crushmap算法详解-2
本文主要通过一个crushmap的例子,来探讨crushmap将PG映射到OSD的过程。
1. 生成crushmap.bin
我们有如下crushmap.txt:
[root@localhost ceph-test]# cat crushmap.txt
# begin crush map
tunable choose_local_tries 0
tunable choose_local_fallback_tries 0
tunable choose_total_tries 50
tunable chooseleaf_descend_once 1
tunable straw_calc_version 1
# devices
device 0 osd.0
device 1 osd.1
device 2 osd.2
device 3 osd.3
device 4 osd.4
device 5 osd.5
device 6 osd.6
device 7 osd.7
device 8 osd.8
# types
type 0 osd
type 1 host
type 2 chassis
type 3 rack
type 4 row
type 5 pdu
type 6 pod
type 7 room
type 8 datacenter
type 9 region
type 10 root
type 11 osd-domain
type 12 host-domain
type 13 replica-domain
type 14 failure-domain
# buckets
host node7-1 {
id -2 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 0.450
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item osd.0 weight 0.150
item osd.1 weight 0.150
item osd.2 weight 0.150
}
rack rack-01 {
id -3 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 0.450
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item node7-1 weight 0.450
}
host node7-2 {
id -4 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 0.450
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item osd.3 weight 0.150
item osd.4 weight 0.150
item osd.5 weight 0.150
}
rack rack-02 {
id -5 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 0.450
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item node7-2 weight 0.450
}
host node7-3 {
id -6 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 0.450
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item osd.6 weight 0.150
item osd.7 weight 0.150
item osd.8 weight 0.150
}
rack rack-03 {
id -7 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 0.450
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item node7-3 weight 0.450
}
root default {
id -1 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 1.350
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item rack-01 weight 0.450
item rack-02 weight 0.450
item rack-03 weight 0.450
}
host-domain host-group-0-rack-01 {
id -8 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 0.450
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item node7-1 weight 0.450
}
host-domain host-group-0-rack-02 {
id -11 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 0.450
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item node7-2 weight 0.450
}
host-domain host-group-0-rack-03 {
id -12 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 0.450
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item node7-3 weight 0.450
}
replica-domain replica-0 {
id -9 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 1.350
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item host-group-0-rack-01 weight 0.450
item host-group-0-rack-02 weight 0.450
item host-group-0-rack-03 weight 0.450
}
failure-domain sata-00 {
id -10 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 1.350
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item replica-0 weight 1.350
}
# rules
rule replicated_ruleset {
ruleset 0
type replicated
min_size 1
max_size 10
step take default
step choose firstn 0 type osd
step emit
}
rule replicated_rule-5 {
ruleset 5
type replicated
min_size 1
max_size 10
step take sata-00
step choose firstn 1 type replica-domain
step chooseleaf firstn 0 type host-domain
step emit
}
# end crush map
调用如下命令生成crushmap.bin:
crushtool -c crushmap.txt -o crushmap-new.bin整个crushmap的层级结构如下:
[root@localhost ceph-test]# crushtool --test -i crushmap-new.bin --tree WARNING: no output selected; use --output-csv or --show-X ID WEIGHT TYPE NAME -10 1.34999 failure-domain sata-00 -9 1.34999 replica-domain replica-0 -8 0.45000 host-domain host-group-0-rack-01 -2 0.45000 host node7-1 0 0.14999 osd.0 1 0.14999 osd.1 2 0.14999 osd.2 -11 0.45000 host-domain host-group-0-rack-02 -4 0.45000 host node7-2 3 0.14999 osd.3 4 0.14999 osd.4 5 0.14999 osd.5 -12 0.45000 host-domain host-group-0-rack-03 -6 0.45000 host node7-3 6 0.14999 osd.6 7 0.14999 osd.7 8 0.14999 osd.8 -1 1.34999 root default -3 0.45000 rack rack-01 -2 0.45000 host node7-1 0 0.14999 osd.0 1 0.14999 osd.1 2 0.14999 osd.2 -5 0.45000 rack rack-02 -4 0.45000 host node7-2 3 0.14999 osd.3 4 0.14999 osd.4 5 0.14999 osd.5 -7 0.45000 rack rack-03 -6 0.45000 host node7-3 6 0.14999 osd.6 7 0.14999 osd.7 8 0.14999 osd.8
2. 测试PG映射到OSD的过程
如下我们使用crushtool工具来测试PG到OSD的映射。上面我们有两个rule,其对应的ruleset分别是ruleset 0与ruleset 5。
#方式1: 指定使用rule 1(即ruleset 5),映射[0,10]这11个PG
crushtool --test -i crushmap-new.bin --show-mappings --rule 1 --num-rep=3 --min_x=0 --max_x=10
#方式2: 指定使用ruleset 5,映射[0,10]这11个PG
crushtool --test -i crushmap-new.bin --show-mappings --ruleset 5 --num-rep=3 --min_x=0 --max_x=10
#方式3: 单独指定映射某个PG
crushtool --test -i crushmap-new.bin --show-mappings --ruleset 5 --num-rep=3 --x=100注意: 这里如果不指定min_x与max_x,则系统默认会映射[0,1023]这1024个PG
如下我们采用ruleset 5映射PG 0~PG 10:
[root@localhost ceph-test]# crushtool --test -i crushmap-new.bin --show-mappings --ruleset 5 --num-rep=3 --min_x=0 --max_x=10 CRUSH rule 1 x 0 [3,0,7] CRUSH rule 1 x 1 [5,0,7] CRUSH rule 1 x 2 [8,3,1] CRUSH rule 1 x 3 [8,0,4] CRUSH rule 1 x 4 [1,4,7] CRUSH rule 1 x 5 [3,8,0] CRUSH rule 1 x 6 [3,6,1] CRUSH rule 1 x 7 [5,8,2] CRUSH rule 1 x 8 [7,5,0] CRUSH rule 1 x 9 [8,3,1] CRUSH rule 1 x 10 [4,0,8]
3. 源代码分析
下面我们结合crushtool源代码来分析上述命令的执行过程,以进一步了解crushmap.
3.1 解析test参数
表明以test方式运行,在这里--test参数是必须的,否则将不能执行到我们的映射函数:
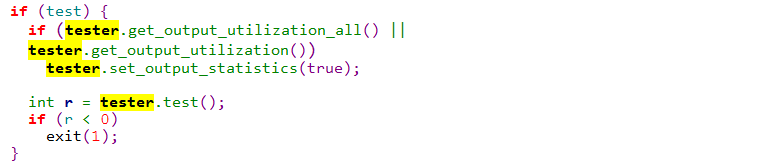
3.2 解析i参数
参数-i指定输入的crushmap.bin文件,crushtool工具需要通过解析该文件来获取crushmap对象:
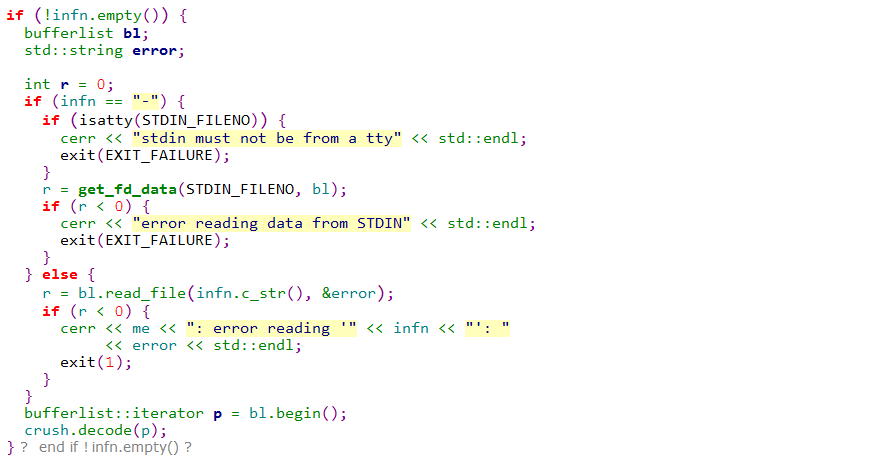
这里crush.decode(p)是《crushmap详解-1》中crushmap 编码的一个逆过程,这里不做详细解释。
3.3 解析show-mappings参数
参数--show-mappings告诉crushtool将PG->OSD的映射打印出来。
3.4 解析ruleset参数

3.5 解析num-rep参数
参数num-rep指定数据的副本数,直接关系到一个PG会映射到多少个OSD上。
3.6 解析min_x与max_x参数
通过这两个参数来指定映射哪个范围的内PG,如果未指定,后续可以看到默认会映射PG0~PG1023范围内的所有PG。
3.7 主要函数分析
上述命令的主要执行过程为如下函数:
int CrushTester::test()
{
if (min_rule < 0 || max_rule < 0) {
min_rule = 0;
max_rule = crush.get_max_rules() - 1;
}
if (min_x < 0 || max_x < 0) {
min_x = 0;
max_x = 1023;
}
// initial osd weights
vector<__u32> weight;
/*
* note device weight is set by crushtool
* (likely due to a given a command line option)
*/
for (int o = 0; o < crush.get_max_devices(); o++) {
if (device_weight.count(o)) {
weight.push_back(device_weight[o]);
} else if (crush.check_item_present(o)) {
weight.push_back(0x10000);
} else {
weight.push_back(0);
}
}
if (output_utilization_all)
err << "devices weights (hex): " << hex << weight << dec << std::endl;
// make adjustments
adjust_weights(weight);
int num_devices_active = 0;
for (vector<__u32>::iterator p = weight.begin(); p != weight.end(); ++p)
if (*p > 0)
num_devices_active++;
if (output_choose_tries)
crush.start_choose_profile();
for (int r = min_rule; r < crush.get_max_rules() && r <= max_rule; r++) {
if (!crush.rule_exists(r)) {
if (output_statistics)
err << "rule " << r << " dne" << std::endl;
continue;
}
if (ruleset >= 0 &&
crush.get_rule_mask_ruleset(r) != ruleset) {
continue;
}
int minr = min_rep, maxr = max_rep;
if (min_rep < 0 || max_rep < 0) {
minr = crush.get_rule_mask_min_size(r);
maxr = crush.get_rule_mask_max_size(r);
}
if (output_statistics)
err << "rule " << r << " (" << crush.get_rule_name(r)
<< "), x = " << min_x << ".." << max_x
<< ", numrep = " << minr << ".." << maxr
<< std::endl;
for (int nr = minr; nr <= maxr; nr++) {
vector<int> per(crush.get_max_devices());
map<int,int> sizes;
int num_objects = ((max_x - min_x) + 1);
float num_devices = (float) per.size(); // get the total number of devices, better to cast as a float here
// create a structure to hold data for post-processing
tester_data_set tester_data;
vector<int> vector_data_buffer;
vector<float> vector_data_buffer_f;
// create a map to hold batch-level placement information
map<int, vector<int> > batch_per;
int objects_per_batch = num_objects / num_batches;
int batch_min = min_x;
int batch_max = min_x + objects_per_batch - 1;
// get the total weight of the system
int total_weight = 0;
for (unsigned i = 0; i < per.size(); i++)
total_weight += weight[i];
if (total_weight == 0)
continue;
// compute the expected number of objects stored per device in the absence of weighting
float expected_objects = min(nr, get_maximum_affected_by_rule(r)) * num_objects;
// compute each device's proportional weight
vector<float> proportional_weights( per.size() );
for (unsigned i = 0; i < per.size(); i++)
proportional_weights[i] = (float) weight[i] / (float) total_weight;
if (output_data_file) {
// stage the absolute weight information for post-processing
for (unsigned i = 0; i < per.size(); i++) {
tester_data.absolute_weights[i] = (float) weight[i] / (float)0x10000;
}
// stage the proportional weight information for post-processing
for (unsigned i = 0; i < per.size(); i++) {
if (proportional_weights[i] > 0 )
tester_data.proportional_weights[i] = proportional_weights[i];
tester_data.proportional_weights_all[i] = proportional_weights[i];
}
}
// compute the expected number of objects stored per device when a device's weight is considered
vector<float> num_objects_expected(num_devices);
for (unsigned i = 0; i < num_devices; i++)
num_objects_expected[i] = (proportional_weights[i]*expected_objects);
for (int current_batch = 0; current_batch < num_batches; current_batch++) {
if (current_batch == (num_batches - 1)) {
batch_max = max_x;
objects_per_batch = (batch_max - batch_min + 1);
}
float batch_expected_objects = min(nr, get_maximum_affected_by_rule(r)) * objects_per_batch;
vector<float> batch_num_objects_expected( per.size() );
for (unsigned i = 0; i < per.size() ; i++)
batch_num_objects_expected[i] = (proportional_weights[i]*batch_expected_objects);
// create a vector to hold placement results temporarily
vector<int> temporary_per ( per.size() );
for (int x = batch_min; x <= batch_max; x++) {
// create a vector to hold the results of a CRUSH placement or RNG simulation
vector<int> out;
if (use_crush) {
if (output_mappings)
err << "CRUSH"; // prepend CRUSH to placement output
crush.do_rule(r, x, out, nr, weight);
} else {
if (output_mappings)
err << "RNG"; // prepend RNG to placement output to denote simulation
// test our new monte carlo placement generator
random_placement(r, out, nr, weight);
}
if (output_mappings)
err << " rule " << r << " x " << x << " " << out << std::endl;
if (output_data_file)
write_integer_indexed_vector_data_string(tester_data.placement_information, x, out);
bool has_item_none = false;
for (unsigned i = 0; i < out.size(); i++) {
if (out[i] != CRUSH_ITEM_NONE) {
per[out[i]]++;
temporary_per[out[i]]++;
} else {
has_item_none = true;
}
}
batch_per[current_batch] = temporary_per;
sizes[out.size()]++;
if (output_bad_mappings &&
(out.size() != (unsigned)nr ||
has_item_none)) {
err << "bad mapping rule " << r << " x " << x << " num_rep " << nr << " result " << out << std::endl;
}
}
batch_min = batch_max + 1;
batch_max = batch_min + objects_per_batch - 1;
}
for (unsigned i = 0; i < per.size(); i++)
if (output_utilization && !output_statistics)
err << " device " << i
<< ":\t" << per[i] << std::endl;
for (map<int,int>::iterator p = sizes.begin(); p != sizes.end(); ++p)
if (output_statistics)
err << "rule " << r << " (" << crush.get_rule_name(r) << ") num_rep " << nr
<< " result size == " << p->first << ":\t"
<< p->second << "/" << (max_x-min_x+1) << std::endl;
if (output_statistics)
for (unsigned i = 0; i < per.size(); i++) {
if (output_utilization) {
if (num_objects_expected[i] > 0 && per[i] > 0) {
err << " device " << i << ":\t"
<< "\t" << " stored " << ": " << per[i]
<< "\t" << " expected " << ": " << num_objects_expected[i]
<< std::endl;
}
} else if (output_utilization_all) {
err << " device " << i << ":\t"
<< "\t" << " stored " << ": " << per[i]
<< "\t" << " expected " << ": " << num_objects_expected[i]
<< std::endl;
}
}
if (output_data_file)
for (unsigned i = 0; i < per.size(); i++) {
vector_data_buffer_f.clear();
vector_data_buffer_f.push_back( (float) per[i]);
vector_data_buffer_f.push_back( (float) num_objects_expected[i]);
write_integer_indexed_vector_data_string(tester_data.device_utilization_all, i, vector_data_buffer_f);
if (num_objects_expected[i] > 0 && per[i] > 0)
write_integer_indexed_vector_data_string(tester_data.device_utilization, i, vector_data_buffer_f);
}
if (output_data_file && num_batches > 1) {
// stage batch utilization information for post-processing
for (int i = 0; i < num_batches; i++) {
write_integer_indexed_vector_data_string(tester_data.batch_device_utilization_all, i, batch_per[i]);
write_integer_indexed_vector_data_string(tester_data.batch_device_expected_utilization_all, i, batch_per[i]);
}
}
string rule_tag = crush.get_rule_name(r);
if (output_csv)
write_data_set_to_csv(output_data_file_name+rule_tag,tester_data);
}
}
if (output_choose_tries) {
__u32 *v = 0;
int n = crush.get_choose_profile(&v);
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
cout.setf(std::ios::right);
cout << std::setw(2)
<< i << ": " << std::setw(9) << v[i];
cout.unsetf(std::ios::right);
cout << std::endl;
}
crush.stop_choose_profile();
}
return 0;
}1) 判断min_rule,max_rule,min_x,max_x等的值
这里我们在传参时没有设置min_rule,max_rule,因此这里min_rule被设置为0,max_rule被设置为1(crush.get_max_rules() -1);而min_x与max_x则直接为我们传入的参数值0,10.
2) 初始化osd weights
// initial osd weights
vector<__u32> weight;
/*
* note device weight is set by crushtool
* (likely due to a given a command line option)
*/
for (int o = 0; o < crush.get_max_devices(); o++) {
if (device_weight.count(o)) {
weight.push_back(device_weight[o]);
} else if (crush.check_item_present(o)) {
weight.push_back(0x10000);
} else {
weight.push_back(0);
}
}
if (output_utilization_all)
err << "devices weights (hex): " << hex << weight << dec << std::endl;
// make adjustments
adjust_weights(weight);首先遍历所有的device,这里有osd.0~osd.8共9个OSD。如果该设备权重通过crushtool命令行参数--weight设置过了,则采用参数传递进的权重。否则,检查该device是否在bucket中有用到,如果用到则将该device权重标志为0x10000,没有被使用则将该设备权重置为0.
再接着调用adjust_weights(weight)调整设备权重,在函数中需要mark_down_device_ratio > 0,因此这里并不会被执行。
3) 计算当前active devices
int num_devices_active = 0;
for (vector<__u32>::iterator p = weight.begin(); p != weight.end(); ++p)
if (*p > 0)
num_devices_active++;这里所有9个device均为active
4) 遍历所有的rule
for (int r = min_rule; r < crush.get_max_rules() && r <= max_rule; r++) {
//1: 检测指定的rule是否存在,以及是否是我们使用crushtool时指定的ruleset 5
//2: 获得表示副本数的minr,maxr。 由于我们在参数中传入了--num-rep=3,因此这里minr=maxr=3
for (int nr = minr; nr <= maxr; nr++) {
per.size() = 9;
num_objects = 11;
num_devices = 9;
num_batches = 1;
objects_per_batch = 11;
batch_min = min_x;
batch_max = min_x + objects_per_batch - 1;
//3: 计算total_weight(9*0x10000)
//4: get_maximum_affected_by_rule(r),这里采用ruleset 5时,结果为1。因此expected_objects = 11
//5: 计算每一个device的权重占比,这里为均为1/9
//6: 根据权重占比计算平均每个device所存储的对象数
for (unsigned i = 0; i < num_devices; i++)
num_objects_expected[i] = (proportional_weights[i]*expected_objects);
//7: 遍历当前所有的batches
for (int current_batch = 0; current_batch < num_batches; current_batch++) {
//nr为当前的副本数,这里取值为3;object_per_batch取值为11,因为我们只有一个batch
float batch_expected_objects = min(nr, get_maximum_affected_by_rule(r)) * objects_per_batch;
//对当前batch内的所有PG做映射,这里batch_min为0,batch_max为10,及映射PG0~PG10
for (int x = batch_min; x <= batch_max; x++) {
if (use_crush) {
if (output_mappings)
err << "CRUSH"; // prepend CRUSH to placement output
//8: do_rule是关键的PG映射函数。 第一个参数当前所采用的rule;第二个参数为所映射的PG;第三个参数为映射结果;
// 第四个参数为当前的副本数; 第五个参数为各device的权重列表
crush.do_rule(r, x, out, nr, weight);
} else {
if (output_mappings)
err << "RNG"; // prepend RNG to placement output to denote simulation
// test our new monte carlo placement generator
random_placement(r, out, nr, weight);
}
}
}
//9:
}
}从上面的分析,其实就是找到对应的rule,然后在该rule下,针对每一个rep数,对PG进行crushmap映射。
while(rules)
{
for(rep in rep_min:rep_max)
{
do_rule(rule,pg_id,out_vec,rep,device_weight_vec);
}
}
在讨论完了crushtool映射PG的一个整体流程之后,我们接下来就会详细讨论具体的do_rule算法。由于这一部分较为复杂,我们将其作为另外单独一章来讲解。

