phxpaxos源码分析: 状态机
Paxos协议是分布式系统设计中的一个非常重要的协议,本文转载自微信后台团队公众号团队所发表一系列Paxos的文章,中间针对自己的理解略有修改或注释。在此处做一个备份,一方面为了加深对Paxos协议的理解,另一方面也方便自己的后续查找,防止文章丢失。
1. 基本概念
- Paxos Log
通过Paxos算法选中的一组有序的提案值。例如,PhxSQL中使用PhxPaxos确定的有序值为binlog。
- 状态机
业务自定义的如何使用Paxos log的数据消费逻辑。状态机的一个特点是:只要初始状态一致,输入一致,那么引出的最终状态也是一致的。在PhxSQL中,这个状态机就是binlog的replay机制,即在其他节点上执行和主节点一致的binlog操作,保证各个节点数据的一致性。
2. 代码设计
状态机相关类的类图如下:
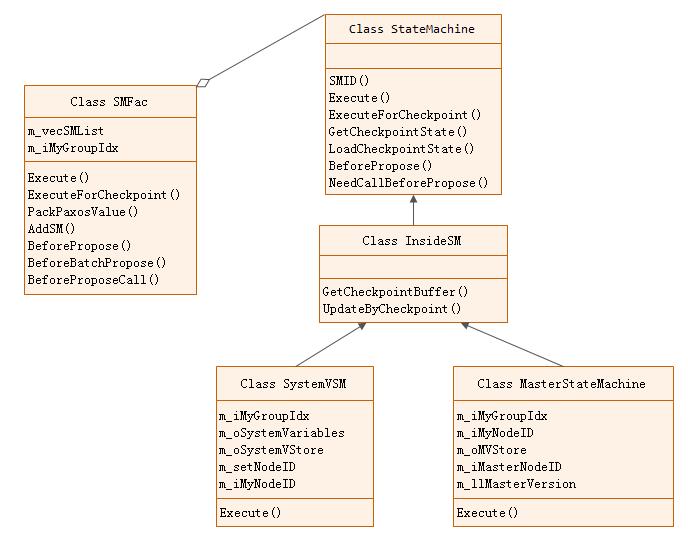
下面我们简要介绍一下各class的功能:
-
SMFac: 状态机管理类,内部维护一个状态机(StateMachine)列表,对外提供统一的状态机访问接口。
-
StateMachine: 状态机抽象类。允许PhxPaxos使用者继承该类,定制自己的业务状态机。
-
InsideSM: 内部状态机抽象类
-
MasterStateMachine: 主节点状态机。用于集群选主
3. 状态机管理(SMFac)
PhxPaxos的每个Group允许同时存在多个状态机,但一个paxos log只能被一个状态机消费。不同的状态机之间的数据相互隔离,但它们共享同一份Group资源:Proposer、Acceptor、Learner、InstanceID等等。其中SystemVSM、MasterStateMachine这两个内置的状态机默认添加到所有的Group之中。
SMFac作为管理类,除支持添加各种状态机,还对外提供了统一的状态机执行接口:
class SMFac
{
public:
//执行状态机
bool Execute(const int iGroupIdx, const uint64_t llInstanceID,
const std::string& sPaxosValue, SMCtx* poSMCtx);
//执行状态机的Checkpoint操作
bool ExecuteForCheckpoint(const int iGroupIdx, const uint64_t llInstanceID, const std::string& sPaxosValue);
//打包
void PackPaxosValue(std::string& sPaxosValue, const int iSMID = 0);
//添加状态机
void AddSM(StateMachine* poSM);
public:
void BeforePropose(const int iGroupIdx, std::string& sValue);
void BeforeBatchPropose(const int iGroupIdx, std::string& sValue);
void BeforeProposeCall(const int iGroupIdx, const int iSMID, std::string& sValue, bool& change);
public:
const uint64_t GetCheckpointInstanceID(const int iGroupIdx) const;
//返回状态机列表
std::vector<StateMachine*> GetSMList();
......
};状态机用于消费paxos log,即一旦paxos的提案值确定立即交由状态机消费。入口逻辑如下:
int Instance :: ReceiveMsgForLearner(const PaxosMsg& oPaxosMsg)
{
//Learner消息处理逻辑
......
//当前Instance Id的提案值已习得
if (m_oLearner.IsLearned())
{
BP->GetInstanceBP()->OnInstanceLearned();
//获取状态机上下文信息
SMCtx* poSMCtx = nullptr;
bool bIsMyCommit = m_oCommitCtx.IsMyCommit(m_oLearner.GetInstanceID(), m_oLearner.GetLearnValue(), poSMCtx);
if (!bIsMyCommit)
{
BP->GetInstanceBP()->OnInstanceLearnedNotMyCommit();
PLGDebug("this value is not my commit");
}
else
{
int iUseTimeMs = m_oTimeStat.Point();
BP->GetInstanceBP()->OnInstanceLearnedIsMyCommit(iUseTimeMs);
PLGHead("My commit ok, usetime %dms", iUseTimeMs);
}
//执行状态机
if (!SMExecute(m_oLearner.GetInstanceID(), m_oLearner.GetLearnValue(), bIsMyCommit, poSMCtx))
{
BP->GetInstanceBP()->OnInstanceLearnedSMExecuteFail();
PLGErr("SMExecute fail, instanceid %lu, not increase instanceid", m_oLearner.GetInstanceID());
m_oCommitCtx.SetResult(PaxosTryCommitRet_ExecuteFail,
m_oLearner.GetInstanceID(), m_oLearner.GetLearnValue());
m_oProposer.CancelSkipPrepare();
return -1;
}
......
}
}SMExecute()只是一个跳板函数,直接调用SMFac的Execute()方法:
bool SMFac :: Execute(const int iGroupIdx, const uint64_t llInstanceID, const std::string& sPaxosValue, SMCtx* poSMCtx)
{
if (sPaxosValue.size() < sizeof(int))
{
PLG1Err("Value wrong, instanceid %lu size %zu", llInstanceID, sPaxosValue.size());
//need do nothing, just skip
return true;
}
//必须为有效的SM ID
int iSMID = 0;
memcpy(&iSMID, sPaxosValue.data(), sizeof(int));
if (iSMID == 0)
{
PLG1Imp("Value no need to do sm, just skip, instanceid %lu", llInstanceID);
return true;
}
//提前paxos log数据
std::string sBodyValue = string(sPaxosValue.data() + sizeof(int), sPaxosValue.size() - sizeof(int));
//批量处理
if (iSMID == BATCH_PROPOSE_SMID)
{
BatchSMCtx* poBatchSMCtx = nullptr;
if (poSMCtx != nullptr && poSMCtx->m_pCtx != nullptr)
{
poBatchSMCtx = (BatchSMCtx*)poSMCtx->m_pCtx;
}
return BatchExecute(iGroupIdx, llInstanceID, sBodyValue, poBatchSMCtx);
}
else
{
//指定状态机处理
return DoExecute(iGroupIdx, llInstanceID, sBodyValue, iSMID, poSMCtx);
}
}前面提到一个paxos log只能被一个状态机消费,但上面却提供了一个状态机批量处理的逻辑。是否相互矛盾呢?来看代码实现:
bool SMFac :: BatchExecute(const int iGroupIdx, const uint64_t llInstanceID, const std::string& sBodyValue, BatchSMCtx* poBatchSMCtx)
{
BatchPaxosValues oBatchValues;
bool bSucc = oBatchValues.ParseFromArray(sBodyValue.data(), sBodyValue.size());
if (!bSucc)
{
PLG1Err("ParseFromArray fail, valuesize %zu", sBodyValue.size());
return false;
}
if (poBatchSMCtx != nullptr)
{
if ((int)poBatchSMCtx->m_vecSMCtxList.size() != oBatchValues.values_size())
{
PLG1Err("values size %d not equal to smctx size %zu",
oBatchValues.values_size(), poBatchSMCtx->m_vecSMCtxList.size());
return false;
}
}
//依次处理每条记录
for (int i = 0; i < oBatchValues.values_size(); i++)
{
const PaxosValue& oValue = oBatchValues.values(i);
SMCtx* poSMCtx = poBatchSMCtx != nullptr ? poBatchSMCtx->m_vecSMCtxList[i] : nullptr;
bool bExecuteSucc = DoExecute(iGroupIdx, llInstanceID, oValue.value(), oValue.smid(), poSMCtx);
if (!bExecuteSucc)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}实际上,批量的含义指的是数据中包含多个paxos log值,而非批量的对多个状态机执行操作。依次处理每条paxos log时,调用的DoExecute()携带了有效的smID信息。DoExecute()查找smID配套的状态机,交由状态机消费数据:
bool SMFac :: DoExecute(const int iGroupIdx, const uint64_t llInstanceID,
const std::string & sBodyValue, const int iSMID, SMCtx * poSMCtx)
{
if (iSMID == 0)
{
PLG1Imp("Value no need to do sm, just skip, instanceid %lu", llInstanceID);
return true;
}
if (m_vecSMList.size() == 0)
{
PLG1Imp("No any sm, need wait sm, instanceid %lu", llInstanceID);
return false;
}
for (auto & poSM : m_vecSMList)
{
if (poSM->SMID() == iSMID)
{
return poSM->Execute(iGroupIdx, llInstanceID, sBodyValue, poSMCtx);
}
}
PLG1Err("Unknown smid %d instanceid %lu", iSMID, llInstanceID);
return false;
}SMFac中的其他逻辑,此处不再赘述,有兴趣可以参考源码。
4. 状态机(StateMachine)
状态机抽象类的接口定义如下:
class StateMachine
{
public:
virtual ~StateMachine() {}
//状态机标识,需要保证唯一性。
virtual const int SMID() const = 0;
//状态机执行函数,返回true意味着execute执行完成,不需要重新执行。
virtual bool Execute(const int iGroupIdx, const uint64_t llInstanceID,
const std::string& sPaxosValue, SMCtx* poSMCtx) = 0;
//真正发起Propose之前,调用状态机中该函数,修改请求数据或做其他处理
virtual void BeforePropose(const int iGroupIdx, std::string& sValue);
//是否需要调用BeforePropose,默认为false
virtual const bool NeedCallBeforePropose();
//--------------------------------------Checkpoint机制相关----------------------------------------
//Checkpoint机制执行函数
virtual bool ExecuteForCheckpoint(const int iGroupIdx, const uint64_t llInstanceID,
const std::string& sPaxosValue);
//返回checkpoint已执行的、最大的instance id;PhxPaxos将频繁调用此接口。
virtual const uint64_t GetCheckpointInstanceID(const int iGroupIdx) const;
//调用此接口锁定Checkpoint文件,后续调用GetCheckpointState获取的文件不允许有任何变更
virtual int LockCheckpointState();
//返回Checkpoint的文件路径及文件列表
virtual int GetCheckpointState(const int iGroupIdx, std::string& sDirPath,
std::vector<std::string>& vecFileList);
//Checkpoint文件使用完毕,解锁Checkpoint文件
virtual void UnLockCheckpointState();
//使用指定路径的Checkpoint文件,PhxPaxos在执行完该函数后将重启当前进程。
virtual int LoadCheckpointState(const int iGroupIdx, const std::string& sCheckpointTmpFileDirPath,
const std::vector<std::string>& vecFileList, const uint64_t llCheckpointInstanceID);
};按功能划分为如下两类:
1) 状态机职责函数。包括状态机标识(SMID)、状态迁移(Execute)、BeforePropose()、NeedCallBeforePropose()
2) Checkpoint相关函数。上述代码中由“Checkpoint机制相关”分割部分逻辑,这一部分在后面的“Checkpoint机制”一章中还会提到。
5. 集群变更状态机(SystemVSM)
SystemVSM(System Variable State Machine)用于PhxPaxos集群成员变更,这是对外提供的一组功能接口,PhxPaxos本身并不会主动触发集群变更。我们可以通过Node类中提供的相关方法来触发变更操作:
class Node
{
public:
virtual int ShowMembership(const int iGroupIdx, NodeInfoList& vecNodeInfoList) = 0;
virtual int AddMember(const int iGroupIdx, const NodeInfo& oNode) = 0;
virtual int RemoveMember(const int iGroupIdx, const NodeInfo& oNode) = 0;
virtual int ChangeMember(const int iGroupIdx, const NodeInfo& oFromNode, const NodeInfo& oToNode) = 0;
}注意: 如果需要启用集群成员变更功能,需要设置Options中bUseMembership配置项为true。
集群的初始节点信息通过Options::vecNodeInfoList配置项传递给PhxPaxos。如果启用了节点变更功能,将在首次发送消息前同步集群状态:
void Instance :: CheckNewValue()
{
......
//启用系统变更 and (首个提案实例 or 当前集群状态需要更新)
if (m_poConfig->GetIsUseMembership()
&& (m_oProposer.GetInstanceID() == 0 || m_poConfig->GetGid() == 0))
{
//Init system variables.
PLGHead("Need to init system variables, Now.InstanceID %lu Now.Gid %lu",
m_oProposer.GetInstanceID(), m_poConfig->GetGid());
uint64_t llGid = OtherUtils::GenGid(m_poConfig->GetMyNodeID());
string sInitSVOpValue;
int ret = m_poConfig->GetSystemVSM()->CreateGid_OPValue(llGid, sInitSVOpValue);
assert(ret == 0);
//发起定向由SystemVSM处理的paxos消息
m_oSMFac.PackPaxosValue(sInitSVOpValue, m_poConfig->GetSystemVSM()->SMID());
m_oProposer.NewValue(sInitSVOpValue);
}
}因为集群节点可能发生变更,因此集群信息不能再以配置文件中的Options::vecNodeInfoList为准,需要单独做持久化。这部分逻辑在状态机的Execute()中触发,调用UpdateSystemVariables()完成:
int SystemVSM :: UpdateSystemVariables(const SystemVariables& oVariables)
{
WriteOptions oWriteOptions;
oWriteOptions.bSync = true;
//以选中的提案值为准,持久化到数据库
int ret = m_oSystemVStore.Write(oWriteOptions, m_iMyGroupIdx, oVariables);
if (ret != 0)
{
PLG1Err("SystemVStore::Write fail, ret %d", ret);
return -1;
}
//以选中的提案值为准
m_oSystemVariables = oVariables;
RefleshNodeID();
return 0;
}集群节点变更包括新增、修改、删除,处理逻辑如下:
在已有集群新增,替换机器
- 准备好新的机器,新的机器以空成员启动PhxPaxos(Options::vecNodeInfoList设置为空)
- 在任意一个已有的集群成员节点中调用Node::AddMember()或Node::ChangeMember()
在已有集群删除机器
- 在任意一个已有的成员节点中调用Node::RemoveMember()
如果所有节点都希望立即获得这个成员变更操作的通知,可通过options.h设置Options::pMembershipChangeCallback回调函数
代码实现上,增、删、改处理逻辑类似,以AddMember()为例:
int PNode :: AddMember(const int iGroupIdx, const NodeInfo& oNode)
{
if (!CheckGroupID(iGroupIdx))
{
return Paxos_GroupIdxWrong;
}
SystemVSM* poSystemVSM = m_vecGroupList[iGroupIdx]->GetConfig()->GetSystemVSM();
if (poSystemVSM->GetGid() == 0)
{
return Paxos_MembershipOp_NoGid;
}
//获取当前集群已有的节点列表
uint64_t llVersion = 0;
NodeInfoList vecNodeInfoList;
poSystemVSM->GetMembership(vecNodeInfoList, llVersion);
for (auto & oNodeInfo : vecNodeInfoList)
{
if (oNodeInfo.GetNodeID() == oNode.GetNodeID())
{
return Paxos_MembershipOp_Add_NodeExist;
}
}
//补充需要新增的节点信息
vecNodeInfoList.push_back(oNode);
//以完整的集群信息发起提案,即将该信息同步到各个节点
return ProposalMembership(poSystemVSM, iGroupIdx, vecNodeInfoList, llVersion);
}6. 选主服务状态机(MasterStateMachine)
MasterStateMachine称为主节点状态机,用于和选主及租约相关操作的状态维护、更新。除MasterStateMachine之外,另一个和选主服务相关的类为MasterMgr,PhxPaxos为它启动了一个单独的线程。这次我们从MasterMgr开始说起。
MasterMgr内部组合了MasterStateMachine,也是MasterStateMachine的唯一实例点:
MasterStateMachine * MasterMgr :: GetMasterSM()
{
return &m_oDefaultMasterSM;
}在PhxPaxos节点启动时,为每个Group创建一个选主服务对象,启动选主服务MasterMgr。选主服务线程定期检测主节点状态、执行续约等操作:
void MasterMgr :: run()
{
m_bIsStarted = true;
while (true)
{
if (m_bIsEnd)
{
return;
}
//租约时长,单位毫秒
int iLeaseTime = m_iLeaseTime;
uint64_t llBeginTime = Time::GetSteadyClockMS();
//尝试选主
TryBeMaster(iLeaseTime);
//计算下次选主操作的时间间隔
int iContinueLeaseTimeout = (iLeaseTime - 100) / 4;
iContinueLeaseTimeout = iContinueLeaseTimeout / 2 + OtherUtils::FastRand() % iContinueLeaseTimeout;
//如果需要主动触发重新选主,将下次选主周期设置为:租约*2
if (m_bNeedDropMaster)
{
BP->GetMasterBP()->DropMaster();
m_bNeedDropMaster = false;
iContinueLeaseTimeout = iLeaseTime * 2;
PLG1Imp("Need drop master, this round wait time %dms", iContinueLeaseTimeout);
}
//实际间隔 = 计算间隔 - 本次操作运行时间
uint64_t llEndTime = Time::GetSteadyClockMS();
int iRunTime = llEndTime > llBeginTime ? llEndTime - llBeginTime : 0;
int iNeedSleepTime = iContinueLeaseTimeout > iRunTime ? iContinueLeaseTimeout - iRunTime : 0;
PLG1Imp("TryBeMaster, sleep time %dms", iNeedSleepTime);
Time::MsSleep(iNeedSleepTime);
}
}假设租约时长为5s,每次选主操作耗时500ms,那么选主间隔为:
step1: (5000 - 100)/4 = 1225 step2: 1225/2 + rand() % 1225 = 612 + 600(0~1225的任意值) = 1212 step3: 1212-500 = 712ms
也就是说,选主和续约周期大约为租约的1/4时间。
下面我们再来看TryBeMaster():
void MasterMgr :: TryBeMaster(const int iLeaseTime)
{
nodeid_t iMasterNodeID = nullnode;
uint64_t llMasterVersion = 0;
//获取当前的主节点信息
//step 1 check exist master and get version
m_oDefaultMasterSM.SafeGetMaster(iMasterNodeID, llMasterVersion);
//1. 如果当前已经存在主节点,那么需要执行续约动作,该动作只能由主节点发起
//2. 如果当前无主节点,需要执行选主动作,任意节点发起
if (iMasterNodeID != nullnode && (iMasterNodeID != m_poPaxosNode->GetMyNodeID()))
{
PLG1Imp("Ohter as master, can't try be master, masterid %lu myid %lu",
iMasterNodeID, m_poPaxosNode->GetMyNodeID());
return;
}
BP->GetMasterBP()->TryBeMaster();
//step 2 try be master
std::string sPaxosValue;
//构建选主、续约数据(node id、租约时长等)
if (!MasterStateMachine::MakeOpValue(
m_poPaxosNode->GetMyNodeID(),
llMasterVersion,
iLeaseTime,
MasterOperatorType_Complete,
sPaxosValue))
{
PLG1Err("Make paxos value fail");
return;
}
const int iMasterLeaseTimeout = iLeaseTime - 100;
uint64_t llAbsMasterTimeout = Time::GetSteadyClockMS() + iMasterLeaseTimeout;
uint64_t llCommitInstanceID = 0;
SMCtx oCtx;
oCtx.m_iSMID = MASTER_V_SMID;
oCtx.m_pCtx = (void*)&llAbsMasterTimeout;
//各节点间同步选主、续约数据
int ret = m_poPaxosNode->Propose(m_iMyGroupIdx, sPaxosValue, llCommitInstanceID, &oCtx);
if (ret != 0)
{
BP->GetMasterBP()->TryBeMasterProposeFail();
}
}一旦节点发起了选主、续约操作到各个节点,各节点习得该数据后执行MasterStateMachine的Execute()操作。Execute()做了基本检查后调用LearnMaster,我们来直接看看该函数:
int MasterStateMachine :: LearnMaster(
const uint64_t llInstanceID,
const MasterOperator & oMasterOper,
const uint64_t llAbsMasterTimeout)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> oLockGuard(m_oMutex);
PLG1Debug("my last version %lu other last version %lu this version %lu instanceid %lu",
m_llMasterVersion, oMasterOper.lastversion(), oMasterOper.version(), llInstanceID);
//master version不一致,且由其他节点发送来的master version更新,尝试使用新的master
if (oMasterOper.lastversion() != 0
&& llInstanceID > m_llMasterVersion
&& oMasterOper.lastversion() != m_llMasterVersion)
{
BP->GetMasterBP()->MasterSMInconsistent();
PLG1Err("other last version %lu not same to my last version %lu, instanceid %lu",
oMasterOper.lastversion(), m_llMasterVersion, llInstanceID);
PLG1Err("try to fix, set my master version %lu as other last version %lu, instanceid %lu",
m_llMasterVersion, oMasterOper.lastversion(), llInstanceID);
m_llMasterVersion = oMasterOper.lastversion();
}
if (oMasterOper.version() != m_llMasterVersion)
{
PLG1Debug("version conflit, op version %lu now master version %lu",
oMasterOper.version(), m_llMasterVersion);
return 0;
}
//将新主、续约时间等更新到数据库中
int ret = UpdateMasterToStore(oMasterOper.nodeid(), llInstanceID, oMasterOper.timeout());
if (ret != 0)
{
PLG1Err("UpdateMasterToStore fail, ret %d", ret);
return -1;
}
bool bMasterChange = false;
if (m_iMasterNodeID != oMasterOper.nodeid())
{
bMasterChange = true;
}
//内存数据更新
m_iMasterNodeID = oMasterOper.nodeid();
if (m_iMasterNodeID == m_iMyNodeID)
{
//self be master
//use local abstimeout
m_llAbsExpireTime = llAbsMasterTimeout;
BP->GetMasterBP()->SuccessBeMaster();
PLG1Head("Be master success, absexpiretime %lu", m_llAbsExpireTime);
}
else
{
//other be master
//use new start timeout
m_llAbsExpireTime = Time::GetSteadyClockMS() + oMasterOper.timeout();
BP->GetMasterBP()->OtherBeMaster();
PLG1Head("Ohter be master, absexpiretime %lu", m_llAbsExpireTime);
}
m_iLeaseTime = oMasterOper.timeout();
m_llMasterVersion = llInstanceID;
if (bMasterChange)
{
if (m_pMasterChangeCallback != nullptr)
{
m_pMasterChangeCallback(m_iMyGroupIdx, NodeInfo(m_iMasterNodeID), m_llMasterVersion);
}
}
PLG1Imp("OK, masternodeid %lu version %lu abstimeout %lu",
m_iMasterNodeID, m_llMasterVersion, m_llAbsExpireTime);
return 0;
}总结如下:
1) 每个Group启动一个选主服务线程,定期触发选主、续约操作
2) 通过Propose发起选主,选主成功后主节点信息持久化到数据库
3) 主节点定期发起续约保活,周期约为租期的1/4;
4) 节点重启,优先沿用原来的主节点信息
都已经到这了,但有一件事一直没提。选了Master又能怎么样呢? PhxPaxos在哪些场景使用了Master这个身份?
答: PhxPaxos对Master角色没有任何依赖,即便没有Master,PhxPaxos依旧可以正常工作。Master提供给外部业务使用。
7. 业务状态机
业务状态机即由业务实现的状态机,负责业务自身逻辑。业务状态机继承自StateMachine,并通过Node的AddStateMachine()添加到PhxPaxos:
class Node
{
public:
//为所有Group添加状态机
virtual void AddStateMachine(StateMachine* poSM) = 0;
//为指定Group添加状态机
virtual void AddStateMachine(const int iGroupIdx, StateMachine* poSM) = 0;
......
}那么,如何使用状态机呢? 也非常简单,在Node的Propose()方法中指定SMCtx(StateMachine Context),指明本次Propose配套的状态机:
class SMCtx
{
public:
SMCtx();
SMCtx(const int iSMID, void* pCtx);
//状态机ID
int m_iSMID;
//自定义数据
void* m_pCtx;
};
class Node
{
public:
//Base function.
virtual int Propose(const int iGroupIdx, const std::string& sValue, uint64_t& llInstanceID) = 0;
virtual int Propose(const int iGroupIdx, const std::string& sValue, uint64_t& llInstanceID, SMCtx* poSMCtx) = 0; 0;
......
}8. 总结
本章讲解了PhxPaxos中的状态机、状态机管理机制以及两个内置的状态机。每个节点的paxos log只会被一个状态机消费,因此保存的paxos log中记录了本条数据所属的状态机。
-
内置的SystemVSM用于处理集群节点变更,变更操作包括成员的新增、修改、删除。它通过Propose方式完成集群间节点状态变更;
-
内置的MasterStateMachine用于选举服务,它配套的MasterMgr定时触发选举或者续约行为,保证整个集群有一个主节点;
-
业务状态机通过Node提供的AddStateMachine接口添加到PhxPaxos,并通过在Propose时指定状态机
上一节我们提到:“PhxPaxos并未对paxos做任何变种,甚至还做了一点简化”。看过状态机的相关逻辑后,不知道各位是否能回答这个问题?所指的是《Paxos Made Simple》下面这部分逻辑并未实现:
In general, suppose a leader can get α commands ahead—that is, it can propose commands i + 1 through i +α after commands 1 through i are chosen. A gap of up to α−1 commands could then arise.
在我看来,PhxPaxos这么做应该是出于以下几点考虑:
-
预取并发确定多个提案值,将导致程序复杂度指数上升;
-
通过支持BatchPropose同样可以同时确定多个值;
至此,《Paxos Made Simple》中介绍的主要概念已经讲解完毕。但有一个问题: 如果paxos持续运行,将产生大量的paxos log(选中的提案值)。存储介质不可能支持无限量的数据,但同时新节点加入需要习得全部paxos log。Paxos协议并没有给出解决方案,那PhxPaxos又给出了什么方案呢?来看下一节。
参看:

