ceph本地对象存储CollectionIndex
本节我们讲述一下Ceph本地对象存储中的CollectionIndex。
1. CollectionIndex
Collection的概念对应到本地文件系统中就是一个目录,用于存储一个PG里的所有的对象。
一个collection对应本地文件系统的一个目录,一个PG对应于一个Collection,该PG的所有对象都保存在这个目录里,定义在类coll_t中:
class coll_t {
enum type_t {
TYPE_META = 0,
TYPE_LEGACY_TEMP = 1, /* no longer used */
TYPE_PG = 2,
TYPE_PG_TEMP = 3,
};
type_t type; //类型: meta、pg、temp
spg_t pgid; //对应的pgid
uint64_t removal_seq; //这个字段不再使用,没有编码持久化存储
char _str_buff[spg_t::calc_name_buf_size];
char *_str; //缓存的字符串
};collection有三种不同的类型: TYPE_META类型表示这个PG里保存的是元数据(meta)相关的对象;TYPE_PG表示该collection保存的是PG相关的数据; TYPE_TEMP保存临时对象。
当一个PG的对象数量比较多时,就会在一个目录里保存大量的文件。对于底层文件系统来说,如果一个目录里保存大量文件,当达到一定的程度后,性能会急剧下降。那么就需要一个collection里对应多个层级的子目录来存储大量文件,从而提高性能。如下是一个真实环境下的osd目录:
# pwd /var/lib/ceph/osd/ceph-48/current # ls 180.f_head 189.112_head 189.26a_head 189.2c8_head 189.3ba_head 189.440_head 189.52b_head 189.637_head 189.701_head 189.79_head 189.b6_head 192.37_head 180.f_TEMP 189.112_TEMP 189.26a_TEMP 189.2c8_TEMP 189.3ba_TEMP 189.440_TEMP 189.52b_TEMP 189.637_TEMP 189.701_TEMP 189.79_TEMP 189.b6_TEMP 192.37_TEMP 181.e_head 189.11f_head 189.271_head 189.2e0_head 189.3ea_head 189.458_head 189.56a_head 189.64e_head 189.70b_head 189.7a3_head 189.f2_head 192.47_head 181.e_TEMP 189.11f_TEMP 189.271_TEMP 189.2e0_TEMP 189.3ea_TEMP 189.458_TEMP 189.56a_TEMP 189.64e_TEMP 189.70b_TEMP 189.7a3_TEMP 189.f2_TEMP 192.47_TEMP 184.10_head 189.122_head 189.295_head 189.302_head 189.3ef_head 189.465_head 189.58c_head 189.66d_head 189.735_head 189.7a6_head 190.2_head 192.5b_head 184.10_TEMP 189.122_TEMP 189.295_TEMP 189.302_TEMP 189.3ef_TEMP 189.465_TEMP 189.58c_TEMP 189.66d_TEMP 189.735_TEMP 189.7a6_TEMP 190.2_TEMP 192.5b_TEMP 184.4_head 189.147_head 189.2a5_head 189.306_head 189.3fa_head 189.46_head 189.594_head 189.682_head 189.75c_head 189.7c7_head 190.7_head 192.7b_head 184.4_TEMP 189.147_TEMP 189.2a5_TEMP 189.306_TEMP 189.3fa_TEMP 189.46_TEMP 189.594_TEMP 189.682_TEMP 189.75c_TEMP 189.7c7_TEMP 190.7_TEMP 192.7b_TEMP 187.3_head 189.188_head 189.2a7_head 189.345_head 189.3fc_head 189.497_head 189.5a3_head 189.69c_head 189.76_head 189.7ce_head 190.c_head 38.1a_head 187.3_TEMP 189.188_TEMP 189.2a7_TEMP 189.345_TEMP 189.3fc_TEMP 189.497_TEMP 189.5a3_TEMP 189.69c_TEMP 189.76_TEMP 189.7ce_TEMP 190.c_TEMP 38.1a_TEMP 187.8_head 189.21a_head 189.2ab_head 189.364_head 189.40d_head 189.49b_head 189.5d_head 189.6bb_head 189.772_head 189.7da_head 192.10_head 38.a_head 187.8_TEMP 189.21a_TEMP 189.2ab_TEMP 189.364_TEMP 189.40d_TEMP 189.49b_TEMP 189.5d_TEMP 189.6bb_TEMP 189.772_TEMP 189.7da_TEMP 192.10_TEMP 38.a_TEMP 188.2a_head 189.225_head 189.2bc_head 189.369_head 189.41b_head 189.4e9_head 189.606_head 189.6e6_head 189.773_head 189.92_head 192.1e_head commit_op_seq 188.2a_TEMP 189.225_TEMP 189.2bc_TEMP 189.369_TEMP 189.41b_TEMP 189.4e9_TEMP 189.606_TEMP 189.6e6_TEMP 189.773_TEMP 189.92_TEMP 192.1e_TEMP meta 189.0_head 189.236_head 189.2c0_head 189.3a3_head 189.426_head 189.4f6_head 189.60e_head 189.6e8_head 189.792_head 189.9d_head 192.23_head nosnap 189.0_TEMP 189.236_TEMP 189.2c0_TEMP 189.3a3_TEMP 189.426_TEMP 189.4f6_TEMP 189.60e_TEMP 189.6e8_TEMP 189.792_TEMP 189.9d_TEMP 192.23_TEMP omap 189.110_head 189.23a_head 189.2c1_head 189.3b9_head 189.43_head 189.4f9_head 189.62e_head 189.6f8_head 189.795_head 189.9e_head 192.2e_head 189.110_TEMP 189.23a_TEMP 189.2c1_TEMP 189.3b9_TEMP 189.43_TEMP 189.4f9_TEMP 189.62e_TEMP 189.6f8_TEMP 189.795_TEMP 189.9e_TEMP 192.2e_TEMP # cd 180.f_head/ && ls DIR_F # cd DIR_F/ && ls DIR_0 DIR_2 DIR_4 DIR_6 DIR_8 DIR_A DIR_C DIR_E
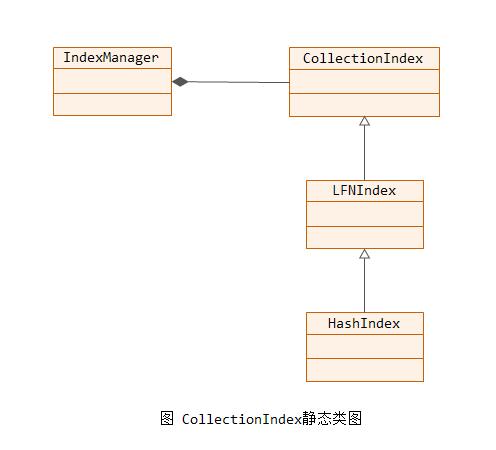
下图为CollectionIndex的静态类图。IndexManager类为管理CollectionIndex的实现。HashIndex实现了LFNIndex,LFNIndex实现了CollectionIndex接口。
1.1 CollectionIndex接口
CollectionIndex使一个Collection里的对象保存在多层子目录中。类CollectionIndex是对象在文件系统中多层目录存储的接口。
通过接口说明,就可以看到其提供的功能:
- 查找一个对象,返回对象对应文件的存储路径
virtual int lookup(
const ghobject_t &oid, ///< [in] Object to lookup
IndexedPath *path, ///< [out] Path to object
int *hardlink ///< [out] number of hard links of this object. *hardlink=0 mean object no-exist.
) = 0;- 根据对象的路径,修改相应路径的属性信息(对象创建后,可能会影响相应路径的属性)
virtual int created(
const ghobject_t &oid, ///< [in] Created object.
const char *path ///< [in] Path to created object.
) = 0;- 删除一个对象
virtual int unlink(
const ghobject_t &oid ///< [in] Object to remove
) = 0;- 分裂目录, 当上次目录里保存的文件或者子目录达到一定数量,就需要分裂成两个目录
virtual int split(
uint32_t match, //< [in] value to match
uint32_t bits, //< [in] bits to check
CollectionIndex* dest //< [in] destination index
) { assert(0); return 0; }- 根据对象的hash值,按序列出对象
virtual int collection_list_partial(
const ghobject_t &start, ///< [in] object at which to start
const ghobject_t &end, ///< [in] list only objects < end
bool sort_bitwise, ///< [in] use bitwise sort
int max_count, ///< [in] return at most max_count objects
vector<ghobject_t> *ls, ///< [out] Listed objects
ghobject_t *next ///< [out] Next object to list
) = 0;从上述接口介绍可知,CollectionIndex提供了对象到其对应文件保存的目录路径映射管理。
1.2 HashIndex
HashIndex是CollectionIndex的一个实现。HashIndex实现了用对象的Hash值作为对象存储的目录。
1. 对象保存目录方式
以对象的HASH值为基准,从低位到高位十六进制的字符保存。
string HashIndex::get_hash_str(uint32_t hash) {
char buf[MAX_HASH_LEVEL + 1];
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%.*X", MAX_HASH_LEVEL, hash);
string retval;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_HASH_LEVEL; ++i) {
retval.push_back(buf[MAX_HASH_LEVEL - 1 - i]);
}
return retval;
}
string HashIndex::get_path_str(const ghobject_t &oid) {
assert(!oid.is_max());
return get_hash_str(oid.hobj.get_hash());
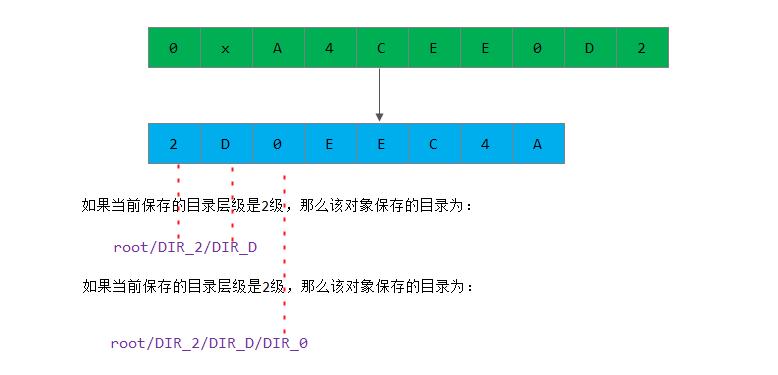
}从上面代码,假如当前一个Hash值为0xA4CEE0D2,那么返回的字符串就为2D0EEC4A。
现在假若有一个对象:
ghobject_t("object", CEPH_NO_SNAP, 0xA4CEE0D2);
其哈希值是0xA4CEE0D2,那么该对象的保存目录如下图所示:
2. 目录层级
如何确定当前保存目录的层级呢?何时创建一个新的子目录呢?当一个目录中的对象数目超过如下数值:
bool HashIndex::must_split(const subdir_info_s &info) {
return (info.hash_level < (unsigned)MAX_HASH_LEVEL &&
info.objs > ((unsigned)(abs(merge_threshold)) * 16 * split_multiplier));
}就重新创建一个子目录,原来的子目录要分裂为两个目录。其中:
merge_threshold由配置选项 g_ceph_context->_conf->filestore_merge_threshold 设置
split_multiplier由配置选项 g_ceph_context->_conf->filestore_split_multiplier 设置一个目录保存对象的统计信息保存在目录的扩展属性中,数据结构subdir_info_s定义了相关的属性:
struct subdir_info_s {
uint64_t objs; // 该目录中对象的数目
uint32_t subdirs; // 该目录中子目录的数目
uint32_t hash_level; // 子目录的hash层级数
}如下我们来看一个实际场景的例子:
# pwd /var/lib/ceph/osd/ceph-0/current # ls 37.d_head/ | wc -l 121 # getfattr -e hex -n user.cephos.phash.contents ./37.d_head/ # file: 37.d_head/ user.cephos.phash.contents=0x0179000000000000000000000000000000
从上面我们contents,我们计算出目录中国的对象数目为0x79==121。
1.3 LFNIndex
HashIndex继承了LFNIndex接口。LFNIndex是Long File Name Index的缩写。从名称就可以知道,LFNIndex用来处理如下情况: 当对象名太长,超过了本地文件系统支持的长度时,LFNIndex实现把超出的部分文件名保存到文件的扩展属性中。有可能保存到扩展属性的多个key-value存储对中。
关于LFNIndex,我们可以通过src/test/os/TestLFNIndex.cc相关单元测试来进一步了解该类的使用。
# ./unittest_lfnindex
[参看]

