event/ngx_event_pipe.c源文件分析
nginx_event_pipe用于实现upstream对上游服务器包体数据的读取,然后在处理之后,将结果返回给请求端(downstream)。
1. 相关静态函数声明
/*
* Copyright (C) Igor Sysoev
* Copyright (C) Nginx, Inc.
*/
#include <ngx_config.h>
#include <ngx_core.h>
#include <ngx_event.h>
#include <ngx_event_pipe.h>
//读取来自上游服务器的数据
static ngx_int_t ngx_event_pipe_read_upstream(ngx_event_pipe_t *p);
//将处理后的数据发送到下游客户端
static ngx_int_t ngx_event_pipe_write_to_downstream(ngx_event_pipe_t *p);
//将p->in或p->buf_to_file缓存中的数据写到临时文件
static ngx_int_t ngx_event_pipe_write_chain_to_temp_file(ngx_event_pipe_t *p);
//移除buf上的shadow
static ngx_inline void ngx_event_pipe_remove_shadow_links(ngx_buf_t *buf);
//busy, out, in 三个缓冲chain释放, 同时释放shadow缓冲,并将空闲的buffer加入到p->free_raw_bufs中
static ngx_int_t ngx_event_pipe_drain_chains(ngx_event_pipe_t *p);2. 函数ngx_event_pipe()
ngx_int_t
ngx_event_pipe(ngx_event_pipe_t *p, ngx_int_t do_write)
{
ngx_int_t rc;
ngx_uint_t flags;
ngx_event_t *rev, *wev;
for ( ;; ) {
if (do_write) {
p->log->action = "sending to client";
rc = ngx_event_pipe_write_to_downstream(p);
if (rc == NGX_ABORT) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
if (rc == NGX_BUSY) {
return NGX_OK;
}
}
p->read = 0;
p->upstream_blocked = 0;
p->log->action = "reading upstream";
if (ngx_event_pipe_read_upstream(p) == NGX_ABORT) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
if (!p->read && !p->upstream_blocked) {
break;
}
do_write = 1;
}
if (p->upstream->fd != (ngx_socket_t) -1) {
rev = p->upstream->read;
flags = (rev->eof || rev->error) ? NGX_CLOSE_EVENT : 0;
if (ngx_handle_read_event(rev, flags) != NGX_OK) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
if (!rev->delayed) {
if (rev->active && !rev->ready) {
ngx_add_timer(rev, p->read_timeout);
} else if (rev->timer_set) {
ngx_del_timer(rev);
}
}
}
if (p->downstream->fd != (ngx_socket_t) -1
&& p->downstream->data == p->output_ctx)
{
wev = p->downstream->write;
if (ngx_handle_write_event(wev, p->send_lowat) != NGX_OK) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
if (!wev->delayed) {
if (wev->active && !wev->ready) {
ngx_add_timer(wev, p->send_timeout);
} else if (wev->timer_set) {
ngx_del_timer(wev);
}
}
}
return NGX_OK;
}用于实现upstream对上游服务器包体数据的读取,然后在处理之后,将结果返回给请求端(downstream)。下面我们仔细分析一下函数的实现:
ngx_int_t
ngx_event_pipe(ngx_event_pipe_t *p, ngx_int_t do_write)
{
//通常情况下,假如p中原来就还有缓存数据,那么会将参数do_write设置为1,否则要等到ngx_event_pipe_read_upstream()
//读取到数据之后,才会将do_write置为1
for(;;){
if (do_write) {
//1) 包体数据写入到下游请求端
rc = ngx_event_pipe_write_to_downstream(p);
// 写入出错,直接返回
if (rc == NGX_ABORT) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
// 来不及处理,此时不会再从上游服务器读数据,也不会再向下游请求端发送数据,直接返回
if (rc == NGX_BUSY) {
return NGX_OK;
}
}
// 2) 此处p->read置为0,表示暂没有读取到上游服务器的数据; p->upstream_blocked表示暂时阻塞读取上游响应的流程
p->read = 0;
p->upstream_blocked = 0;
//3) 读取upstream数据
if (ngx_event_pipe_read_upstream(p) == NGX_ABORT) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
//3) 在上游包体读取未阻塞状态下, 没有读取到数据,break跳出
if (!p->read && !p->upstream_blocked) {
break;
}
//4) 将do_write标志位置为1,指示需要向下游请求端发送数据
do_write = 1;
}
if (p->upstream->fd != (ngx_socket_t) -1) {
//5)上游包体读取出错或者没有数据可读,那么事件会被清理, 否则什么也不做
flags = (rev->eof || rev->error) ? NGX_CLOSE_EVENT : 0;
if (ngx_handle_read_event(rev, flags) != NGX_OK) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
//6) rev->delayed用于标记由于速率限制(rate limiting)的原因导致IO被延迟,此处表示没有被延迟
if (!rev->delayed) {
if(rev->active && !rev->ready){
//6.1) 此处添加定时器主要是为了预防读取上游服务器数据超时
}else if (rev->timer_set){
//6.2) 将上一次所设置的定时器移除
}
}
}
if (p->downstream->fd != (ngx_socket_t) -1
&& p->downstream->data == p->output_ctx){
//7) 将写事件添加到事件驱动机制
wev = p->downstream->write;
if (ngx_handle_write_event(wev, p->send_lowat) != NGX_OK) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
//8) wev->delayed用于标记由于速率限制(rate limiting)的原因导致IO被延迟,此处表示没有被延迟
if (!wev->delayed) {
if (wev->active && !wev->ready) {
//8.1) 此处添加定时器主要是为了预防向下游服务器写数据超时
} else if (wev->timer_set) {
//8.2) 将上一次设置的定时器移除
}
}
}
return NGX_OK;
}3. 函数ngx_event_pipe_read_upstream()
static ngx_int_t
ngx_event_pipe_read_upstream(ngx_event_pipe_t *p)
{
off_t limit;
ssize_t n, size;
ngx_int_t rc;
ngx_buf_t *b;
ngx_msec_t delay;
ngx_chain_t *chain, *cl, *ln;
if (p->upstream_eof || p->upstream_error || p->upstream_done) {
return NGX_OK;
}
#if (NGX_THREADS)
if (p->aio) {
ngx_log_debug0(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe read upstream: aio");
return NGX_AGAIN;
}
if (p->writing) {
ngx_log_debug0(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe read upstream: writing");
rc = ngx_event_pipe_write_chain_to_temp_file(p);
if (rc != NGX_OK) {
return rc;
}
}
#endif
ngx_log_debug1(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe read upstream: %d", p->upstream->read->ready);
for ( ;; ) {
if (p->upstream_eof || p->upstream_error || p->upstream_done) {
break;
}
if (p->preread_bufs == NULL && !p->upstream->read->ready) {
break;
}
if (p->preread_bufs) {
/* use the pre-read bufs if they exist */
chain = p->preread_bufs;
p->preread_bufs = NULL;
n = p->preread_size;
ngx_log_debug1(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe preread: %z", n);
if (n) {
p->read = 1;
}
} else {
#if (NGX_HAVE_KQUEUE)
/*
* kqueue notifies about the end of file or a pending error.
* This test allows not to allocate a buf on these conditions
* and not to call c->recv_chain().
*/
if (p->upstream->read->available == 0
&& p->upstream->read->pending_eof)
{
p->upstream->read->ready = 0;
p->upstream->read->eof = 1;
p->upstream_eof = 1;
p->read = 1;
if (p->upstream->read->kq_errno) {
p->upstream->read->error = 1;
p->upstream_error = 1;
p->upstream_eof = 0;
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_ERR, p->log,
p->upstream->read->kq_errno,
"kevent() reported that upstream "
"closed connection");
}
break;
}
#endif
if (p->limit_rate) {
if (p->upstream->read->delayed) {
break;
}
limit = (off_t) p->limit_rate * (ngx_time() - p->start_sec + 1)
- p->read_length;
if (limit <= 0) {
p->upstream->read->delayed = 1;
delay = (ngx_msec_t) (- limit * 1000 / p->limit_rate + 1);
ngx_add_timer(p->upstream->read, delay);
break;
}
} else {
limit = 0;
}
if (p->free_raw_bufs) {
/* use the free bufs if they exist */
chain = p->free_raw_bufs;
if (p->single_buf) {
p->free_raw_bufs = p->free_raw_bufs->next;
chain->next = NULL;
} else {
p->free_raw_bufs = NULL;
}
} else if (p->allocated < p->bufs.num) {
/* allocate a new buf if it's still allowed */
b = ngx_create_temp_buf(p->pool, p->bufs.size);
if (b == NULL) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
p->allocated++;
chain = ngx_alloc_chain_link(p->pool);
if (chain == NULL) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
chain->buf = b;
chain->next = NULL;
} else if (!p->cacheable
&& p->downstream->data == p->output_ctx
&& p->downstream->write->ready
&& !p->downstream->write->delayed)
{
/*
* if the bufs are not needed to be saved in a cache and
* a downstream is ready then write the bufs to a downstream
*/
p->upstream_blocked = 1;
ngx_log_debug0(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe downstream ready");
break;
} else if (p->cacheable
|| p->temp_file->offset < p->max_temp_file_size)
{
/*
* if it is allowed, then save some bufs from p->in
* to a temporary file, and add them to a p->out chain
*/
rc = ngx_event_pipe_write_chain_to_temp_file(p);
ngx_log_debug1(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe temp offset: %O", p->temp_file->offset);
if (rc == NGX_BUSY) {
break;
}
if (rc != NGX_OK) {
return rc;
}
chain = p->free_raw_bufs;
if (p->single_buf) {
p->free_raw_bufs = p->free_raw_bufs->next;
chain->next = NULL;
} else {
p->free_raw_bufs = NULL;
}
} else {
/* there are no bufs to read in */
ngx_log_debug0(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"no pipe bufs to read in");
break;
}
n = p->upstream->recv_chain(p->upstream, chain, limit);
ngx_log_debug1(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe recv chain: %z", n);
if (p->free_raw_bufs) {
chain->next = p->free_raw_bufs;
}
p->free_raw_bufs = chain;
if (n == NGX_ERROR) {
p->upstream_error = 1;
return NGX_ERROR;
}
if (n == NGX_AGAIN) {
if (p->single_buf) {
ngx_event_pipe_remove_shadow_links(chain->buf);
}
break;
}
p->read = 1;
if (n == 0) {
p->upstream_eof = 1;
break;
}
}
delay = p->limit_rate ? (ngx_msec_t) n * 1000 / p->limit_rate : 0;
p->read_length += n;
cl = chain;
p->free_raw_bufs = NULL;
while (cl && n > 0) {
ngx_event_pipe_remove_shadow_links(cl->buf);
size = cl->buf->end - cl->buf->last;
if (n >= size) {
cl->buf->last = cl->buf->end;
/* STUB */ cl->buf->num = p->num++;
if (p->input_filter(p, cl->buf) == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
n -= size;
ln = cl;
cl = cl->next;
ngx_free_chain(p->pool, ln);
} else {
cl->buf->last += n;
n = 0;
}
}
if (cl) {
for (ln = cl; ln->next; ln = ln->next) { /* void */ }
ln->next = p->free_raw_bufs;
p->free_raw_bufs = cl;
}
if (delay > 0) {
p->upstream->read->delayed = 1;
ngx_add_timer(p->upstream->read, delay);
break;
}
}
#if (NGX_DEBUG)
for (cl = p->busy; cl; cl = cl->next) {
ngx_log_debug8(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe buf busy s:%d t:%d f:%d "
"%p, pos %p, size: %z "
"file: %O, size: %O",
(cl->buf->shadow ? 1 : 0),
cl->buf->temporary, cl->buf->in_file,
cl->buf->start, cl->buf->pos,
cl->buf->last - cl->buf->pos,
cl->buf->file_pos,
cl->buf->file_last - cl->buf->file_pos);
}
for (cl = p->out; cl; cl = cl->next) {
ngx_log_debug8(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe buf out s:%d t:%d f:%d "
"%p, pos %p, size: %z "
"file: %O, size: %O",
(cl->buf->shadow ? 1 : 0),
cl->buf->temporary, cl->buf->in_file,
cl->buf->start, cl->buf->pos,
cl->buf->last - cl->buf->pos,
cl->buf->file_pos,
cl->buf->file_last - cl->buf->file_pos);
}
for (cl = p->in; cl; cl = cl->next) {
ngx_log_debug8(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe buf in s:%d t:%d f:%d "
"%p, pos %p, size: %z "
"file: %O, size: %O",
(cl->buf->shadow ? 1 : 0),
cl->buf->temporary, cl->buf->in_file,
cl->buf->start, cl->buf->pos,
cl->buf->last - cl->buf->pos,
cl->buf->file_pos,
cl->buf->file_last - cl->buf->file_pos);
}
for (cl = p->free_raw_bufs; cl; cl = cl->next) {
ngx_log_debug8(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe buf free s:%d t:%d f:%d "
"%p, pos %p, size: %z "
"file: %O, size: %O",
(cl->buf->shadow ? 1 : 0),
cl->buf->temporary, cl->buf->in_file,
cl->buf->start, cl->buf->pos,
cl->buf->last - cl->buf->pos,
cl->buf->file_pos,
cl->buf->file_last - cl->buf->file_pos);
}
ngx_log_debug1(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe length: %O", p->length);
#endif
if (p->free_raw_bufs && p->length != -1) {
cl = p->free_raw_bufs;
if (cl->buf->last - cl->buf->pos >= p->length) {
p->free_raw_bufs = cl->next;
/* STUB */ cl->buf->num = p->num++;
if (p->input_filter(p, cl->buf) == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
ngx_free_chain(p->pool, cl);
}
}
if (p->length == 0) {
p->upstream_done = 1;
p->read = 1;
}
if ((p->upstream_eof || p->upstream_error) && p->free_raw_bufs) {
/* STUB */ p->free_raw_bufs->buf->num = p->num++;
if (p->input_filter(p, p->free_raw_bufs->buf) == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
p->free_raw_bufs = p->free_raw_bufs->next;
if (p->free_bufs && p->buf_to_file == NULL) {
for (cl = p->free_raw_bufs; cl; cl = cl->next) {
if (cl->buf->shadow == NULL) {
ngx_pfree(p->pool, cl->buf->start);
}
}
}
}
if (p->cacheable && (p->in || p->buf_to_file)) {
ngx_log_debug0(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe write chain");
rc = ngx_event_pipe_write_chain_to_temp_file(p);
if (rc != NGX_OK) {
return rc;
}
}
return NGX_OK;
}本函数用于读取上游服务器的包体数据,然后调用相应的方法进行处理。下面我们简要分析一下函数的实现:
static ngx_int_t
ngx_event_pipe_read_upstream(ngx_event_pipe_t *p)
{
//1) p->upstream_eof为1,表示上游服务器关闭了连接; p->upstream_error表示读取上游服务器数据出错; p->upstream_done
//为1表示Nginx与上游交互已经结束,即上游包体数据读取完毕
if (p->upstream_eof || p->upstream_error || p->upstream_done) {
return NGX_OK;
}
//2) 多线程情况处理,目前我们不支持NGX_THREADS宏定义
#if (NGX_THREADS)
#endif
//3) 从上游服务器读取数据
for(;;){
//3.1) 同上
if (p->upstream_eof || p->upstream_error || p->upstream_done) {
break;
}
//3.2) 如果没有预先读取到包体数据(p->preread_bufs),并且当前又读取不到新的数据,那么循环跳出
if (p->preread_bufs == NULL && !p->upstream->read->ready) {
break;
}
if(p->preread_bufs){
//3.3) 处理预先读取到的包体数据
chain = p->preread_bufs;
p->preread_bufs = NULL;
n = p->preread_size;
ngx_log_debug1(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe preread: %z", n);
if (n) {
p->read = 1; //此处p->read表示读取到了上游的响应
}
}else{
#if (NGX_HAVE_KQUEUE)
//3.4) kqueue notifies about the end of file or a pending error.This test allows not to
//allocate a buf on these conditions and not to call c->recv_chain().
#endif
//3.5) 对速率限制的处理
if (p->limit_rate) {
if (p->upstream->read->delayed) {
break;
}
//这里我们看到,对速率处理的限制也比较简单,就是计算预计到当前最大接收的数据量:
// p->limit_rate * (ngx_time() - p->start_sec +1), 减去当前实际的数据接收量
limit = (off_t) p->limit_rate * (ngx_time() - p->start_sec + 1) - p->read_length;
//此处小于等于0, 表示超出了速率限制,将p->upstream->read->delayed置为1,进行相应的延迟
if (limit <= 0) {
p->upstream->read->delayed = 1;
//此处计算延迟读取的毫秒数(乘以1000)
delay = (ngx_msec_t) (- limit * 1000 / p->limit_rate + 1);
ngx_add_timer(p->upstream->read, delay);
break;
}
} else {
limit = 0;
}
//3.6) 如下用于腾出空间来接收上游服务器的数据
if (p->free_raw_bufs){
//3.6.1) 假如有空闲链接的话,那么使用空闲链接的空间来接收上游服务器数据
if (p->single_buf) {
//表示接收上游响应时,一次只能接收一个ngx_buf_t缓冲区。通常IOCP事件驱动机制下,此值为1
}else{
//表示使用整个空闲链来接收上游服务器返回的数据
}
}else if (p->allocated < p->bufs.num) {
//3.6.2) 没有空闲链接,那么尝试从p->pool池中分配一个size大小的缓冲块来接收数据
b = ngx_create_temp_buf(p->pool, p->bufs.size);
if (b == NULL) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
p->allocated++;
//创建一个chain来包装这个ngx_buf_t结构
chain = ngx_alloc_chain_link(p->pool);
if (chain == NULL) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
chain->buf = b;
chain->next = NULL;
}else if (!p->cacheable
&& p->downstream->data == p->output_ctx
&& p->downstream->write->ready
&& !p->downstream->write->delayed){
//3.6.3) 假如数据不需要写入到缓存,并且downstream当前已经准备好了写,并且未被延迟,那么
//此处break跳出循环,以优先处理当前已有的数据
p->upstream_blocked = 1;
break;
}else if (p->cacheable
|| p->temp_file->offset < p->max_temp_file_size){
//3.6.4) 可以缓存,那么先写缓存数据以腾出空间
rc = ngx_event_pipe_write_chain_to_temp_file(p);
if (rc == NGX_BUSY) {
break; //跳出循环,以优先处理当前已经读取到的数据
}
if (rc != NGX_OK) {
return rc; //写入失败,退出
}
//获取已经腾出的空间
chain = p->free_raw_bufs;
if (p->single_buf) {
p->free_raw_bufs = p->free_raw_bufs->next;
chain->next = NULL;
} else {
p->free_raw_bufs = NULL;
}
}else{
//3.6.5) 当前已经没有可用空间以接收上游数据
}
//3.7) 调用recv_chain()方法接收来自上游服务器的数据。limit用于速率限制,以指定读取多少数据。
// 值为0,表示不进行限制
n = p->upstream->recv_chain(p->upstream, chain, limit);
//3.8) 将chain又重新挂到p->free_raw_bufs链表的表头
if (p->free_raw_bufs) {
chain->next = p->free_raw_bufs;
}
p->free_raw_bufs = chain;
//3.9) 读取上游数据出错
if (n == NGX_ERROR) {
p->upstream_error = 1;
return NGX_ERROR;
}
//3.10) 没有读取到数据
if (n == NGX_AGAIN) {
//移除存在于该buf上的shadow
if (p->single_buf) {
ngx_event_pipe_remove_shadow_links(chain->buf);
}
break;
}
//3.11) 表示已经读取到了上游的响应
p->read = 1;
//3.12) 上游连接已经关闭
if (n == 0) {
p->upstream_eof = 1;
break;
}
} //end else
//运行到此处,表示从上游服务器读取到了相应的数据
//4) 读取完这一次之后,看是否需要进行速率限制。
delay = p->limit_rate ? (ngx_msec_t) n * 1000 / p->limit_rate : 0;
//5) 当前读取到的总的包体数据大小为p->read_length +=n
p->read_length += n;
cl = chain;
p->free_raw_bufs = NULL;
//6) 处理本次读取到的上游数据
while (cl && n > 0) {
ngx_event_pipe_remove_shadow_links(cl->buf);
size = cl->buf->end - cl->buf->last;
if (n >= size) {
/* STUB */ cl->buf->num = p->num++; //此处cl->buf->num保存当前已使用的buf块的个数
//6.1) 调用input_filter处理接收到的上游数据
if (p->input_filter(p, cl->buf) == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
}else{
//6.2) 此处为接收到的数据所占用的最后一个buf,且只使用了部分空间。(注意,此一部分数据暂时保存在缓存
//中并未做任何处理)
cl->buf->last += n;
n = 0;
}
}
//7) 将相应的空闲空间插入到p->free_raw_bufs中。(注意: 这里cl链的第一个节点可能仍保存有部分数据)
if (cl) {
for (ln = cl; ln->next; ln = ln->next) { /* void */ }
ln->next = p->free_raw_bufs;
p->free_raw_bufs = cl;
}
//8) 由于速率限制,这里我们需要按时延迟读取上游数据
if (delay > 0) {
p->upstream->read->delayed = 1;
ngx_add_timer(p->upstream->read, delay);
break;
}
} //end for
//9) 打印各链表的相关信息:p->busy、p->out、p->in、p->free_raw_bufs
#if NGX_DEBUG
#endif
//10) 在符合条件的情况下,处理存在于p->free_raw_bufs链表第一个节点的残留的部分数据(请参看上述步骤6.2)
if (p->free_raw_bufs && p->length != -1) {
cl = p->free_raw_bufs;
if (cl->buf->last - cl->buf->pos >= p->length) {
p->free_raw_bufs = cl->next;
/* STUB */ cl->buf->num = p->num++;
if (p->input_filter(p, cl->buf) == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
ngx_free_chain(p->pool, cl);
}
}
//11) 表示上游数据读取完毕
if (p->length == 0) {
p->upstream_done = 1;
p->read = 1;
}
//12) 读取数据出现异常的情况下,把p->free_raw_bufs链表第一个节点残留的部分数据处理完(请参看上述步骤6.2)
if ((p->upstream_eof || p->upstream_error) && p->free_raw_bufs) {
/* STUB */ p->free_raw_bufs->buf->num = p->num++;
if (p->input_filter(p, p->free_raw_bufs->buf) == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
//12.1) 指示尽快清理p->free_raw_bufs空间
if (p->free_bufs && p->buf_to_file == NULL) {
for (cl = p->free_raw_bufs; cl; cl = cl->next) {
if (cl->buf->shadow == NULL) {
ngx_pfree(p->pool, cl->buf->start);
}
}
}
}
//13) 将相应的未处理完的数据进行缓存
if (p->cacheable && (p->in || p->buf_to_file)) {
rc = ngx_event_pipe_write_chain_to_temp_file(p);
if (rc != NGX_OK) {
return rc;
}
}
}上面关于使用多线程写temp文件(ngx_write_chain_to_temp_file()),这里我们再多说一句:
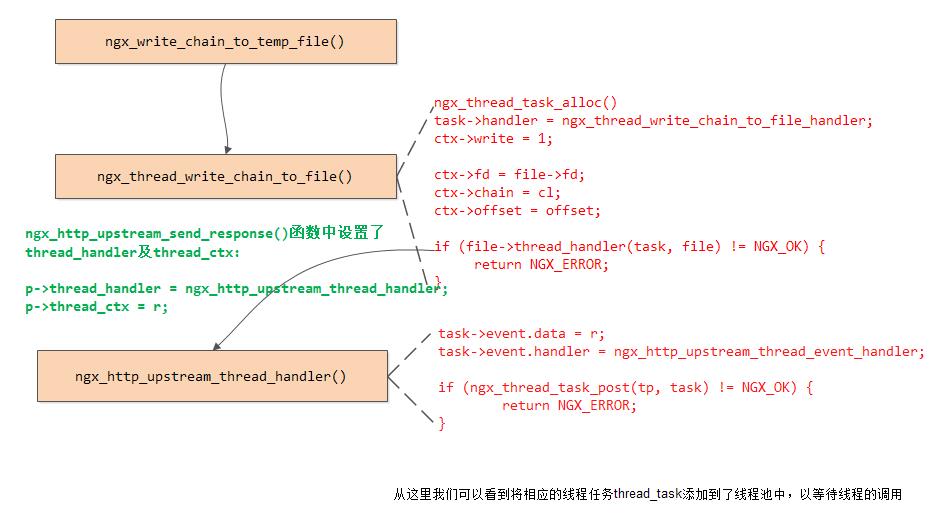
4. 函数ngx_event_pipe_write_to_downstream()
static ngx_int_t
ngx_event_pipe_write_to_downstream(ngx_event_pipe_t *p)
{
u_char *prev;
size_t bsize;
ngx_int_t rc;
ngx_uint_t flush, flushed, prev_last_shadow;
ngx_chain_t *out, **ll, *cl;
ngx_connection_t *downstream;
downstream = p->downstream;
ngx_log_debug1(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe write downstream: %d", downstream->write->ready);
#if (NGX_THREADS)
if (p->writing) {
rc = ngx_event_pipe_write_chain_to_temp_file(p);
if (rc == NGX_ABORT) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
}
#endif
flushed = 0;
for ( ;; ) {
if (p->downstream_error) {
return ngx_event_pipe_drain_chains(p);
}
if (p->upstream_eof || p->upstream_error || p->upstream_done) {
/* pass the p->out and p->in chains to the output filter */
for (cl = p->busy; cl; cl = cl->next) {
cl->buf->recycled = 0;
}
if (p->out) {
ngx_log_debug0(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe write downstream flush out");
for (cl = p->out; cl; cl = cl->next) {
cl->buf->recycled = 0;
}
rc = p->output_filter(p->output_ctx, p->out);
if (rc == NGX_ERROR) {
p->downstream_error = 1;
return ngx_event_pipe_drain_chains(p);
}
p->out = NULL;
}
if (p->writing) {
break;
}
if (p->in) {
ngx_log_debug0(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe write downstream flush in");
for (cl = p->in; cl; cl = cl->next) {
cl->buf->recycled = 0;
}
rc = p->output_filter(p->output_ctx, p->in);
if (rc == NGX_ERROR) {
p->downstream_error = 1;
return ngx_event_pipe_drain_chains(p);
}
p->in = NULL;
}
ngx_log_debug0(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe write downstream done");
/* TODO: free unused bufs */
p->downstream_done = 1;
break;
}
if (downstream->data != p->output_ctx
|| !downstream->write->ready
|| downstream->write->delayed)
{
break;
}
/* bsize is the size of the busy recycled bufs */
prev = NULL;
bsize = 0;
for (cl = p->busy; cl; cl = cl->next) {
if (cl->buf->recycled) {
if (prev == cl->buf->start) {
continue;
}
bsize += cl->buf->end - cl->buf->start;
prev = cl->buf->start;
}
}
ngx_log_debug1(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe write busy: %uz", bsize);
out = NULL;
if (bsize >= (size_t) p->busy_size) {
flush = 1;
goto flush;
}
flush = 0;
ll = NULL;
prev_last_shadow = 1;
for ( ;; ) {
if (p->out) {
cl = p->out;
if (cl->buf->recycled) {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_ALERT, p->log, 0,
"recycled buffer in pipe out chain");
}
p->out = p->out->next;
} else if (!p->cacheable && !p->writing && p->in) {
cl = p->in;
ngx_log_debug3(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe write buf ls:%d %p %z",
cl->buf->last_shadow,
cl->buf->pos,
cl->buf->last - cl->buf->pos);
if (cl->buf->recycled && prev_last_shadow) {
if (bsize + cl->buf->end - cl->buf->start > p->busy_size) {
flush = 1;
break;
}
bsize += cl->buf->end - cl->buf->start;
}
prev_last_shadow = cl->buf->last_shadow;
p->in = p->in->next;
} else {
break;
}
cl->next = NULL;
if (out) {
*ll = cl;
} else {
out = cl;
}
ll = &cl->next;
}
flush:
ngx_log_debug2(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe write: out:%p, f:%ui", out, flush);
if (out == NULL) {
if (!flush) {
break;
}
/* a workaround for AIO */
if (flushed++ > 10) {
return NGX_BUSY;
}
}
rc = p->output_filter(p->output_ctx, out);
ngx_chain_update_chains(p->pool, &p->free, &p->busy, &out, p->tag);
if (rc == NGX_ERROR) {
p->downstream_error = 1;
return ngx_event_pipe_drain_chains(p);
}
for (cl = p->free; cl; cl = cl->next) {
if (cl->buf->temp_file) {
if (p->cacheable || !p->cyclic_temp_file) {
continue;
}
/* reset p->temp_offset if all bufs had been sent */
if (cl->buf->file_last == p->temp_file->offset) {
p->temp_file->offset = 0;
}
}
/* TODO: free buf if p->free_bufs && upstream done */
/* add the free shadow raw buf to p->free_raw_bufs */
if (cl->buf->last_shadow) {
if (ngx_event_pipe_add_free_buf(p, cl->buf->shadow) != NGX_OK) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
cl->buf->last_shadow = 0;
}
cl->buf->shadow = NULL;
}
}
return NGX_OK;
}此函数用于向下游请求端发送相应的响应信息。下面我们详细分析一下函数的执行流程:
static ngx_int_t
ngx_event_pipe_write_to_downstream(ngx_event_pipe_t *p)
{
//1) 多线程情况处理,目前我们不支持NGX_THREADS宏定义
#if (NGX_THREADS)
//采用多线程将相应的缓存数据写入到临时文件
if (p->writing) {
rc = ngx_event_pipe_write_chain_to_temp_file(p);
}
#endif
//2) 向下游请求端写数据
for(;;){
//3) 向下游请求端写数据失败,释放p->busy、p->out、p->in这些空间
if (p->downstream_error) {
return ngx_event_pipe_drain_chains(p);
}
//4) 此处表示发送最后一部分数据(p->upstream_eof表示上游服务器连接已经断开,再没有数据了; p->upstream_error表示读取上游服务器
// 响应出错,也不会再有数据了; p->upstream_done表示读取上游服务器响应完成
if (p->upstream_eof || p->upstream_error || p->upstream_done) {
if(p->out){
//4.1) 将最后一部分out数据发送给downstream
}
// 4.2) 如果还有临时文件中的数据也需要发送给请求端,则直接跳出跳出循环
if (p->writing) {
break;
}
if(p->in){
//4.3) 将p->in中数据通过output_filter发送到downstream
}
//4.4) 向downstream发送完了所有数据,跳出循环
p->downstream_done = 1;
break;
}
//5) 不符合条件,不向请求端写数据
if (downstream->data != p->output_ctx
|| !downstream->write->ready
|| downstream->write->delayed)
{
break;
}
//6) 计算当前总的busy recycled bufs所占用的总的空间大小
prev = NULL;
bsize = 0;
for (cl = p->busy; cl; cl = cl->next) {
if (cl->buf->recycled) {
if (prev == cl->buf->start) {
continue;
}
bsize += cl->buf->end - cl->buf->start;
prev = cl->buf->start;
}
}
//7) 当前busy缓冲区中等待发送响应长度已经达到p->busy_size,必须等待busy缓冲区发送了足够的数据,才能继续发送out和in中的内容
if (bsize >= (size_t) p->busy_size) {
flush = 1;
goto flush;
}
//8) 发送p->out以及p->in中的数据
flush = 0;
ll = NULL;
prev_last_shadow = 1;
for(;;){
if(p->out){
//8.1) 处理p->out链中的缓存数据
cl = p->out;
if (cl->buf->recycled) {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_ALERT, p->log, 0,
"recycled buffer in pipe out chain");
}
p->out = p->out->next;
}else if (!p->cacheable && !p->writing && p->in) {
//8.2) 处理p->in链中的缓冲数据
}else{
break;
}
// 将上述链中的缓存链接到out链表
cl->next = NULL;
if (out) {
*ll = cl;
} else {
out = cl;
}
ll = &cl->next;
}
//如下用于处理将数据通过output_filter发送给请求端
flush:
//9) 当前p->out以及p->in中没有数据要发送
if (out == NULL) {
if (!flush) {
// 9.1) busy链中也没有数据要发送,此时flush值才会为0, 因此直接跳出循环
break;
}
/* a workaround for AIO */
if (flushed++ > 10) {
return NGX_BUSY;
}
}
//10) 调用output_filter向请求端发送数据
rc = p->output_filter(p->output_ctx, out);
//11) 将p->busy以及out链中的缓存空间释放,加入到p->free链中
ngx_chain_update_chains(p->pool, &p->free, &p->busy, &out, p->tag);
//12) 向下游请求端写数据失败,释放p->busy、p->out、p->in这些空间
if (rc == NGX_ERROR) {
p->downstream_error = 1;
return ngx_event_pipe_drain_chains(p);
}
for (cl = p->free; cl; cl = cl->next) {
//13) 复位p->free链表中的相关节点信息
}
}
}5. 函数ngx_event_pipe_write_chain_to_temp_file()
static ngx_int_t
ngx_event_pipe_write_chain_to_temp_file(ngx_event_pipe_t *p)
{
ssize_t size, bsize, n;
ngx_buf_t *b;
ngx_uint_t prev_last_shadow;
ngx_chain_t *cl, *tl, *next, *out, **ll, **last_out, **last_free;
#if (NGX_THREADS)
if (p->writing) {
if (p->aio) {
return NGX_AGAIN;
}
out = p->writing;
p->writing = NULL;
n = ngx_write_chain_to_temp_file(p->temp_file, NULL);
if (n == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
goto done;
}
#endif
if (p->buf_to_file) {
out = ngx_alloc_chain_link(p->pool);
if (out == NULL) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
out->buf = p->buf_to_file;
out->next = p->in;
} else {
out = p->in;
}
if (!p->cacheable) {
size = 0;
cl = out;
ll = NULL;
prev_last_shadow = 1;
ngx_log_debug1(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe offset: %O", p->temp_file->offset);
do {
bsize = cl->buf->last - cl->buf->pos;
ngx_log_debug4(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0,
"pipe buf ls:%d %p, pos %p, size: %z",
cl->buf->last_shadow, cl->buf->start,
cl->buf->pos, bsize);
if (prev_last_shadow
&& ((size + bsize > p->temp_file_write_size)
|| (p->temp_file->offset + size + bsize
> p->max_temp_file_size)))
{
break;
}
prev_last_shadow = cl->buf->last_shadow;
size += bsize;
ll = &cl->next;
cl = cl->next;
} while (cl);
ngx_log_debug1(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0, "size: %z", size);
if (ll == NULL) {
return NGX_BUSY;
}
if (cl) {
p->in = cl;
*ll = NULL;
} else {
p->in = NULL;
p->last_in = &p->in;
}
} else {
p->in = NULL;
p->last_in = &p->in;
}
#if (NGX_THREADS)
if (p->thread_handler) {
p->temp_file->thread_write = 1;
p->temp_file->file.thread_task = p->thread_task;
p->temp_file->file.thread_handler = p->thread_handler;
p->temp_file->file.thread_ctx = p->thread_ctx;
}
#endif
n = ngx_write_chain_to_temp_file(p->temp_file, out);
if (n == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
#if (NGX_THREADS)
if (n == NGX_AGAIN) {
p->writing = out;
p->thread_task = p->temp_file->file.thread_task;
return NGX_AGAIN;
}
done:
#endif
if (p->buf_to_file) {
p->temp_file->offset = p->buf_to_file->last - p->buf_to_file->pos;
n -= p->buf_to_file->last - p->buf_to_file->pos;
p->buf_to_file = NULL;
out = out->next;
}
if (n > 0) {
/* update previous buffer or add new buffer */
if (p->out) {
for (cl = p->out; cl->next; cl = cl->next) { /* void */ }
b = cl->buf;
if (b->file_last == p->temp_file->offset) {
p->temp_file->offset += n;
b->file_last = p->temp_file->offset;
goto free;
}
last_out = &cl->next;
} else {
last_out = &p->out;
}
cl = ngx_chain_get_free_buf(p->pool, &p->free);
if (cl == NULL) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
b = cl->buf;
ngx_memzero(b, sizeof(ngx_buf_t));
b->tag = p->tag;
b->file = &p->temp_file->file;
b->file_pos = p->temp_file->offset;
p->temp_file->offset += n;
b->file_last = p->temp_file->offset;
b->in_file = 1;
b->temp_file = 1;
*last_out = cl;
}
free:
for (last_free = &p->free_raw_bufs;
*last_free != NULL;
last_free = &(*last_free)->next)
{
/* void */
}
for (cl = out; cl; cl = next) {
next = cl->next;
cl->next = p->free;
p->free = cl;
b = cl->buf;
if (b->last_shadow) {
tl = ngx_alloc_chain_link(p->pool);
if (tl == NULL) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
tl->buf = b->shadow;
tl->next = NULL;
*last_free = tl;
last_free = &tl->next;
b->shadow->pos = b->shadow->start;
b->shadow->last = b->shadow->start;
ngx_event_pipe_remove_shadow_links(b->shadow);
}
}
return NGX_OK;
}此函数用于将ngx_event_pipe相关缓存中的信息写到临时文件中。下面我们详细分析一下函数的实现流程:
static ngx_int_t
ngx_event_pipe_write_chain_to_temp_file(ngx_event_pipe_t *p)
{
//1) 采用多线程来将缓存数据写入到临时文件。当前我们并不支持NGX_THREADS宏定义
#if (NGX_THREADS)
if (p->writing) {
n = ngx_write_chain_to_temp_file(p->temp_file, NULL);
}
#endif
//2) 此处需要将p->buf_to_file以及p->bin中的数据写入到临时文件
if (p->buf_to_file) {
out = ngx_alloc_chain_link(p->pool);
if (out == NULL) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
out->buf = p->buf_to_file;
out->next = p->in;
} else {
out = p->in;
}
//
if(!p->cacheable){
//3) 不能使用缓存,那么此种情况下会检查当前out是否已经有过多的数据。如果有太多的数据的话,还是会把部分数据写入临时文件。然后
// 把剩余一部分数据放回到p->in中
}else{
//4) 此处标志将所有数据都写入临时文件
p->in = NULL;
p->last_in = &p->in;
}
//5) 此处设置写临时文件的线程相关信息
#if (NGX_THREADS)
if (p->thread_handler) {
p->temp_file->thread_write = 1;
p->temp_file->file.thread_task = p->thread_task;
p->temp_file->file.thread_handler = p->thread_handler;
p->temp_file->file.thread_ctx = p->thread_ctx;
}
#endif
//6) 将缓存信息写入到临时文件
n = ngx_write_chain_to_temp_file(p->temp_file, out);
//7) 多线程情况下,将未写完的数据保存到p->writing中
#if (NGX_THREADS)
if (n == NGX_AGAIN) {
p->writing = out;
p->thread_task = p->temp_file->file.thread_task;
return NGX_AGAIN;
}
done:
#endif
//8) p->buf_to_file这一部分数据作为p->preread_bufs来使用
if (p->buf_to_file) {
p->temp_file->offset = p->buf_to_file->last - p->buf_to_file->pos;
n -= p->buf_to_file->last - p->buf_to_file->pos;
p->buf_to_file = NULL;
out = out->next;
}
if (n > 0) {
//此处将写入临时文件的这部分缓存数据加入到p->out链表,使得后续可以向downstream发送这一部分数据。
}
free:
//9) 此处遍历到p->free_raw_bufs的末尾
for (last_free = &p->free_raw_bufs;
*last_free != NULL;
last_free = &(*last_free)->next)
{
/* void */
}
for (cl = out; cl; cl = next) {
//10) 将写入了临时文件的这一部分缓存加到p->free链表中
if (b->last_shadow) {
//11) 将对应的buf加入到p->free_raw_bufs链表的表尾
}
}
}6. 函数ngx_event_pipe_copy_input_filter()
/* the copy input filter */
ngx_int_t
ngx_event_pipe_copy_input_filter(ngx_event_pipe_t *p, ngx_buf_t *buf)
{
ngx_buf_t *b;
ngx_chain_t *cl;
if (buf->pos == buf->last) {
return NGX_OK;
}
cl = ngx_chain_get_free_buf(p->pool, &p->free);
if (cl == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
b = cl->buf;
ngx_memcpy(b, buf, sizeof(ngx_buf_t));
b->shadow = buf;
b->tag = p->tag;
b->last_shadow = 1;
b->recycled = 1;
buf->shadow = b;
ngx_log_debug1(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_EVENT, p->log, 0, "input buf #%d", b->num);
if (p->in) {
*p->last_in = cl;
} else {
p->in = cl;
}
p->last_in = &cl->next;
if (p->length == -1) {
return NGX_OK;
}
p->length -= b->last - b->pos;
return NGX_OK;
}此函数较为简单,用于拷贝buf,并将其插入到p->in链表的表尾。
7. 函数ngx_event_pipe_remove_shadow_links()
static ngx_inline void
ngx_event_pipe_remove_shadow_links(ngx_buf_t *buf)
{
ngx_buf_t *b, *next;
b = buf->shadow;
if (b == NULL) {
return;
}
while (!b->last_shadow) {
next = b->shadow;
b->temporary = 0;
b->recycled = 0;
b->shadow = NULL;
b = next;
}
b->temporary = 0;
b->recycled = 0;
b->last_shadow = 0;
b->shadow = NULL;
buf->shadow = NULL;
}此函数用于移除一个buf上的所有shadow
8. 函数ngx_event_pipe_add_free_buf()
ngx_int_t
ngx_event_pipe_add_free_buf(ngx_event_pipe_t *p, ngx_buf_t *b)
{
ngx_chain_t *cl;
cl = ngx_alloc_chain_link(p->pool);
if (cl == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
if (p->buf_to_file && b->start == p->buf_to_file->start) {
b->pos = p->buf_to_file->last;
b->last = p->buf_to_file->last;
} else {
b->pos = b->start;
b->last = b->start;
}
b->shadow = NULL;
cl->buf = b;
if (p->free_raw_bufs == NULL) {
p->free_raw_bufs = cl;
cl->next = NULL;
return NGX_OK;
}
if (p->free_raw_bufs->buf->pos == p->free_raw_bufs->buf->last) {
/* add the free buf to the list start */
cl->next = p->free_raw_bufs;
p->free_raw_bufs = cl;
return NGX_OK;
}
/* the first free buf is partially filled, thus add the free buf after it */
cl->next = p->free_raw_bufs->next;
p->free_raw_bufs->next = cl;
return NGX_OK;
}此函数用于将b添加到p->free_raw_bufs中。参看前面的代码,我们知道p->free_raw_bufs可能仍有一部分空间被使用,因此在添加b这一块缓存空间时要特别注意。下面我们简要分析一下此函数:
ngx_int_t
ngx_event_pipe_add_free_buf(ngx_event_pipe_t *p, ngx_buf_t *b)
{
//1) 分配一个ngx_chain_t节点,以容纳b
//2) 说明参数b指向的这块缓存空间与p->buf_to_file这一块特殊空间有重叠,此时需要特殊处理
if (p->buf_to_file && b->start == p->buf_to_file->start) {
b->pos = p->buf_to_file->last;
b->last = p->buf_to_file->last;
} else {
b->pos = b->start;
b->last = b->start;
}
//3) 直接插入到p->free_raw_bufs即可
if (p->free_raw_bufs == NULL) {
p->free_raw_bufs = cl;
cl->next = NULL;
return NGX_OK;
}
if (p->free_raw_bufs->buf->pos == p->free_raw_bufs->buf->last) {
//4) 说明p->free_raw_bufs的第一个节点并没有部分被占用,此时可以直接插入到链表表头
}
//5) 说明p->free_raw_bufs链表第一个节点部分空间仍残留有数据,因此需要插入到p->free_raw_bufs的第一个节点之后
}9. 函数ngx_event_pipe_drain_chains()
static ngx_int_t
ngx_event_pipe_drain_chains(ngx_event_pipe_t *p)
{
ngx_chain_t *cl, *tl;
for ( ;; ) {
if (p->busy) {
cl = p->busy;
p->busy = NULL;
} else if (p->out) {
cl = p->out;
p->out = NULL;
} else if (p->in) {
cl = p->in;
p->in = NULL;
} else {
return NGX_OK;
}
while (cl) {
if (cl->buf->last_shadow) {
if (ngx_event_pipe_add_free_buf(p, cl->buf->shadow) != NGX_OK) {
return NGX_ABORT;
}
cl->buf->last_shadow = 0;
}
cl->buf->shadow = NULL;
tl = cl->next;
cl->next = p->free;
p->free = cl;
cl = tl;
}
}
}本函数用于p->busy、p->out、p->in这些缓存空间释放回p->free中,并将c1->buf->shadow空间释放回p->free_raw_bufs中.
[参看]

