_REAL, &itv, NULL) == -1) {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_ALERT, cycle->log, ngx_errno,
"setitimer() failed");
}
}
if (ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_FD_EVENT) {
struct rlimit rlmt;
if (getrlimit(RLIMIT_NOFILE, &rlmt) == -1) {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_ALERT, cycle->log, ngx_errno,
"getrlimit(RLIMIT_NOFILE) failed");
return NGX_ERROR;
}
cycle->files_n = (ngx_uint_t) rlmt.rlim_cur;
cycle->files = ngx_calloc(sizeof(ngx_connection_t *) * cycle->files_n,
cycle->log);
if (cycle->files == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
}
#else
if (ngx_timer_resolution && !(ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_TIMER_EVENT)) {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_WARN, cycle->log, 0,
"the \"timer_resolution\" directive is not supported "
"with the configured event method, ignored");
ngx_timer_resolution = 0;
}
#endif
cycle->connections =
ngx_alloc(sizeof(ngx_connection_t) * cycle->connection_n, cycle->log);
if (cycle->connections == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
c = cycle->connections;
cycle->read_events = ngx_alloc(sizeof(ngx_event_t) * cycle->connection_n,
cycle->log);
if (cycle->read_events == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
rev = cycle->read_events;
for (i = 0; i < cycle->connection_n; i++) {
rev[i].closed = 1;
rev[i].instance = 1;
}
cycle->write_events = ngx_alloc(sizeof(ngx_event_t) * cycle->connection_n,
cycle->log);
if (cycle->write_events == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
wev = cycle->write_events;
for (i = 0; i < cycle->connection_n; i++) {
wev[i].closed = 1;
}
i = cycle->connection_n;
next = NULL;
do {
i--;
c[i].data = next;
c[i].read = &cycle->read_events[i];
c[i].write = &cycle->write_events[i];
c[i].fd = (ngx_socket_t) -1;
next = &c[i];
} while (i);
cycle->free_connections = next;
cycle->free_connection_n = cycle->connection_n;
/* for each listening socket */
ls = cycle->listening.elts;
for (i = 0; i < cycle->listening.nelts; i++) {
#if (NGX_HAVE_REUSEPORT)
if (ls[i].reuseport && ls[i].worker != ngx_worker) {
continue;
}
#endif
c = ngx_get_connection(ls[i].fd, cycle->log);
if (c == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
c->type = ls[i].type;
c->log = &ls[i].log;
c->listening = &ls[i];
ls[i].connection = c;
rev = c->read;
rev->log = c->log;
rev->accept = 1;
#if (NGX_HAVE_DEFERRED_ACCEPT)
rev->deferred_accept = ls[i].deferred_accept;
#endif
if (!(ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_IOCP_EVENT)) {
if (ls[i].previous) {
/*
* delete the old accept events that were bound to
* the old cycle read events array
*/
old = ls[i].previous->connection;
if (ngx_del_event(old->read, NGX_READ_EVENT, NGX_CLOSE_EVENT)
== NGX_ERROR)
{
return NGX_ERROR;
}
old->fd = (ngx_socket_t) -1;
}
}
#if (NGX_WIN32)
if (ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_IOCP_EVENT) {
ngx_iocp_conf_t *iocpcf;
rev->handler = ngx_event_acceptex;
if (ngx_use_accept_mutex) {
continue;
}
if (ngx_add_event(rev, 0, NGX_IOCP_ACCEPT) == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
ls[i].log.handler = ngx_acceptex_log_error;
iocpcf = ngx_event_get_conf(cycle->conf_ctx, ngx_iocp_module);
if (ngx_event_post_acceptex(&ls[i], iocpcf->post_acceptex)
== NGX_ERROR)
{
return NGX_ERROR;
}
} else {
rev->handler = ngx_event_accept;
if (ngx_use_accept_mutex) {
continue;
}
if (ngx_add_event(rev, NGX_READ_EVENT, 0) == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
}
#else
rev->handler = (c->type == SOCK_STREAM) ? ngx_event_accept
: ngx_event_recvmsg;
if (ngx_use_accept_mutex
#if (NGX_HAVE_REUSEPORT)
&& !ls[i].reuseport
#endif
)
{
continue;
}
if (ngx_add_event(rev, NGX_READ_EVENT, 0) == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
#endif
}
return NGX_OK;
}此函数作为nginx event core模块的init_process回调函数,一般会在worker进程初始化时被调用。下面我们简要介绍一下本函数的执行流程:
static ngx_int_t
ngx_event_process_init(ngx_cycle_t *cycle)
{
//1) 获取nginx core模块、event core模块的配置信息
ngx_core_conf_t *ccf;
ngx_event_conf_t *ecf;
ngx_event_module_t *module;
ccf = (ngx_core_conf_t *) ngx_get_conf(cycle->conf_ctx, ngx_core_module);
ecf = ngx_event_get_conf(cycle->conf_ctx, ngx_event_core_module);
//2) 判断是否要采用accept_mutex: 只有在worker进程数大于1,且以master/worker方式工作,
// 且配置文件制定了accept_mutex配置时,才会启用。accept_mutex在系统并发性相对较低时,
// 通过避免惊群的方式提高系统性能;而在并发很高的情况下,让多个worker进程随时去accept新
// 进来的连接,反而能提高效率
if (ccf->master && ccf->worker_processes > 1 && ecf->accept_mutex) {
ngx_use_accept_mutex = 1;
ngx_accept_mutex_held = 0;
ngx_accept_mutex_delay = ecf->accept_mutex_delay;
} else {
ngx_use_accept_mutex = 0;
}
//3) 初始化ngx_posted_accept_events、ngx_posted_events队列,定时器红黑树,以及通过
//actions.init()回调函数完成事件驱动机制的初始化
#if !(NGX_WIN32)
//4) 如果在nginx配置文件中指定了ngx_timer_resolution,那么这里通过setitimer()来
// 产生一个指定时间分辨率的定时器(这可能会导致nginx定时器红黑树中的各timer events
// 的精确性产生一定影响,之所以采用timer resolution,主要是性能方面的考虑)
if (ngx_timer_resolution && !(ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_TIMER_EVENT)) {
}
//5) 表示本event filter没有透明数据,并需要一个文件描述符表。这里进行建立
if (ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_FD_EVENT) {
}
#else
//6) windows平台,一般不支持timer resolution,此时可以通过红黑树中的当前最小定时间隔
// 来设置事件驱动机制的超时时间
if (ngx_timer_resolution && !(ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_TIMER_EVENT)) {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_WARN, cycle->log, 0,
"the \"timer_resolution\" directive is not supported "
"with the configured event method, ignored");
ngx_timer_resolution = 0;
}
#endif
//7) 为cycle->connections分配好空间
cycle->connections = ngx_alloc(sizeof(ngx_connection_t) * cycle->connection_n, cycle->log);
if (cycle->connections == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
c = cycle->connections;
//8) 为cycle->read_events分配好空间
cycle->read_events = ngx_alloc(sizeof(ngx_event_t) * cycle->connection_n,cycle->log);
if (cycle->read_events == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
rev = cycle->read_events;
for (i = 0; i < cycle->connection_n; i++) {
rev[i].closed = 1; //此处,closed标志表示当前connection所关联的socket是否处于打开状态
rev[i].instance = 1; //
}
//9) 为cycle->write_events分配好空间
cycle->write_events = ngx_alloc(sizeof(ngx_event_t) * cycle->connection_n,cycle->log);
if (cycle->write_events == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
wev = cycle->write_events;
for (i = 0; i < cycle->connection_n; i++) {
wev[i].closed = 1; //此处,closed标志表示当前connection所关联的socket是否处于打开状态
}
//10) 将上面建立好的connection结构分别于read_events、write_events关联起来
i = cycle->connection_n;
next = NULL;
do {
i--;
c[i].data = next;
c[i].read = &cycle->read_events[i];
c[i].write = &cycle->write_events[i];
c[i].fd = (ngx_socket_t) -1;
next = &c[i];
} while (i);
cycle->free_connections = next;
cycle->free_connection_n = cycle->connection_n;
//11)
ls = cycle->listening.elts;
for (i = 0; i < cycle->listening.nelts; i++) {
//12) 将监听ngx_listening_t对象与对应的connection对象关联起来
//13) 对于监听connection,要求能够accept
rev = c->read;
rev->log = c->log;
rev->accept = 1;
//14) 非IOCP事件驱动机制,要求在Nginx重启的时候将绑定在old cycle上的accept events删除
// 这样在重启之后,old cycle将不会再接收到新的连接,之后就可以优雅的关闭掉旧的nginx进程
if (!(ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_IOCP_EVENT)) {
/*
* delete the old accept events that were bound to
* the old cycle read events array
*/
}
#if (NGX_WIN32)
//15) 绑定读事件的接收处理函数
rev->handler = ngx_event_acceptex;
#else
//16) 绑定读事件的接收处理函数
rev->handler = (c->type == SOCK_STREAM) ? ngx_event_accept:
ngx_event_recvmsg;
//17) 对于不使用accept_mutex的监听socket来说,当前就设置NGX_READ_EVENT
if (ngx_use_accept_mutex
#if (NGX_HAVE_REUSEPORT)
&& !ls[i].reuseport
#endif
)
{
continue;
}
if (ngx_add_event(rev, NGX_READ_EVENT, 0) == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
#endif
}
}12. 函数ngx_send_lowat()
ngx_int_t
ngx_send_lowat(ngx_connection_t *c, size_t lowat)
{
int sndlowat;
#if (NGX_HAVE_LOWAT_EVENT)
if (ngx_event_flags & NGX_USE_KQUEUE_EVENT) {
c->write->available = lowat;
return NGX_OK;
}
#endif
if (lowat == 0 || c->sndlowat) {
return NGX_OK;
}
sndlowat = (int) lowat;
if (setsockopt(c->fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDLOWAT,
(const void *) &sndlowat, sizeof(int))
== -1)
{
ngx_connection_error(c, ngx_socket_errno,
"setsockopt(SO_SNDLOWAT) failed");
return NGX_ERROR;
}
c->sndlowat = 1;
return NGX_OK;
}本函数用于设置socket的SO_SNDLOWAT选项,用于指示socket在发送缓冲区中可用空间大于sndlowat时提示socket可写。我们当前不支持NGX_HAVE_LOWAT_EVENT宏定义。
13. 函数ngx_events_block()
static char *
ngx_events_block(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
{
char *rv;
void ***ctx;
ngx_uint_t i;
ngx_conf_t pcf;
ngx_event_module_t *m;
if (*(void **) conf) {
return "is duplicate";
}
/* count the number of the event modules and set up their indices */
ngx_event_max_module = ngx_count_modules(cf->cycle, NGX_EVENT_MODULE);
ctx = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(void *));
if (ctx == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
*ctx = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, ngx_event_max_module * sizeof(void *));
if (*ctx == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
*(void **) conf = ctx;
for (i = 0; cf->cycle->modules[i]; i++) {
if (cf->cycle->modules[i]->type != NGX_EVENT_MODULE) {
continue;
}
m = cf->cycle->modules[i]->ctx;
if (m->create_conf) {
(*ctx)[cf->cycle->modules[i]->ctx_index] =
m->create_conf(cf->cycle);
if ((*ctx)[cf->cycle->modules[i]->ctx_index] == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
}
}
pcf = *cf;
cf->ctx = ctx;
cf->module_type = NGX_EVENT_MODULE;
cf->cmd_type = NGX_EVENT_CONF;
rv = ngx_conf_parse(cf, NULL);
*cf = pcf;
if (rv != NGX_CONF_OK) {
return rv;
}
for (i = 0; cf->cycle->modules[i]; i++) {
if (cf->cycle->modules[i]->type != NGX_EVENT_MODULE) {
continue;
}
m = cf->cycle->modules[i]->ctx;
if (m->init_conf) {
rv = m->init_conf(cf->cycle,
(*ctx)[cf->cycle->modules[i]->ctx_index]);
if (rv != NGX_CONF_OK) {
return rv;
}
}
}
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}本函数作为nginx配置文件中解析到events{}指令时的回调函数。下面我们简要讲述一下本函数的实现:
static char *
ngx_events_block(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
{
//1) 统计当前NGX_EVENT_MODULE模块的个数,并为个event模块上下文分配空间。
//2) 调用event模块的create_conf回调函数创建相应上下文
//3) 解析event{}配置块中的指令(注意这里为了防止配置在解析过程中被修改,使用了一个临时变量pcf)
pcf = *cf;
cf->ctx = ctx;
cf->module_type = NGX_EVENT_MODULE;
cf->cmd_type = NGX_EVENT_CONF;
rv = ngx_conf_parse(cf, NULL);
*cf = pcf;
//4) 调用event模块的init_conf回调函数初始化向下文
}nginx event模块上下文在cycle->conf_ctx中的内存图景:
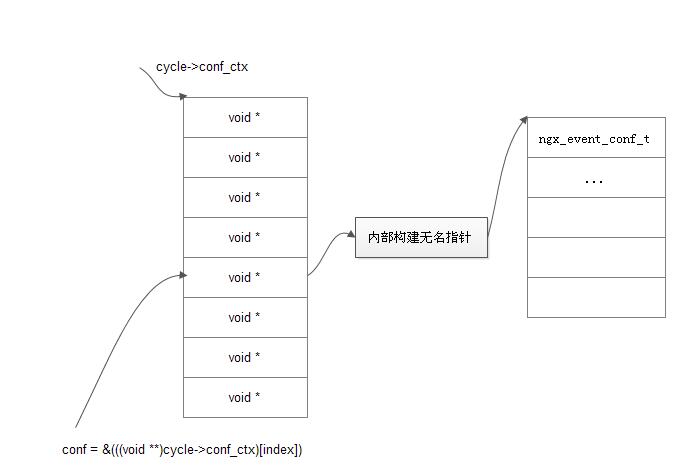
14. 函数ngx_event_connections()
static char *
ngx_event_connections(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
{
ngx_event_conf_t *ecf = conf;
ngx_str_t *value;
if (ecf->connections != NGX_CONF_UNSET_UINT) {
return "is duplicate";
}
value = cf->args->elts;
ecf->connections = ngx_atoi(value[1].data, value[1].len);
if (ecf->connections == (ngx_uint_t) NGX_ERROR) {
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0,
"invalid number \"%V\"", &value[1]);
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
cf->cycle->connection_n = ecf->connections;
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}用于解析events{}中的worker_connections指令。该指令配置语法如下:
Syntax: worker_connections number; Default: worker_connections 512; Context: events
15. 函数ngx_event_use()
static char *
ngx_event_use(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
{
ngx_event_conf_t *ecf = conf;
ngx_int_t m;
ngx_str_t *value;
ngx_event_conf_t *old_ecf;
ngx_event_module_t *module;
if (ecf->use != NGX_CONF_UNSET_UINT) {
return "is duplicate";
}
value = cf->args->elts;
if (cf->cycle->old_cycle->conf_ctx) {
old_ecf = ngx_event_get_conf(cf->cycle->old_cycle->conf_ctx,
ngx_event_core_module);
} else {
old_ecf = NULL;
}
for (m = 0; cf->cycle->modules[m]; m++) {
if (cf->cycle->modules[m]->type != NGX_EVENT_MODULE) {
continue;
}
module = cf->cycle->modules[m]->ctx;
if (module->name->len == value[1].len) {
if (ngx_strcmp(module->name->data, value[1].data) == 0) {
ecf->use = cf->cycle->modules[m]->ctx_index;
ecf->name = module->name->data;
if (ngx_process == NGX_PROCESS_SINGLE
&& old_ecf
&& old_ecf->use != ecf->use)
{
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0,
"when the server runs without a master process "
"the \"%V\" event type must be the same as "
"in previous configuration - \"%s\" "
"and it cannot be changed on the fly, "
"to change it you need to stop server "
"and start it again",
&value[1], old_ecf->name);
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}
}
}
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0,
"invalid event type \"%V\"", &value[1]);
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}本函数用于解析events{}配置模块的use指令。该指令的配置语法是:
Syntax: use method; Default: — Context: events
method的值可以为select、poll、epoll…
解析use指令时,如果当前nginx是以NGX_PROCESS_SINGLE模式工作,要求所采用事件驱动机制的ctx_index没有改变。
16. 函数ngx_event_debug_connection()
static char *
ngx_event_debug_connection(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
{
#if (NGX_DEBUG)
ngx_event_conf_t *ecf = conf;
ngx_int_t rc;
ngx_str_t *value;
ngx_url_t u;
ngx_cidr_t c, *cidr;
ngx_uint_t i;
struct sockaddr_in *sin;
#if (NGX_HAVE_INET6)
struct sockaddr_in6 *sin6;
#endif
value = cf->args->elts;
#if (NGX_HAVE_UNIX_DOMAIN)
if (ngx_strcmp(value[1].data, "unix:") == 0) {
cidr = ngx_array_push(&ecf->debug_connection);
if (cidr == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
cidr->family = AF_UNIX;
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}
#endif
rc = ngx_ptocidr(&value[1], &c);
if (rc != NGX_ERROR) {
if (rc == NGX_DONE) {
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_WARN, cf, 0,
"low address bits of %V are meaningless",
&value[1]);
}
cidr = ngx_array_push(&ecf->debug_connection);
if (cidr == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
*cidr = c;
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}
ngx_memzero(&u, sizeof(ngx_url_t));
u.host = value[1];
if (ngx_inet_resolve_host(cf->pool, &u) != NGX_OK) {
if (u.err) {
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0,
"%s in debug_connection \"%V\"",
u.err, &u.host);
}
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
cidr = ngx_array_push_n(&ecf->debug_connection, u.naddrs);
if (cidr == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
ngx_memzero(cidr, u.naddrs * sizeof(ngx_cidr_t));
for (i = 0; i < u.naddrs; i++) {
cidr[i].family = u.addrs[i].sockaddr->sa_family;
switch (cidr[i].family) {
#if (NGX_HAVE_INET6)
case AF_INET6:
sin6 = (struct sockaddr_in6 *) u.addrs[i].sockaddr;
cidr[i].u.in6.addr = sin6->sin6_addr;
ngx_memset(cidr[i].u.in6.mask.s6_addr, 0xff, 16);
break;
#endif
default: /* AF_INET */
sin = (struct sockaddr_in *) u.addrs[i].sockaddr;
cidr[i].u.in.addr = sin->sin_addr.s_addr;
cidr[i].u.in.mask = 0xffffffff;
break;
}
}
#else
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_WARN, cf, 0,
"\"debug_connection\" is ignored, you need to rebuild "
"nginx using --with-debug option to enable it");
#endif
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}本函数用于解析events{}配置模块的debug_connection指令。该指令的配置示例如下:
events {
debug_connection 127.0.0.1;
debug_connection localhost;
debug_connection 192.0.2.0/24;
debug_connection ::1;
debug_connection 2001:0db8::/32;
debug_connection unix:;
...
}
本函数分别解析三种不同类型的配置:
-
unix域socket
-
cidr格式配置的地址
-
通过主机名配置的地址
17. 函数ngx_event_core_create_conf()
static void *
ngx_event_core_create_conf(ngx_cycle_t *cycle)
{
ngx_event_conf_t *ecf;
ecf = ngx_palloc(cycle->pool, sizeof(ngx_event_conf_t));
if (ecf == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
ecf->connections = NGX_CONF_UNSET_UINT;
ecf->use = NGX_CONF_UNSET_UINT;
ecf->multi_accept = NGX_CONF_UNSET;
ecf->accept_mutex = NGX_CONF_UNSET;
ecf->accept_mutex_delay = NGX_CONF_UNSET_MSEC;
ecf->name = (void *) NGX_CONF_UNSET;
#if (NGX_DEBUG)
if (ngx_array_init(&ecf->debug_connection, cycle->pool, 4,
sizeof(ngx_cidr_t)) == NGX_ERROR)
{
return NULL;
}
#endif
return ecf;
}本函数作为nginx event core模块上下文在创建时候执行的回调函数,会在ngx_events_block()函数中被调用,此处主要是创建event core模块的配置上下文结构:ngx_event_conf_t
18. 函数
static char *
ngx_event_core_init_conf(ngx_cycle_t *cycle, void *conf)
{
ngx_event_conf_t *ecf = conf;
#if (NGX_HAVE_EPOLL) && !(NGX_TEST_BUILD_EPOLL)
int fd;
#endif
ngx_int_t i;
ngx_module_t *module;
ngx_event_module_t *event_module;
module = NULL;
#if (NGX_HAVE_EPOLL) && !(NGX_TEST_BUILD_EPOLL)
fd = epoll_create(100);
if (fd != -1) {
(void) close(fd);
module = &ngx_epoll_module;
} else if (ngx_errno != NGX_ENOSYS) {
module = &ngx_epoll_module;
}
#endif
#if (NGX_HAVE_DEVPOLL) && !(NGX_TEST_BUILD_DEVPOLL)
module = &ngx_devpoll_module;
#endif
#if (NGX_HAVE_KQUEUE)
module = &ngx_kqueue_module;
#endif
#if (NGX_HAVE_SELECT)
if (module == NULL) {
module = &ngx_select_module;
}
#endif
if (module == NULL) {
for (i = 0; cycle->modules[i]; i++) {
if (cycle->modules[i]->type != NGX_EVENT_MODULE) {
continue;
}
event_module = cycle->modules[i]->ctx;
if (ngx_strcmp(event_module->name->data, event_core_name.data) == 0)
{
continue;
}
module = cycle->modules[i];
break;
}
}
if (module == NULL) {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cycle->log, 0, "no events module found");
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
ngx_conf_init_uint_value(ecf->connections, DEFAULT_CONNECTIONS);
cycle->connection_n = ecf->connections;
ngx_conf_init_uint_value(ecf->use, module->ctx_index);
event_module = module->ctx;
ngx_conf_init_ptr_value(ecf->name, event_module->name->data);
ngx_conf_init_value(ecf->multi_accept, 0);
ngx_conf_init_value(ecf->accept_mutex, 1);
ngx_conf_init_msec_value(ecf->accept_mutex_delay, 500);
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}本函数作为nginx event core模块上下文在初始化时候执行的回调函数,会在ngx_events_block()函数中被调用,此处主要是给ngx_event_conf_t赋默认值。这里特别注意选择默认事件驱动机制的处理
[参看]

