OpenResty lua模块指令
本章我们介绍一下OpenResty Lua模块的指令,并对其中一些指令的用法进行说明。
1. lua指令
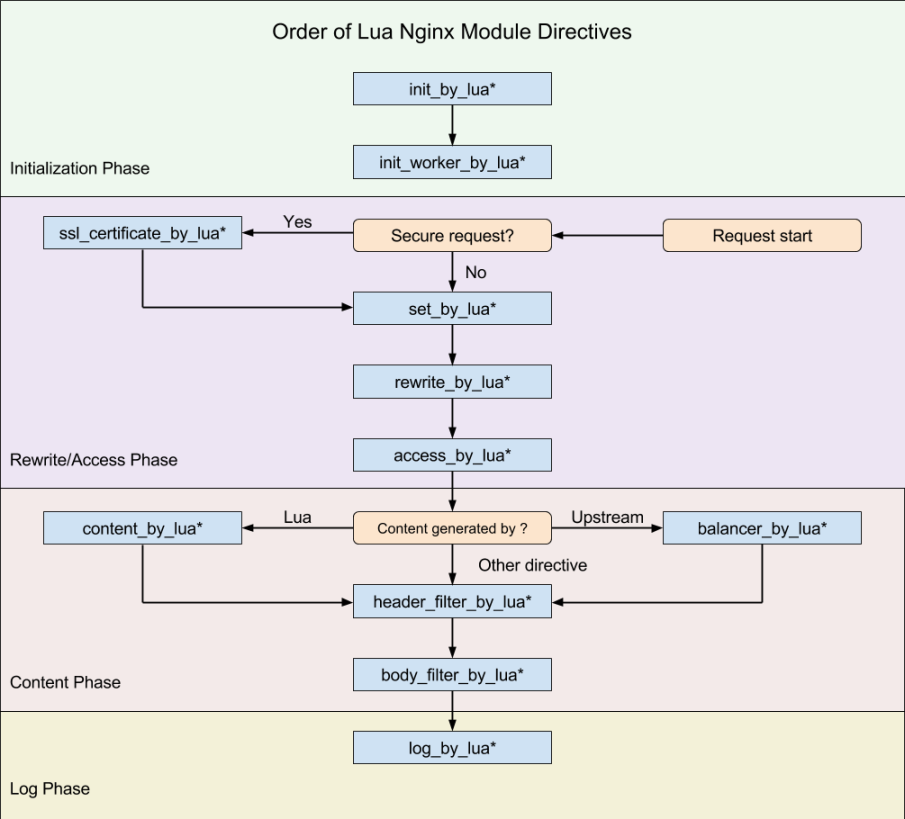
使用Lua来构建nginx脚本就是通过一条条指令来完成的,指令常用于指定 Lua 代码是什么时候执行的以及如何使用运行的结果。下图展示了指令执行的顺序:
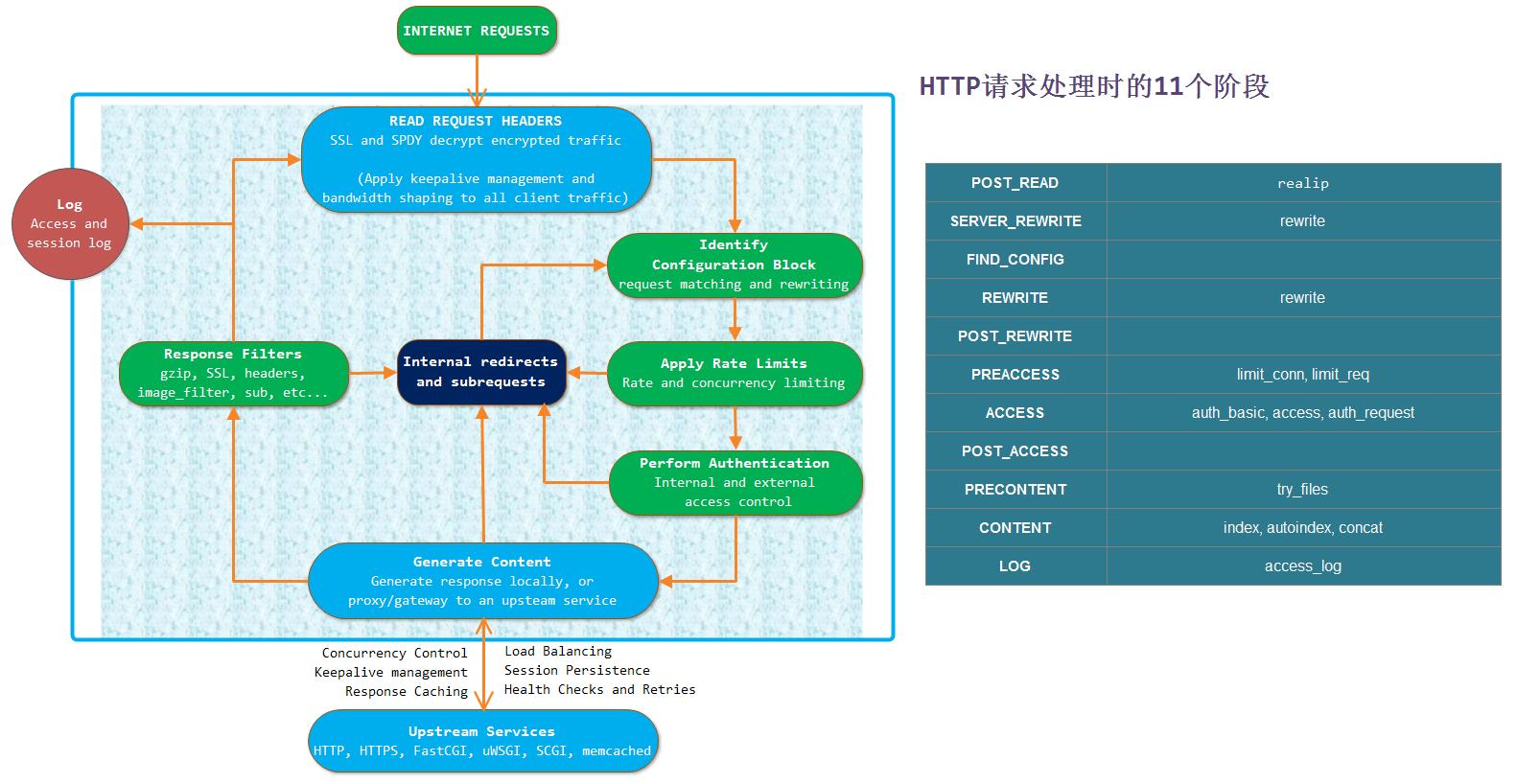
下面我们再给出Nginx http的11个处理阶段的图,以做比较:
如下我们列出nginx lua相关的一些指令:
lua_load_resty_core lua_capture_error_log lua_use_default_type lua_malloc_trim lua_code_cache lua_regex_cache_max_entries lua_regex_match_limit lua_package_path lua_package_cpath init_by_lua init_by_lua_block init_by_lua_file init_worker_by_lua init_worker_by_lua_block init_worker_by_lua_file set_by_lua set_by_lua_block set_by_lua_file content_by_lua content_by_lua_block content_by_lua_file rewrite_by_lua rewrite_by_lua_block rewrite_by_lua_file access_by_lua access_by_lua_block access_by_lua_file header_filter_by_lua header_filter_by_lua_block header_filter_by_lua_file body_filter_by_lua body_filter_by_lua_block body_filter_by_lua_file log_by_lua log_by_lua_block log_by_lua_file balancer_by_lua_block balancer_by_lua_file lua_need_request_body ssl_certificate_by_lua_block ssl_certificate_by_lua_file ssl_session_fetch_by_lua_block ssl_session_fetch_by_lua_file ssl_session_store_by_lua_block ssl_session_store_by_lua_file lua_shared_dict lua_socket_connect_timeout lua_socket_send_timeout lua_socket_send_lowat lua_socket_read_timeout lua_socket_buffer_size lua_socket_pool_size lua_socket_keepalive_timeout lua_socket_log_errors lua_ssl_ciphers lua_ssl_crl lua_ssl_protocols lua_ssl_trusted_certificate lua_ssl_verify_depth lua_http10_buffering rewrite_by_lua_no_postpone access_by_lua_no_postpone lua_transform_underscores_in_response_headers lua_check_client_abort lua_max_pending_timers lua_max_running_timers lua_sa_restart
下面我们简单的介绍一下其中一些lua指令:
1) lua_load_resty_core
syntax: lua_load_resty_core on|off
default: lua_load_resty_core on
context: http自v0.10.16版本起该指令就在本模块失效了。当前resty.core模块会在Lua VM初始化的时候被强制加载。在当前的版本,使用此指令不会用任何的作用。
2) lua_capture_error_log
syntax: lua_capture_error_log size
default: none
context: http使用一个指定大小的缓存来捕获所有的nginx错误日志(注: 不仅包括http、http subsystem所产生的错误日志,而是所有),而不是保存到文件或磁盘中。
在设置缓冲区大小时可以使用k、m等单位,例如:
lua_capture_error_log 100k;
根据我们的实践经验,一个4k的缓存大概可以容纳20条典型的错误日志信息。因此,假如我们需要容纳10000条错误日志,那大概就需要2000K大小的缓存空间。
注意事项:
-
当我们设置好缓存之后,该空间就不会增大了。当缓存满时,新的错误日志就会覆盖缓存中最老的日志条目。
-
缓存的大小必须大于单条错误日志消息的最大长度(openresty中单条错误日志消息的长度最大可以是4K, nginx生产版本单条错误日志消息的最大长度可以是2k)
-
可以通过lua-resty-core库的ngx.errlog模块的get_logs()函数来读取Lua land缓冲区的消息。这个lua API将返回捕获的错误日志消息,并且将读取到的消息从全局捕获缓冲区中移除,从而为任何新的错误日志消息腾出空间。基于这个原因,如果可以保证用户读取缓冲区中的错误日志消息足够快的话,则我们可以不必将缓冲区空间配置的过大。
-
error_log指令指定的日志级别将会影响该缓冲区的捕获,该缓冲区仅捕获不低于error_log指令指定的日志级别的消息。用户可以通过Lua API函数errlog.set_filter_level()来动态设置更高的过滤日志级别,这会比静态的error_log指令更灵活。
-
如果没有使用
./configure选项--with-debug来编译openresty或nginx,则无法捕获调试日志。由于高昂的开销,在生产版本中强烈建议禁用调试日志。
3) lua_code_cache
syntax: lua_code_cache on | off
default: lua_code_cache on
context: http, server, location, location if启用或禁用对Lua代码的缓存。当启用对Lua代码的缓存时,其可以缓存由*_by_lua_file指令(如set_by_lua_file、content_by_lua_file)Lua代码,也可以缓存Lua模块中的脚本代码。
-
从
0.9.3版本开始,当关闭lua_code_cache时,通过ngx_lua处理的每个请求都将在一个单独的Lua VM实例中运行。因此,由set_by_lua_file、content_by_lua_file、access_by_lua_file等指令所引用的Lua files都不会被缓存,所有使用到的Lua模块都将从头开始加载。通过该指令,开发人员就可以采用edit-and-refresh模式来调试。 -
注意,当我们编辑nginx.conf配置文件中的内联Lua代码(比如set_by_lua、content_by_lua、access_by_lua、rewrite_by_lua指令中的Lua代码)时,运行中的nginx将不能够动态的感知到这些更新,这是因为只有nginx配置文件解析器才能够解析nginx.conf配置文件。因此当我们更改这些内联lua代码时,我们可能必须得重启nginx。
-
即使是启用了代码缓存,由
*_by_lua_file指令中的dofile或loadfile所加载的Lua脚本也不能被缓存(除非你自己缓存了结果)。通常我们可以使用init_by_lua或者init_by_lua_file指令来加载所有这些文件,又或者使这些Lua文件成为真正的Lua模块,然后通过require来进行加载。 -
ngx_lua模块不支持Apache mod_lua模块可用的stat模式;
-
强烈建议在生产环境中启用Lua代码缓存,在调试环境中如果不会太影响性能的话我们可以不启用。例如,在禁用lua代码缓存后,
hello, worldLua示例的性能可能会下降一个数量级。
4) lua_package_path
syntax: lua_package_path <lua-style-path-str>
default: The content of LUA_PATH environment variable or Lua's compiled-in defaults.
context: http设置set_by_lua、content_by_lua等指令中搜索Lua模块的路径。这个路径字符串是标准的 lua 路径格式,;;常用于表示原始的搜索路径。
从发行版 v0.5.0rc29 开始,可以在搜索路径中使用特殊符号 $prefix 或 ${prefix}来指示服务器前缀的路径,通常在 Nginx 服务器启动时通过-p PATH命令行选项来指定server prefix。
5) lua_package_cpath
syntax: lua_package_cpath <lua-style-cpath-str>
default: The content of LUA_CPATH environment variable or Lua's compiled-in defaults.
context: http设置set_by_lua、content_by_lua等指令中Lua C模块的搜索路径。这个cpath字符串是标准的lua C路径格式,;;常用于表示原始的cpath搜索路径。
从发行版 v0.5.0rc29 开始,可以在搜索路径中使用特殊符号 $prefix 或 ${prefix}来指示服务器前缀的路径,通常在 Nginx 服务器启动时通过-p PATH命令行选项来指定server prefix。
对于openresy默认路径下的基础lua库,openresy可以自动找到,我们不必在nginx.conf的http配置段中通过如下命令来显式指定(这里假设默认安装路径为/usr/local/openresty):
lua_package_path "/usr/local/openresty/lualib/?.lua;;"; lua_package_cpath "/usr/local/openresty/lualib/?.so;;";
6) init_by_lua
syntax: init_by_lua <lua-script-str>
context: http
phase: loading-config注:注意在 v0.9.17 发行版以后不鼓励使用该指令,应使用init_by_lua_block指令代替
-
当Nginx Master进程(如果有)加载Nginx配置文件的时候,在全局Lua VM级别上运行由参数
<lua-script-str>指定的Lua代码; -
当Nginx接收到
HUP信号并开始重新加载配置文件时,Lua VM将会被重新创建,且init_by_lua也将在新的VM上再次运行。如果lua_code_cache是关闭的(默认打开), init_by_lua处理程序将在每个请求上都运行一次,因此在这种特殊模式下,总是每个请求创建一个独立的Lua VM。 -
通常,你可以通过该hook在服务启动时预加载
一些所用到的Lua模块,并充分利用现代操作系统的写时复制(COW)优化。如下是一个预加载Lua modules的例子:
# this runs before forking out nginx worker processes:
init_by_lua_block { require "cjson" }
server {
location = /api {
content_by_lua_block {
-- the following require() will just return
-- the already loaded module from package.loaded:
ngx.say(require "cjson".encode{dog = 5, cat = 6})
}
}
}
也可以在这个阶段初始化lua_shared_dict shm共享内存。如下是一个例子:
lua_shared_dict dogs 1m;
init_by_lua_block {
local dogs = ngx.shared.dogs;
dogs:set("Tom", 56)
}
server {
location = /api {
content_by_lua_block {
local dogs = ngx.shared.dogs;
ngx.say(dogs:get("Tom"))
}
}
}
但需要注意的是,lua_shared_dict shm共享内存并不能够通过重新加载配置文件(如发送HUP信号)来来进行清除。因此,假如你并不想在init_by_lua代码中重新初始化shm共享内存的话,那么你可以在共享内存中自定义一个flag标志,然后在init_by_lua代码中检查该标志即可。
因为该Lua代码在Nginx fork出 worker子进程之前运行,所以在这里加载的数据或代码将享受到操作系统的COW特性,在worker进程创建时并不会真正的复制数据,从而节省大量的内存。
-
不要在此上下文中初始化你自己的Lua全局变量,因为使用Lua全局变量将会造成一定的性能损失,并可能造成全局名称空间(namespace)污染(请参看Lua Variable Scope章节)。我们推荐的做法是使用适当的
Lua module文件(但不要使用标准Lua函数模块去定义Lua模块,因为它也会污染全局命名空间),同时在 init_by_lua 或其他上下文中调用 require 去加载你自己的模块文件。(require() 会将加载的模块缓存在全局的 Lua 注册表 package.loaded 中,因此你的模块仅在整个 Lua VM 实例中加载一次) -
在该上下文中,仅支持一小部分Nginx Lua API:
-
日志API: ngx.log()和print()
-
共享字典API: ngx.shared.DICT
-
在未来用户请求中,该上下文将支持更多的 Lua 的 Nginx API。
基本上,你可以在此上下文中安全地使用阻塞IO的Lua库,因为在服务器启动期间阻塞master进程完全是可以的。甚至Nginx内核也会在配置加载阶段阻塞(至少在解析 upstream 域名时)。
此外,应该非常小心在此上下文中注册的Lua代码中潜在的安全漏洞,因为Nginx master进程通常在 root 用户下运行。
7) init_by_lua_block
syntax: init_by_lua_block { lua-script }
context: http
phase: loading-config与init_by_lua指令类似,不同之处在于此指令直接在一对花括号({})内部而不是在 Nginx 字符串(需要特殊字符串转义)中内联 lua 代码。例如:
init_by_lua_block {
print("I need no extra escaping here, for example: \r\nblah")
}
8) init_by_lua_file
syntax: init_by_lua_file <path-to-lua-script-file>
context: http
phase: loading-config与init_by_lua等价,除了这里是通过path-to-lua-script-file来指定所要执行的Lua脚本外。
注:当我们使用类似于foo/bar.lua这样的相对路径时,会转换成相对于server prefix的绝对路径。我们可以在Nginx启动的时候通过-p Path来指定server prefix path。
9) init_worker_by_lua
syntax: init_worker_by_lua <lua-script-str>
context: http
phase: starting-worker注:注意在 v0.9.17 发行版以后不鼓励使用该指令,应使用init_worker_by_lua_block指令代替
当启用了Nginx master进程时,则通过init_worker_by_lua所指定的Lua代码会在每个Nginx worker进程启动时执行; 而如果禁用了Nginx master,那么此hook将会在init_by_lua*指令之后执行。
本hook常用于创建每个worker重复发生的计时器(通过ngx.timer.at Lua API),用于后端运行状况检查或其他定时工作。参看如下示例:
init_worker_by_lua '
local delay = 3 -- in seconds
local new_timer = ngx.timer.at
local log = ngx.log
local ERR = ngx.ERR
local check
check = function(premature)
if not premature then
-- do the health check or other routine work
local ok, err = new_timer(delay, check)
if not ok then
log(ERR, "failed to create timer: ", err)
return
end
end
-- do something in timer
end
local hdl, err = new_timer(delay, check)
if not hdl then
log(ERR, "failed to create timer: ", err)
return
end
-- other job in init_worker_by_lua
';
自v0.10.12版本以来,该钩子不再在 cache manager 和 cache loader 进程中运行。
10) init_worker_by_lua_block
syntax: init_worker_by_lua_block { lua-script }
context: http
phase: starting-worker与init_worker_by_lua指令类似,不同之处在于此指令直接在一对花括号({})内部而不是在NGINX字符串文字(需要特殊字符转义)中内联Lua代码。例如:
init_worker_by_lua_block {
print("I need no extra escaping here, for example: \r\nblah")
}
自v0.10.12版本以来,该钩子不再在 cache manager 和 cache loader 进程中运行
11) init_worker_by_lua_file
syntax: init_worker_by_lua_file <lua-file-path>
context: http
phase: starting-worker与init_worker_by_lua等价,除了这里是通过lua-file-path来指定所要执行的Lua脚本外。
自v0.10.12版本以来,该钩子不再在 cache manager 和 cache loader 进程中运行。
12) set_by_lua
syntax: set_by_lua $res <lua-script-str> [$arg1 $arg2 ...]
context: server, server if, location, location if
phase: rewrite注:注意在 v0.9.17 发行版以后不鼓励使用该指令,应使用set_by_lua_block指令代替
-
执行
lua-script-str所指定的Lua代码,参数通过$arg1 $arg2 ....传入,并将输出字符串保存到res中。lua-script-str可以执行Nginx Lua API调用,并且可以从ngx.arg表中获取输入参数(参数索引从1开始)。 -
本指令被设计用于执行
简短、快速的Lua脚本,因为当在执行这一Lua脚本时,其会阻塞Nginx event loop。因此,我们应该尽力避免在lua-script-str中执行耗时任务。 -
本指令的实现原理是通过向ngx_http_rewrite_module的命令列表注入自定义命令。由于本身ngx_http_rewrite_module中的命令并不支持非阻塞IO,因此在本指令中并不能运行Lua API中涉及的
light thread。 -
不能在set_by_lua上下文中执行如下的API函数:
-
输出API函数(例如: ngx.say、ngx.send_headers)
-
控制API函数(例如: ngx.exit)
-
subrequest API函数(例如: ngx.location.capture、ngx.location.capture_multi)
-
Cosocket API函数(例如: ngx.socket.tcp、ngx.req.socket)
-
Sleeping API函数(例如: ngx.sleep)
-
另外,值得注意的是本指令一次只能返回一个值。然而,我们可以使用ngx.var.VARIABLE来实现返回多个值。例如:
location /foo {
set $diff ''; # we have to predefine the $diff variable here
set_by_lua $sum '
local a = 32
local b = 56
ngx.var.diff = a - b; -- write to $diff directly
return a + b; -- return the $sum value normally
';
echo "sum = $sum, diff = $diff";
}
本指令可以和ngx_http_rewrite_module、set-misc-nginx-module、array-var-nginx-module中的指令混合使用。这些指令的执行顺序会按照配置文件中的配置顺序执行(注: 一般nginx 配置文件中的指令是没有顺序的)
set $foo 32; set_by_lua $bar 'return tonumber(ngx.var.foo) + 1'; set $baz "bar: $bar"; # $baz == "bar: 33"
13) set_by_lua_block
syntax: set_by_lua_block $res { lua-script }
context: server, server if, location, location if
phase: rewrite与set-by-lua指令类似,不同之处在于:
-
此指令直接在一对花括号({})内部而不是在NGINX字符串文字(需要特殊字符转义)中内联Lua代码
-
本指令不支持向其传递参数
参看如下使用示例:
set_by_lua_block $res { return 32 + math.cos(32) } # $res now has the value "32.834223360507" or alike.
14) set_by_lua_file
syntax: set_by_lua_file $res <path-to-lua-script-file> [$arg1 $arg2 ...]
context: server, server if, location, location if
phase: rewrite与set-by-lua等价,除了这里是通过path-to-lua-script-file来指定所要执行的Lua脚本外。
-
set-by-lua-file指令支持传递参数字符串,但请注意可能导致的注入攻击
-
当path-to-lua-script-file是一个类似于
foo/bar.lua这样的相对路径,最终会转化成一个相对于server prefix的绝对路径。我们可以在Nginx启动的时候通过-p Path来指定server prefix path -
如果启用了Lua code cache(默认会被启用),则Lua代码会在第一个请求时被加载并缓存。因此,假如我们要修改相应的Lua脚本的话,则我们必须重新加载配置文件。在测试调试过程中,我们可以通过
lua_code_cache指令临时关闭cache,从而避免我们需要每次手动重新加载配置文件。
15) content_by_lua
syntax: content_by_lua <lua-script-str>
context: location, location if
phase: content注:注意在 v0.9.17 发行版以后不鼓励使用该指令,应使用content_by_lua_block指令代替
作为一个content handler,其会为每一个请求执行<lua-script-str>所指定的Lua 代码。该lua代码可能会进行API调用,并且在独立的全局环境(例如 sandbox)中作为一个新派生的协程执行。
不要在同一个location中同时使用该指令和其他的content handler指令。例如,该指令和proxy_pass指令不应该在同一个location中出现。
16) content_by_lua_block
syntax: content_by_lua_block { lua-script }
context: location, location if
phase: content与content_by_lua指令类似,不同之处在于此指令直接在一对花括号({})内部而不是在NGINX字符串文字(需要特殊字符转义)中内联Lua代码。例如:
content_by_lua_block {
ngx.say("I need no extra escaping here, for example: \r\nblah")
}
17) content_by_lua_file
syntax: content_by_lua_file <path-to-lua-script-file>
context: location, location if
phase: content与content_by_lua指令类似,不同之处在于此指令在于通过path-to-lua-script-file来指定所要执行的Lua脚本的路径。
-
可以在
path-to-lua-script-file字串中使用nginx variables以提供更高的灵活性。然而这可能会带来某些风险,不建议使用此方式。 -
当我们指定的是一个类似于
foo/bar.lua这样的相对路径,最终会转化成一个相对于server prefix的绝对路径。我们可以在Nginx启动的时候通过-p Path来指定server prefix path -
如果启用了Lua code cache(默认会被启用),则Lua代码会在第一个请求时被加载并缓存。因此,假如我们要修改相应的Lua脚本的话,则我们必须重新加载配置文件。在测试调试过程中,我们可以通过
lua_code_cache指令临时关闭cache,从而避免我们需要每次手动重新加载配置文件。 -
在文件路径中可以支持nginx variables,这样就可以实现动态的分发。例如:
# CAUTION: contents in nginx var must be carefully filtered,
# otherwise there'll be great security risk!
location ~ ^/app/([-_a-zA-Z0-9/]+) {
set $path $1;
content_by_lua_file /path/to/lua/app/root/$path.lua;
}
注意: 使用此种方式可能存在一定的风险,请对相应的输入参数进行仔细的校验。
18) rewrite_by_lua
syntax: rewrite_by_lua <lua-script-str>
context: http, server, location, location if
phase: rewrite tail注:注意在 v0.9.17 发行版以后不鼓励使用该指令,应使用rewrite_by_lua_block指令代替
-
rewrite_by_lua作为一个rewrite阶段的handler,其会在每一个请求时执行lua-script-str所指定的Lua脚本。在Lua脚本中可以执行nginx lua api调用,并且该调用是通过一个全局环境独立的coroutine来执行。 -
值得注意的是,rewrite_by_lua总是运行于ngx_http_rewrite_module之后,因此如下配置是可以正常工作的:
location /foo {
set $a 12; # create and initialize $a
set $b ""; # create and initialize $b
rewrite_by_lua 'ngx.var.b = tonumber(ngx.var.a) + 1';
echo "res = $b";
}
这是因为set $a 12以及set $b ""是运行与rewrite_by_lua指令之前的。
相反对于下面的配置,将不能够进行正常工作:
? location /foo {
? set $a 12; # create and initialize $a
? set $b ''; # create and initialize $b
? rewrite_by_lua 'ngx.var.b = tonumber(ngx.var.a) + 1';
? if ($b = '13') {
? rewrite ^ /bar redirect;
? break;
? }
?
? echo "res = $b";
? }
这是因为if语句运行于rewrite_by_lua指令之前(这里虽然在配置文件中其写在rewrite_by_lua指令之后)。
针对这种情况,正确的做法是:
location /foo {
set $a 12; # create and initialize $a
set $b ''; # create and initialize $b
rewrite_by_lua '
ngx.var.b = tonumber(ngx.var.a) + 1
if tonumber(ngx.var.b) == 13 then
return ngx.redirect("/bar");
end
';
echo "res = $b";
}
- 通过使用
rewrite_by_lua,我们可以实现类似于ngx_eval模块的功能。例如:
location / {
eval $res {
proxy_pass http://foo.com/check-spam;
}
if ($res = 'spam') {
rewrite ^ /terms-of-use.html redirect;
}
fastcgi_pass ...;
}
如下我们使用rewrite_by_lua来实现:
location = /check-spam {
internal;
proxy_pass http://foo.com/check-spam;
}
location / {
rewrite_by_lua '
local res = ngx.location.capture("/check-spam")
if res.body == "spam" then
return ngx.redirect("/terms-of-use.html")
end
';
fastcgi_pass ...;
}
与任何其他的rewrite阶段的handler一样,rewrite_by_lua也是运行于subrequest中。
-
值得注意的是,当在一个rewrite_by_lua指令中调用ngx.exit(ngx.OK)时,nginx请求处理控制流程仍会继续执行后续的content handler。如果要在
rewrite_by_luahandler中止当前的请求处理,那么在执行ngx.exit时传入如下status参数:-
要返回成功,status的值应该>=200(ngx.HTTP_OK)且<300(ngx.HTTP_SPECIAL_RESPONSE);
-
要返回失败,status的值应该为ngx.HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
-
-
假如使用ngx_http_rewrite_module的rewrite指令来更改URI,并且重新进行location的查找(internal redirections),那么rewrite_by_lua或者rewrite_by_lua_file中的任何Lua脚本序列都将不会被执行。例如:
location /foo {
rewrite ^ /bar;
rewrite_by_lua 'ngx.exit(503)';
}
location /bar {
...
}
这里的Lua代码ngx.exit(503)将不会被执行。这里rewrite ^ /bar与rewrite ^ /bar last类似,都会初始化一个内部重定向。但是假如我们使用break修正符来代替的话,那么将不会执行内部重定向,这样rewrite_by_lua指令就会得到执行。
除非我们启用了rewrite_by_lua_no_postpone,否则rewrite_by_lua指令会在rewrite请求处理的最后阶段才开始执行。
19) rewrite_by_lua_block
syntax: rewrite_by_lua_block { lua-script }
context: http, server, location, location if
phase: rewrite tail与rewrite_by_lua指令类似,不同之处在于此指令直接在一对花括号({})内部而不是在NGINX字符串文字(需要特殊字符转义)中内联Lua代码。例如:
rewrite_by_lua_block {
do_something("hello, world!\nhiya\n")
}
本指令是从v0.9.17版本开始引入的。
20) rewrite_by_lua_file
syntax: rewrite_by_lua_file <path-to-lua-script-file>
context: http, server, location, location if
phase: rewrite tail与rewrite_by_lua指令类似,不同之处在于此指令是通过path-to-lua-script-file来指定要执行的lua脚本的路径。
-
可以在path-to-lua-script-file字串中使用nginx variables,从而可以获得更高的灵活性。但是请注意,这可能会带来某种类型的安全风险,不建议在路径字串中使用nginx variables
-
当我们指定的是一个类似于
foo/bar.lua这样的相对路径,最终会转化成一个相对于server prefix的绝对路径。我们可以在Nginx启动的时候通过-p Path来指定server prefix path -
如果启用了Lua code cache(默认会被启用),则Lua代码会在第一个请求时被加载并缓存。因此,假如我们要修改相应的Lua脚本的话,则我们必须重新加载配置文件。在测试调试过程中,我们可以通过
lua_code_cache指令临时关闭cache,从而避免我们需要每次手动重新加载配置文件。 -
除非我们启用了rewrite_by_lua_no_postpone,否则
rewrite_by_lua指令会在rewrite请求处理的最后阶段才开始执行。
20) access_by_lua
syntax: access_by_lua <lua-script-str>
context: http, server, location, location if
phase: access tail注:注意在 v0.9.17 发行版以后不鼓励使用该指令,应使用access_by_lua_block指令代替
作为一个access阶段的handler,为每一个请求执行lua-script-str所指定的Lua代码。该lua代码可能会进行API调用,并且在独立的全局环境(例如 sandbox)中作为一个新派生的协程执行。
- 本handler会在ngx_http_access_module模块之后运行,因此如下代码可以工作正常:
location / {
deny 192.168.1.1;
allow 192.168.1.0/24;
allow 10.1.1.0/16;
deny all;
access_by_lua '
local res = ngx.location.capture("/mysql", { ... })
...
';
# proxy_pass/fastcgi_pass/...
}
上述代码中,假如client IP在blacklist中,那么在执行access_by_lua指令查询MySQL进行更复杂的身份认证之前,该请求就会被拒绝掉。
- 注意, ngx_auth_request模块可以近似于采用如下代码来实现:
location / {
auth_request /auth;
# proxy_pass/fastcgi_pass/postgres_pass/...
}
采用ngx_lua的实现类似如下:
location / {
access_by_lua '
local res = ngx.location.capture("/auth")
if res.status == ngx.HTTP_OK then
return
end
if res.status == ngx.HTTP_FORBIDDEN then
ngx.exit(res.status)
end
ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
';
# proxy_pass/fastcgi_pass/postgres_pass/...
}
-
与其他的access phase handlers一样,access_by_lua也不能够运行在subrequests中
-
值得注意的是,当在access_by_lua中执行
ngx.exit(ngx.OK)时,nginx请求处理控制流程仍会继续执行后续的content handler。如果想要在access_by_lua脚本中终止当前的请求处理,那么在执行ngx.exit()时传入如下status参数:-
要返回成功,status的值应该>=200(ngx.HTTP_OK)且<300(ngx.HTTP_SPECIAL_RESPONSE);
-
要返回失败,status的值应该为ngx.HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
-
注: 上面请注意ngx.ok与ngx.HTTP_OK的不同,调用ngx.exit(ngx.ok)时才会执行后续的content handler
- 从版本
v0.9.20开始,可以使用access_by_lua_no_postpone指令来控制在access请求处理阶段的哪一个时间点来执行access_by_lua指令;
21) access_by_lua_block
syntax: access_by_lua_block { lua-script }
context: http, server, location, location if
phase: access tail与access_by_lua指令相似,不同之处在于此指令直接在一对花括号({})内部而不是在NGINX字符串文字(需要特殊字符转义)中内联Lua代码。例如:
access_by_lua_block {
do_something("hello, world!\nhiya\n")
}
本指令首次引入是在v0.9.17版本。
22) access_by_lua_file
syntax: access_by_lua_file <path-to-lua-script-file>
context: http, server, location, location if
phase: access tail与access_by_lua指令类似,不同之处在于此指令是通过path-to-lua-script-file来指定要执行的lua脚本的路径。
-
可以在path-to-lua-script-file字串中使用nginx variables,从而可以获得更高的灵活性。但是请注意,这可能会带来某种类型的安全风险,不建议在路径字串中使用nginx variables
-
当我们指定的是一个类似于
foo/bar.lua这样的相对路径,最终会转化成一个相对于server prefix的绝对路径。我们可以在Nginx启动的时候通过-p Path来指定server prefix path -
如果启用了Lua code cache(默认会被启用),则Lua代码会在第一个请求时被加载并缓存。因此,假如我们要修改相应的Lua脚本的话,则我们必须重新加载配置文件。在测试调试过程中,我们可以通过
lua_code_cache指令临时关闭cache,从而避免我们需要每次手动重新加载配置文件。
23) lua_shared_dict
syntax: lua_shared_dict <name> <size>
default: no
context: http
phase: depends on usage声明一个共享内存区域,用于存储Lua共享字典。共享内存由当前Nginx实例的所有worker进程所共享。
在指定size时可以接受k和m两种单位:
http {
lua_shared_dict dogs 10m;
...
}
通常我们要求size最小为8k或12k。
可以查看ngx.shared.DICT以获得更详细的信息介绍。
2. 为Lua提供的Nginx API
nginx.conf配置文件中大量的*_by_lua、*_by_lua_block、*_by_lua_file指令类似于Lua API网关。如下所描述的Nginx Lua API只能够在这些配置指令的Lua代码中调用。
这些所暴露出来的Lua API通常在ngx与ndk这两个标准的package中。这些包位于ngx_lua默认的全局作用域中,在ngx_lua指令中可以直接使用。
同时,这些package也可以被引入到外部的Lua模块中。例如:
local say = ngx.say
local _M = {}
function _M.foo(a)
say(a)
end
return _M
此外,也可以在外部Lua模块直接require这些包:
local ngx = require "ngx" local ndk = require "ndk"
注: 从版本v0.2.1rc19开始就可以采用此种方式引入这些package
如果想在用户自己的Lua代码中执行网络IO操作的话,那么就只能通过Nginx Lua API调用来实现,否则可能会造成Nginx event loop阻塞并严重的降低性能。而对于磁盘操作读写少量数据的话,我们可以使用标准的Lua IO库即可,但无论如何我们还是应该避免大数据量的文件IO读写操作,因为其可能会严重阻塞Nginx进程。我们强烈推荐将所有的Network IO以及disk IO操作委托给nginx subrequest来处理,以达到最高的性能(通过ngx.location.capture或其他类似的指令)。
3. 示例
1) nginx.conf
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
include conf.d/*.conf;
lua_package_path 'conf.d/lua/?.lua;;';
}2) conf.d/alibaba_s3.conf
server {
listen 80 default_server;
server_name alibaba_s3;
chunked_transfer_encoding on;
location /{
deny all;
}
location ~* /proxy {
# note: can not use lua in this block
internal;
set_by_lua $target_backend 'return ngx.ctx.target_backend';
proxy_pass http://$target_backend$request_uri;
}
location ~* ^/([a-z]\w+)/(\S+) {
# this is the object operation
set $bucket $1;
set $object $2;
access_by_lua_block{
if ngx.var.bucket == "aaa" then
ngx.say(ngx.var.bucket)
ngx.say(ngx.var.object)
ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_OK)
end
}
proxy_pass http://rgw;
#echo $bucket;
#echo $2;
}
location ~* ^/([a-z]\w+) {
# this is the bucket operations(Note: must be placed after object operations)
set $bucket $1;
echo "bucket operations";
echo $1;
}
}
[参考]

