crushmap算法详解-3
本文接上篇《crushmap详解-2》,结合ceph源代码及其他参考资料来详尽的探讨具体的crush算法。为了参看的方便,下面我们继续列出当前的crushmap:
[root@localhost ceph-test]# cat crushmap.txt
# begin crush map
tunable choose_local_tries 0
tunable choose_local_fallback_tries 0
tunable choose_total_tries 50
tunable chooseleaf_descend_once 1
tunable straw_calc_version 1
# devices
device 0 osd.0
device 1 osd.1
device 2 osd.2
device 3 osd.3
device 4 osd.4
device 5 osd.5
device 6 osd.6
device 7 osd.7
device 8 osd.8
# types
type 0 osd
type 1 host
type 2 chassis
type 3 rack
type 4 row
type 5 pdu
type 6 pod
type 7 room
type 8 datacenter
type 9 region
type 10 root
type 11 osd-domain
type 12 host-domain
type 13 replica-domain
type 14 failure-domain
# buckets
host node7-1 {
id -2 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 0.450
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item osd.0 weight 0.150
item osd.1 weight 0.150
item osd.2 weight 0.150
}
rack rack-01 {
id -3 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 0.450
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item node7-1 weight 0.450
}
host node7-2 {
id -4 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 0.450
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item osd.3 weight 0.150
item osd.4 weight 0.150
item osd.5 weight 0.150
}
rack rack-02 {
id -5 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 0.450
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item node7-2 weight 0.450
}
host node7-3 {
id -6 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 0.450
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item osd.6 weight 0.150
item osd.7 weight 0.150
item osd.8 weight 0.150
}
rack rack-03 {
id -7 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 0.450
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item node7-3 weight 0.450
}
root default {
id -1 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 1.350
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item rack-01 weight 0.450
item rack-02 weight 0.450
item rack-03 weight 0.450
}
host-domain host-group-0-rack-01 {
id -8 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 0.450
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item node7-1 weight 0.450
}
host-domain host-group-0-rack-02 {
id -11 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 0.450
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item node7-2 weight 0.450
}
host-domain host-group-0-rack-03 {
id -12 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 0.450
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item node7-3 weight 0.450
}
replica-domain replica-0 {
id -9 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 1.350
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item host-group-0-rack-01 weight 0.450
item host-group-0-rack-02 weight 0.450
item host-group-0-rack-03 weight 0.450
}
failure-domain sata-00 {
id -10 # do not change unnecessarily
# weight 1.350
alg straw
hash 0 # rjenkins1
item replica-0 weight 1.350
}
# rules
rule replicated_ruleset {
ruleset 0
type replicated
min_size 1
max_size 10
step take default
step choose firstn 0 type osd
step emit
}
rule replicated_rule-5 {
ruleset 5
type replicated
min_size 1
max_size 10
step take sata-00
step choose firstn 1 type replica-domain
step chooseleaf firstn 0 type host-domain
step emit
}
# end crush map
1. crushmap算法
crushmap是由devices与buckets组成的,都关联有一个数字标识符(numerical identifiers)和权重(weight)。其中buckets可以包含任何数量的devices或者其他buckets,这样就可以形成一个层次结构,注意devices只能处于最下层,即叶子节点。
下面给出crushmap算法的伪代码:

参看上面伪代码,CRUSH函数的输入x是一个整数,通常可以是一个object name或者其他标识符(当前ceph,一般是一个pg号)。take(a)操作用于从存储层次结构(storage hierarchy)中选择一个item(通常是一个bucket)并将其存放到vector i中,以作为后续操作的输入; select(n,t)操作会遍历vector i中的每一个元素,并从以该节点为根的子树中选择类型为t的n个不同的item。

3.1.1) crush映射示例
示例对应的crush层次结构如下:
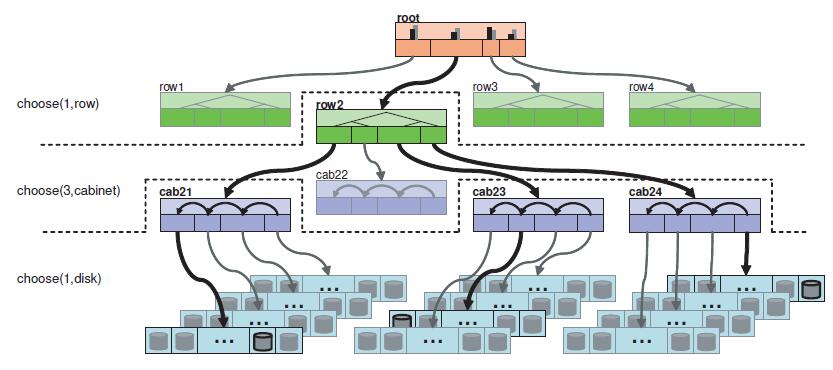
crush对应的rule如下:

上图表格中定义的rule以crush层次结构图的root作为起点。首先使用select(1,row)来选择1个类型为row的bucket(这里选择的是row2); 接下来的select(3,cabinet)从row2中选择类型为cabinet的3个不同的item(这里选择的是cab21、cab23、cab24); 最后一个select(1,disk)会遍历前面所选中的三个cabinet,并分别从中选出一个类型为disk的item。
3.2.1) Collisions, Failure,and Overload
select(n,t)操作可能会遍历存储层次结构(storage hierarchy)的多层,以找出类型为t的n个不同的Item。在这一过程中,CRUSH可能会拒绝并使用一个修正的输入r'来重新选择items,这主要有如下三个原因:
-
当前选中的Item已经处于选中集合(即产生了
冲突) -
某一个device当前已经处于failed状态
-
某一个device当前已经处于overload状态
对于在crushmap中标记为Failed以及Overload状态的device,热门仍然会被保留在层次结构(hierarchy)中,以避免不必要的数据移动。CRUSH会选择性的拒绝一部分数据存放到处于Overload状态的设备上。对于Failed以及Overload状态的设备,CRUSH都按统一的方式进行处理:从头开始重新递归的分配items到整个存储集群(参看Algorithm 1的第11行)。而对于collision这一情形,另外一个值r'会被使用以尝试在buckets内层做一个本地搜索,这样可以避免切换bucket带来的更大冲突的可能(即不跳到外层来切换bucket,参看Algorithm 1的第14行)
3.2.2) Replica Ranks
在奇偶纠删编码模式(Parity and erasure coding schemes)下数据的存放要求与单纯的多副本相比有细微的不同。在主拷贝副本模式下(primary copy replication schemes),假如有一个副本失败,那么另外一个副本可以成为新的primary。在这种情形下,CRUSH可以使用first n通过r' = r + f来重新选择合适的targets,在这里f是当前select(n,t)尝试映射存储地址失败的次数(参看Algorithm 1的第16行)。
而在奇偶纠删编码模式下,存储设备的rank或者position在CRUSH输出中是很关键的,因为每一个target存放对象数据(data object)的不同比特位。特别是,假如某一个存储设备失效(failed),其应该由CRUSH中的R'来进行替换,这样列表中其他的设备就可以保持相同的rank(请参看下图):
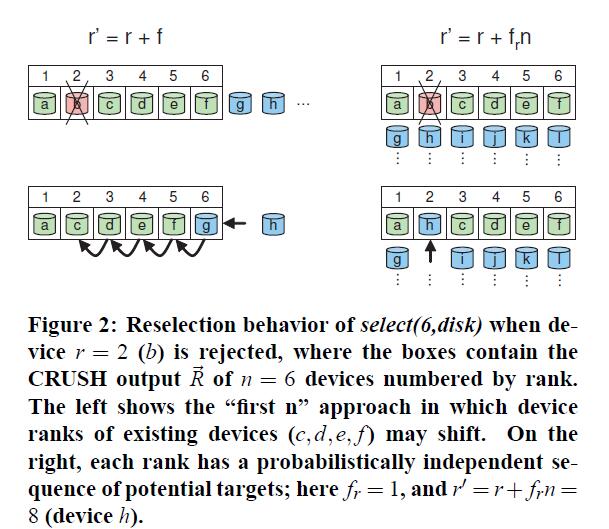
在这种情况下,CRUSH会使用r'=r + fr *n来重新选择一个target,这里fr是在r上失败的次数。
与其他已存在的hash分布函数相比,CRUSH对于那些失效的存储设备并没有一些特殊的处理,CRUSH只是隐式的假定使用first n来跳过那些失效的设备,使他们不出现在CRUSH映射结果中。
2. CRUSH算法源代码解析
在源代码分析过程中,我们可以通过执行如下命令来具体了解程序的执行过程:
/root/ceph-src/ceph/src/crushtool --test -i test_crushmap.bin --show-mappings --ruleset 5 --num-rep=3 --min_x=0 --max_x=10接着上一篇《crushmap详解-2》,函数调用到do_rule:

上面do_rule()函数使用指定的crush及rule规则将输入x映射到OSD设备上(这里rule为1,maxout为3,weight值均为65536)。
下面我们来分析crush_do_rule:
/**
* crush_do_rule - calculate a mapping with the given input and rule
* @map: the crush_map
* @ruleno: the rule id
* @x: hash input
* @result: pointer to result vector
* @result_max: maximum result size
* @weight: weight vector (for map leaves)
* @weight_max: size of weight vector
* @scratch: scratch vector for private use; must be >= 3 * result_max
*/
int crush_do_rule(const struct crush_map *map,
int ruleno, int x, int *result, int result_max,
const __u32 *weight, int weight_max,
int *scratch)
{
int result_len;
int *a = scratch;
int *b = scratch + result_max;
int *c = scratch + result_max*2;
int recurse_to_leaf;
int *w;
int wsize = 0;
int *o;
int osize;
int *tmp;
struct crush_rule *rule;
__u32 step;
int i, j;
int numrep;
int out_size;
/*
* the original choose_total_tries value was off by one (it
* counted "retries" and not "tries"). add one.
*/
int choose_tries = map->choose_total_tries + 1;
int choose_leaf_tries = 0;
/*
* the local tries values were counted as "retries", though,
* and need no adjustment
*/
int choose_local_retries = map->choose_local_tries;
int choose_local_fallback_retries = map->choose_local_fallback_tries;
int vary_r = map->chooseleaf_vary_r;
if ((__u32)ruleno >= map->max_rules) {
dprintk(" bad ruleno %d\n", ruleno);
return 0;
}
rule = map->rules[ruleno];
result_len = 0;
w = a;
o = b;
for (step = 0; step < rule->len; step++) {
int firstn = 0;
struct crush_rule_step *curstep = &rule->steps[step];
switch (curstep->op) {
case CRUSH_RULE_TAKE:
if ((curstep->arg1 >= 0 &&
curstep->arg1 < map->max_devices) ||
(-1-curstep->arg1 >= 0 &&
-1-curstep->arg1 < map->max_buckets &&
map->buckets[-1-curstep->arg1])) {
w[0] = curstep->arg1;
wsize = 1;
} else {
dprintk(" bad take value %d\n", curstep->arg1);
}
break;
case CRUSH_RULE_SET_CHOOSE_TRIES:
if (curstep->arg1 > 0)
choose_tries = curstep->arg1;
break;
case CRUSH_RULE_SET_CHOOSELEAF_TRIES:
if (curstep->arg1 > 0)
choose_leaf_tries = curstep->arg1;
break;
case CRUSH_RULE_SET_CHOOSE_LOCAL_TRIES:
if (curstep->arg1 >= 0)
choose_local_retries = curstep->arg1;
break;
case CRUSH_RULE_SET_CHOOSE_LOCAL_FALLBACK_TRIES:
if (curstep->arg1 >= 0)
choose_local_fallback_retries = curstep->arg1;
break;
case CRUSH_RULE_SET_CHOOSELEAF_VARY_R:
if (curstep->arg1 >= 0)
vary_r = curstep->arg1;
break;
case CRUSH_RULE_CHOOSELEAF_FIRSTN:
case CRUSH_RULE_CHOOSE_FIRSTN:
firstn = 1;
/* fall through */
case CRUSH_RULE_CHOOSELEAF_INDEP:
case CRUSH_RULE_CHOOSE_INDEP:
if (wsize == 0)
break;
recurse_to_leaf =
curstep->op ==
CRUSH_RULE_CHOOSELEAF_FIRSTN ||
curstep->op ==
CRUSH_RULE_CHOOSELEAF_INDEP;
/* reset output */
osize = 0;
for (i = 0; i < wsize; i++) {
int bno;
/*
* see CRUSH_N, CRUSH_N_MINUS macros.
* basically, numrep <= 0 means relative to
* the provided result_max
*/
numrep = curstep->arg1;
if (numrep <= 0) {
numrep += result_max;
if (numrep <= 0)
continue;
}
j = 0;
/* make sure bucket id is valid */
bno = -1 - w[i];
if (bno < 0 || bno >= map->max_buckets) {
// w[i] is probably CRUSH_ITEM_NONE
dprintk(" bad w[i] %d\n", w[i]);
continue;
}
if (firstn) {
int recurse_tries;
if (choose_leaf_tries)
recurse_tries =
choose_leaf_tries;
else if (map->chooseleaf_descend_once)
recurse_tries = 1;
else
recurse_tries = choose_tries;
osize += crush_choose_firstn(
map,
map->buckets[bno],
weight, weight_max,
x, numrep,
curstep->arg2,
o+osize, j,
result_max-osize,
choose_tries,
recurse_tries,
choose_local_retries,
choose_local_fallback_retries,
recurse_to_leaf,
vary_r,
c+osize,
0);
} else {
out_size = ((numrep < (result_max-osize)) ?
numrep : (result_max-osize));
crush_choose_indep(
map,
map->buckets[bno],
weight, weight_max,
x, out_size, numrep,
curstep->arg2,
o+osize, j,
choose_tries,
choose_leaf_tries ?
choose_leaf_tries : 1,
recurse_to_leaf,
c+osize,
0);
osize += out_size;
}
}
if (recurse_to_leaf)
/* copy final _leaf_ values to output set */
memcpy(o, c, osize*sizeof(*o));
/* swap o and w arrays */
tmp = o;
o = w;
w = tmp;
wsize = osize;
break;
case CRUSH_RULE_EMIT:
for (i = 0; i < wsize && result_len < result_max; i++) {
result[result_len] = w[i];
result_len++;
}
wsize = 0;
break;
default:
dprintk(" unknown op %d at step %d\n",
curstep->op, step);
break;
}
}
return result_len;
}该函数接受8个参数:
- map: 当前所采用的crushmap
- ruleno: 当前所使用的规则编号
- x:hash input,即当前所要映射的对象的hash值
- result: 保存输出结果的的数组起始位置
- result_max: 保存输出结果的数组的大小
- weight: 权重向量(用于映射叶子)
- weight_max: 权重向量中元素的个数
- scratch: 辅助空间(内部使用,其大小应确保为>=3*result_max)
2.1 相关变量初始化
根据我们前面的配置(如下tries均为retries含义,在使用时应注意):
# begin crush map tunable choose_local_tries 0 tunable choose_local_fallback_tries 0 tunable choose_total_tries 50 tunable chooseleaf_descend_once 1 tunable straw_calc_version 1
因此,这里choose_tries为51,choose_leaf_tries为0,choose_local_retries为0,choose_local_fallback_retries为0,vary_r为0。 我们这里使用的ruleset 5,因此rule->len为4。
2.2 crush映射步骤
参看下面的映射规则:
rule replicated_rule-5 {
ruleset 5
type replicated
min_size 1
max_size 10
step take sata-00
step choose firstn 1 type replica-domain
step chooseleaf firstn 0 type host-domain
step emit
}根据前面《crushmap详解-1》我们得到如下:
key::rule:rules:rule_id[1]="1" key::rule:rules:rule_name[1]="replicated_rule-5" key::rule:rules:ruleset[1]="5" key::rule:rules:type[1]="1" key::rule:rules:min_size[1]="1" key::rule:rules:max_size[1]="10" key::step:steps:rule:rules:op[3]="take" key::step:steps:rule:rules:item[1]="-10" key::step:steps:rule:rules:item_name[1]="sata-00" key::step:steps:rule:rules:op[4]="choose_firstn" key::step:steps:rule:rules:num[1]="1" key::step:steps:rule:rules:type[1]="replica-domain" key::step:steps:rule:rules:op[5]="chooseleaf_firstn" key::step:steps:rule:rules:num[2]="0" key::step:steps:rule:rules:type[2]="host-domain" key::step:steps:rule:rules:op[6]="emit"
上面每一个step的输出都作为下一个step的输入(参看上面伪代码37行)。
1) CRUSH_RULE_TAKE
首先执行的是CRUSH_RULE_TAKE步骤,因为sata-00是一个bucket,而不是单个的device,因此这里curstep->arg1应小于0。此时有:
w[0] = -10; wsize = 1;
2) CRUSH_RULE_CHOOSE_FIRSTN
printf("\n(Before)wsize:%d bno:%d x:%d numrep:%d curstep->arg1:%d curstep->arg2:%d osize:%d recurse_to_leaf:%d\n",
wsize, // 1
bno, // 9
x, // hash input
numrep, // 1
curstep->arg1, // 1
curstep->arg2, // 13
osize, // 0
recurse_to_leaf); // 0
osize += crush_choose_firstn(
map,
map->buckets[bno],
weight, weight_max,
x, numrep,
curstep->arg2,
o+osize, j,
result_max-osize,
choose_tries,
recurse_tries,
choose_local_retries,
choose_local_fallback_retries,
recurse_to_leaf,
vary_r,
c+osize,
0);
printf("(After)osize:%d\n",osize); // 1如上所示,经过上一步step take sata-00之后,wsize为1;bno为上一步step take sata-00所选中的bucket编号9(-1+10 = 9):
key::bucket:buckets:id[9]="-10" key::bucket:buckets:name[9]="sata-00" key::bucket:buckets:type_id[9]="14" key::bucket:buckets:type_name[9]="failure-domain" key::bucket:buckets:weight[9]="88473" key::bucket:buckets:alg[9]="straw" key::bucket:buckets:hash[9]="rjenkins1" key::item:items:bucket:buckets:id[19]="-9" key::item:items:bucket:buckets:weight[19]="88473" key::item:items:bucket:buckets:pos[19]="0"
numrep为当前step所指定的副本数1; curstep->arg1同numrep为副本数1;curstep->arg2为replica-domain,因此值为13; osize 为0;recurse_to_leaf为0,表示不递归叶子节点。 (After)osize为1.
针对上面的numrep,有如下解释:
/*
* see CRUSH_N, CRUSH_N_MINUS macros.
* basically, numrep <= 0 means relative to
* the provided result_max
*/3) CRUSH_RULE_CHOOSELEAF_FIRSTN
printf("\n(Before)wsize:%d bno:%d x:%d numrep:%d curstep->arg1:%d curstep->arg2:%d osize:%d recurse_to_leaf:%d\n",
wsize, // 1
bno, // 8
x, // hash input
numrep, // 3
curstep->arg1, // 0
curstep->arg2, // 12
osize, // 0
recurse_to_leaf); // 1
osize += crush_choose_firstn(
map,
map->buckets[bno],
weight, weight_max,
x, numrep,
curstep->arg2,
o+osize, j,
result_max-osize,
choose_tries,
recurse_tries,
choose_local_retries,
choose_local_fallback_retries,
recurse_to_leaf,
vary_r,
c+osize,
0);
printf("(After)osize:%d\n",osize); //3
如上所示,经过上一步step choose firstn 1 type replica-domain之后,wsize为1;bno为上一步step choose firstn 1 type replica-domain之后所选中的replica-0; numrep值为3,表示副本数; curstep->arg1为0;curstep->arg2为host-domain,因此值为12;osize值为0;recurse_to_leaf值为1,表示需要递归叶子节点。(After)osize为3.
4) CRUSH_RULE_EMIT
将结果存放到result中:
for (i = 0; i < wsize && result_len < result_max; i++)
{
result[result_len] = w[i];
result_len++;
}
wsize = 0;说明
从上面我们可以看到,是通过:
step choose firstn 1 type replica-domain step chooseleaf firstn 0 type host-domain
使我们最后达到的副本数为3。也即从sata-00下选择到1个replica-domain,然后再从这1个replica-domain下选择3个host-domain,则最后刚好达到3个副本。我们再来看另外一个规则:
rule replicated_ruleset {
ruleset 0
type replicated
min_size 1
max_size 10
step take default
step choose firstn 0 type osd
step emit
}
此规则直接在default下选择osd。因为可以直接选择到osd,因此可以不用递归,否则最后一步一般都要进行递归操作。此处0表示副本数为result_max,即为3。
3 crush_choose_firstn()代码分析
上面我们在进行CRUSHMAP映射时,调用到了crush_choose_firstn()函数,该函数较为复杂,我们下边来分析该函数:
/**
* crush_choose_firstn - choose numrep distinct items of given type
* @map: the crush_map
* @bucket: the bucket we are choose an item from
* @x: crush input value
* @numrep: the number of items to choose
* @type: the type of item to choose
* @out: pointer to output vector
* @outpos: our position in that vector
* @out_size: size of the out vector
* @tries: number of attempts to make
* @recurse_tries: number of attempts to have recursive chooseleaf make
* @local_retries: localized retries
* @local_fallback_retries: localized fallback retries
* @recurse_to_leaf: true if we want one device under each item of given type (chooseleaf instead of choose)
* @vary_r: pass r to recursive calls
* @out2: second output vector for leaf items (if @recurse_to_leaf)
* @parent_r: r value passed from the parent
*/
static int crush_choose_firstn(const struct crush_map *map,
struct crush_bucket *bucket,
const __u32 *weight, int weight_max,
int x, int numrep, int type,
int *out, int outpos,
int out_size,
unsigned int tries,
unsigned int recurse_tries,
unsigned int local_retries,
unsigned int local_fallback_retries,
int recurse_to_leaf,
unsigned int vary_r,
int *out2,
int parent_r)
{
int rep;
unsigned int ftotal, flocal;
int retry_descent, retry_bucket, skip_rep;
struct crush_bucket *in = bucket;
int r;
int i;
int item = 0;
int itemtype;
int collide, reject;
int count = out_size;
dprintk("CHOOSE%s bucket %d x %d outpos %d numrep %d tries %d recurse_tries %d local_retries %d local_fallback_retries %d parent_r %d\n",
recurse_to_leaf ? "_LEAF" : "",
bucket->id, x, outpos, numrep,
tries, recurse_tries, local_retries, local_fallback_retries,
parent_r);
for (rep = outpos; rep < numrep && count > 0 ; rep++) {
/* keep trying until we get a non-out, non-colliding item */
ftotal = 0;
skip_rep = 0;
do {
retry_descent = 0;
in = bucket; /* initial bucket */
/* choose through intervening buckets */
flocal = 0;
do {
collide = 0;
retry_bucket = 0;
r = rep + parent_r;
/* r' = r + f_total */
r += ftotal;
/* bucket choose */
if (in->size == 0) {
reject = 1;
goto reject;
}
if (local_fallback_retries > 0 &&
flocal >= (in->size>>1) &&
flocal > local_fallback_retries)
item = bucket_perm_choose(in, x, r);
else
item = crush_bucket_choose(in, x, r);
if (item >= map->max_devices) {
dprintk(" bad item %d\n", item);
skip_rep = 1;
break;
}
/* desired type? */
if (item < 0)
itemtype = map->buckets[-1-item]->type;
else
itemtype = 0;
dprintk(" item %d type %d\n", item, itemtype);
/* keep going? */
if (itemtype != type) {
if (item >= 0 ||
(-1-item) >= map->max_buckets) {
dprintk(" bad item type %d\n", type);
skip_rep = 1;
break;
}
in = map->buckets[-1-item];
retry_bucket = 1;
continue;
}
/* collision? */
for (i = 0; i < outpos; i++) {
if (out[i] == item) {
collide = 1;
break;
}
}
reject = 0;
if (!collide && recurse_to_leaf) {
if (item < 0) {
int sub_r;
if (vary_r)
sub_r = r >> (vary_r-1);
else
sub_r = 0;
if (crush_choose_firstn(map,
map->buckets[-1-item],
weight, weight_max,
x, outpos+1, 0,
out2, outpos, count,
recurse_tries, 0,
local_retries,
local_fallback_retries,
0,
vary_r,
NULL,
sub_r) <= outpos)
/* didn't get leaf */
reject = 1;
} else {
/* we already have a leaf! */
out2[outpos] = item;
}
}
if (!reject) {
/* out? */
if (itemtype == 0)
reject = is_out(map, weight,
weight_max,
item, x);
else
reject = 0;
}
reject:
if (reject || collide) {
ftotal++;
flocal++;
if (collide && flocal <= local_retries)
/* retry locally a few times */
retry_bucket = 1;
else if (local_fallback_retries > 0 &&
flocal <= in->size + local_fallback_retries)
/* exhaustive bucket search */
retry_bucket = 1;
else if (ftotal < tries)
/* then retry descent */
retry_descent = 1;
else
/* else give up */
skip_rep = 1;
dprintk(" reject %d collide %d "
"ftotal %u flocal %u\n",
reject, collide, ftotal,
flocal);
}
} while (retry_bucket);
} while (retry_descent);
if (skip_rep) {
dprintk("skip rep\n");
continue;
}
dprintk("CHOOSE got %d\n", item);
out[outpos] = item;
outpos++;
count--;
if (map->choose_tries && ftotal <= map->choose_total_tries)
map->choose_tries[ftotal]++;
}
dprintk("CHOOSE returns %d\n", outpos);
return outpos;
}该函数主要功能为:选择指定类型的numrep个不同的item。其接受18个参数:
- map: 当前所使用的crushmap
- bucket: 我们从当前
bucket中选择item - weight: 权重向量基址
- weight_max: 权重向量大小
- x: crush input value
- numrep: 指定要选择的item数量
- type: 要选择的item类型
- out: 输出向量基址
- outpos: 当前我们在输出向量out中的位置
- out_size: 当前输出向量的剩余空间
- tries: 尝试次数
- recurse_tries: 递归选择叶子时候的尝试次数
- local_retries: 本地重试(retry)次数
- local_fallback_retries: 本地fallback重试(retry)次数。 注:在local_retries耗尽时,如果仍未选择到item,则会尝试fallback retry, 此时可能会根据相关算法随机选择一个item。
- recurse_to_leaf: 假若我们需要在给定类型的item下选择一个device, 此时设置为true(表示选择叶子的意思)
- vary_r: 传递r给递归调用
- out2: 第二个输出向量基址,用于存放leaf items(当recurse_to_leaf为true时使用)
- parent_r: 由parent传递过来的r值
因为我们在上面CRUSH_RULE_CHOOSE_FIRSTN与CRUSH_RULE_CHOOSELEAF_FIRSTN中均调用到了该函数,因此下面我们也分成两个步骤来看函数crush_choose_firstn()的执行情况。
1) CRUSH_RULE_CHOOSE_FIRSTN
我们打开dprintk宏定义:
# define dprintk(args...) printf(args)我们可以看到有如下打印信息(第一次调用x为0时):
dprintk("CHOOSE%s bucket %d x %d outpos %d numrep %d tries %d recurse_tries %d local_retries %d local_fallback_retries %d parent_r %d vary_r %d type %d\n",
recurse_to_leaf ? "_LEAF" : "", // ""
bucket->id, // -10
x, // 0
outpos, // 0
numrep, // 1
tries, // 51
recurse_tries, // 1
local_retries, // 0
local_fallback_retries, // 0
parent_r, // 0
vary_r, // 0
type); // 13
查看我们前面的规则:
rule replicated_rule-5 {
ruleset 5
type replicated
min_size 1
max_size 10
step take sata-00
step choose firstn 1 type replica-domain
step chooseleaf firstn 0 type host-domain
step emit
}
本步我们要做的就是从sata-00这个bucket中选择1个类型为replica-domain的bucket。下面我们就来分析这个选择过程:
// Loop over n replicas
for (rep = outpos; rep < numrep && count > 0 ; rep++)
{
/* keep trying until we get a non-out, non-colliding item */
ftotal = 0; //flag to indicate total failures
skip_rep = 0; //flag to indicate whether we should skip the replica
do{
retry_descent = 0;
in = bucket;
do{
retry_bucket = 0;
//1: 选择相应的item
//2: 判断item类型是否为指定的类型
// item >= 0表示为osd设备 其type值为0
// item < 0表示为bucket, 其type值>0
if(typeof(item) != type)
{
//3: 没有找到指定类型bucket,进入下一级遍历
in = next_bucket(item);
retry_bucket = 1;
}
// 4: 判断当前有没有发生collision
// 5: 是否需要递归到叶子
// 6: 如果发生collision/failed/overloaded,调整相应的参数
if(collision || failed || overloaded)
{
ftotal++;
flocal++;
// 设置retry_bucket 或者 retry_descent
}
}while(retry_bucket);
}while(retry_descent);
//将选中的item增加到output中
count--;
}注意
这里之所以有retry_bucket与retry_descent的区别,是因为crush算法里面一般会拥有两种不同的选择bucket的算法。一般情况下,通过适当的调整参数重新retry_bucket就可以选中到想要的bucket;而如果出现异常情况,我们可能会需要进行retry_descent重新调整算法。
(2) CRUSH_RULE_CHOOSELEAF_FIRSTN
我们可以看到有如下打印信息(第一次调用x为0时),此处会进行叶子递归,这里我们打印出第一次调用:
dprintk("CHOOSE%s bucket %d x %d outpos %d numrep %d tries %d recurse_tries %d local_retries %d local_fallback_retries %d parent_r %d vary_r %d type %d\n",
recurse_to_leaf ? "_LEAF" : "", // "_LEAF"
bucket->id, // -9,即replica-domain
x, // 0
outpos, // 0
numrep, // 3
tries, // 51
recurse_tries, // 1
local_retries, // 0
local_fallback_retries, // 0
parent_r, // 0
vary_r, // 0
type); // 12
其他与CRUSH_RULE_CHOOSE_FIRSTN类似,这里不再赘述。
4. 总结
在ceph源代码实现的CRUSH算法,总体调用调用流程如下:
int crush_do_rule(const struct crush_map *map,
int ruleno, int x, int *result, int result_max,
const __u32 *weight, int weight_max,
int *scratch)
{
//1: process take
//2: process `choose` or `chooseleaf`, call function crush_choose_firstn()
for(previous_step_results)
{
crush_choose_firstn(...)
}
//3: process emit
}
static int crush_choose_firstn(const struct crush_map *map,
struct crush_bucket *bucket,
const __u32 *weight, int weight_max,
int x, int numrep, int type,
int *out, int outpos,
int out_size,
unsigned int tries,
unsigned int recurse_tries,
unsigned int local_retries,
unsigned int local_fallback_retries,
int recurse_to_leaf,
unsigned int vary_r,
int *out2,
int parent_r)
{
Loop over n replicas
{
do{
do{
// 1: choose bucket
// 2: process collision/failure/overloaded
}while(retry_bucket);
}while(retry_descent);
//3: 将上面选择的item结果存放到out中
}
}从上我们可以看到,与《CRUSH: Controlled, Scalable, Decentralized Placement of Replicated Data》一文中给出的CRUSH具有极高的相似性。

