os/unix/ngx_setproctitle源代码分析
本文首先介绍一下Linux中setproctitle()的原理,然后给出nginx中相应的源代码并进行解析。
1. 介绍
每一个C程序都有个main函数作为程序启动的入口函数。main函数的原型是:
int main(int argc, char *argv[])其中,argc表示命令行参数的个数; argv是一个指针数组,保存所有命令行字符串。而Linux进程名称是通过命令行参数argv[0]来表示的。
而我们可以通过char **environ这一系统定义的全局变量来访问操作系统环境变量。
命令行参数argv与环境变量environ是放在一块连续的内存中表示的,并且environ仅跟在argv后面。
下面我们给出两个示例程序:
1) 环境变量environ存放位置
test3.c源代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
extern char **environ;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
int i;
for(i = 0;i<argc;i++)
{
printf("0x%x : %s\n",argv[i], argv[i]);
}
printf("\n");
for(i = 0; environ[i] && i < 2; i++)
{
printf("0x%x : %s\n",environ[i], environ[i]);
}
printf("\nargv: 0x%x environ: 0x%x\n",argv, environ);
for(i =0;i<argc+2;i++)
{
printf("&argv[%d]: 0x%x\n",i,&argv[i]);
}
return 0x0;
}编译执行(当前测试允许运行在64位操作系统):
root@ubuntu:~/test-src# gcc -o test3 test3.c root@ubuntu:~/test-src# ./test3 date=2017-10-26 0xbfd1f84e : ./test2 0xbfd1f856 : date=2017-10-26 0xbfd1f866 : XDG_SESSION_ID=1 0xbfd1f877 : SHELL=/bin/bash argv: 0xbfd1e954 environ: 0xbfd1e960 &argv[0]: 0xbfd1e954 &argv[1]: 0xbfd1e958 &argv[2]: 0xbfd1e95c &argv[3]: 0xbfd1e960
由上测试结果,我们发现argv与environ内存是按如下方式组织的:
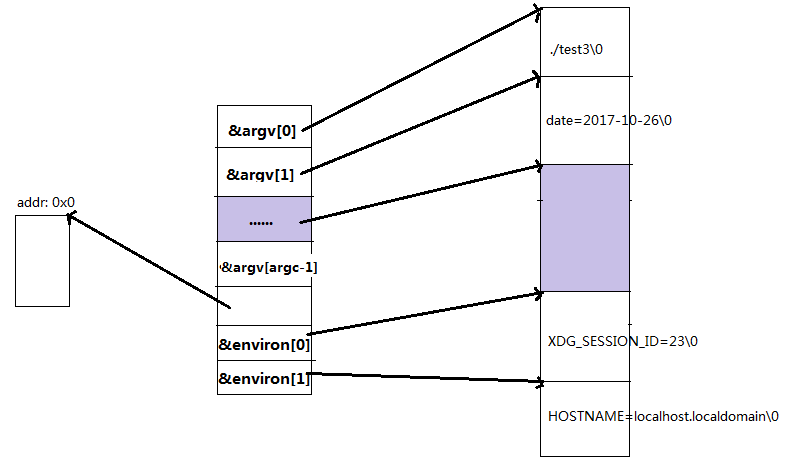
2) 程序proctitle
test4.c源代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
char cmd[128]={0};
const char proctitle[] = "just for test";
char *title2 = "hello, new title";
pid_t id = getpid();
sprintf(cmd,"ps -aux | awk '{ if ($2 == %d) print $0}'",id);
printf("cmd: %s\n\n",cmd);
system(cmd);
strcpy(argv[0],proctitle);
system(cmd);
argv[0] = title2;
printf("\nargv[0]: %s\n",argv[0]);
system(cmd);
return 0;
}编译运行:
[root@localhost test-src]# gcc -o test4 test4.c
[root@localhost test-src]# ./test4
cmd: ps -aux | awk '{ if ($2 == 52608) print $0}'
root 52608 0.0 0.0 4160 340 pts/2 S+ 19:19 0:00 ./test4
root 52608 0.0 0.0 4160 340 pts/2 S+ 19:19 0:00 just for test
argv[0]: hello, new title
root 52608 0.0 0.0 4160 340 pts/2 S+ 19:19 0:00 just for test
通过上述运行结果,程序proctitle存放于argv[0]初始指向的位置, 后续手动更改argv[0]指向位置是不会更改proctitle的。
但是这种方式是以破坏性的方式来修改进程title的。由于程序的参数存储空间的后面紧跟的就是环境变量的存储位置,在不考虑参数的破坏性的情况下,过长的title也会损坏环境变量environ的值。因此在nginx中,是将环境变量进行移位存储处理的。下面我们会介绍nginx设置进程title的思路。
2. nginx修改进程title思路
先看如下说明:
/* * To change the process title in Linux and Solaris we have to set argv[1] * to NULL and to copy the title to the same place where the argv[0] points to. * However, argv[0] may be too small to hold a new title. Fortunately, Linux * and Solaris store argv[] and environ[] one after another. So we should * ensure that is the continuous memory and then we allocate the new memory * for environ[] and copy it. After this we could use the memory starting * from argv[0] for our process title. * * The Solaris's standard /bin/ps does not show the changed process title. * You have to use "/usr/ucb/ps -w" instead. Besides, the UCB ps does not * show a new title if its length less than the origin command line length. * To avoid it we append to a new title the origin command line in the * parenthesis. */
2.1 初始化函数
由于nginx中考虑多进程的情况,因此其会在初始化时就完成environ的迁移。下面首先是初始化函数:
extern char **environ;
static char *ngx_os_argv_last;
ngx_int_t
ngx_init_setproctitle(ngx_log_t *log)
{
u_char *p;
size_t size;
ngx_uint_t i;
size = 0;
for (i = 0; environ[i]; i++) {
size += ngx_strlen(environ[i]) + 1;
}
p = ngx_alloc(size, log);
if (p == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
ngx_os_argv_last = ngx_os_argv[0];
for (i = 0; ngx_os_argv[i]; i++) {
if (ngx_os_argv_last == ngx_os_argv[i]) {
ngx_os_argv_last = ngx_os_argv[i] + ngx_strlen(ngx_os_argv[i]) + 1;
}
}
for (i = 0; environ[i]; i++) {
if (ngx_os_argv_last == environ[i]) {
size = ngx_strlen(environ[i]) + 1;
ngx_os_argv_last = environ[i] + size;
ngx_cpystrn(p, (u_char *) environ[i], size);
environ[i] = (char *) p;
p += size;
}
}
ngx_os_argv_last--;
return NGX_OK;
}结合上面的图,该段代码的主要功能就是: 将紧接着argv后面的环境变量environ拷贝到新的空间中。具体过程如下:
1. 求出environ长度并分配新的空间 2. 求出argv最后一个参数的末尾位置 3. 如果environ仅跟在argv最后一个参数末尾位置后,则条件ngx_os_argv_last == environ[i]成立,此时会将 environ拷贝到新分配的空间中。 4. ngx_os_argv_last最后指向用于存放参数的最后一个位置(注意:从源代码可以看出,*ngx_os_argv_last值为0, 下面ngx_setproctitle()就未对ngx_os_argv_last这一位置再做处理)。
2.2 具体的设置title函数
看如下具体的设置title函数:
void
ngx_setproctitle(char *title)
{
u_char *p;
#if (NGX_SOLARIS)
ngx_int_t i;
size_t size;
#endif
ngx_os_argv[1] = NULL;
p = ngx_cpystrn((u_char *) ngx_os_argv[0], (u_char *) "nginx: ",
ngx_os_argv_last - ngx_os_argv[0]);
p = ngx_cpystrn(p, (u_char *) title, ngx_os_argv_last - (char *) p);
#if (NGX_SOLARIS)
size = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ngx_argc; i++) {
size += ngx_strlen(ngx_argv[i]) + 1;
}
if (size > (size_t) ((char *) p - ngx_os_argv[0])) {
/*
* ngx_setproctitle() is too rare operation so we use
* the non-optimized copies
*/
p = ngx_cpystrn(p, (u_char *) " (", ngx_os_argv_last - (char *) p);
for (i = 0; i < ngx_argc; i++) {
p = ngx_cpystrn(p, (u_char *) ngx_argv[i],
ngx_os_argv_last - (char *) p);
p = ngx_cpystrn(p, (u_char *) " ", ngx_os_argv_last - (char *) p);
}
if (*(p - 1) == ' ') {
*(p - 1) = ')';
}
}
#endif
if (ngx_os_argv_last - (char *) p) {
ngx_memset(p, NGX_SETPROCTITLE_PAD, ngx_os_argv_last - (char *) p);
}
ngx_log_debug1(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_CORE, ngx_cycle->log, 0,
"setproctitle: \"%s\"", ngx_os_argv[0]);
}具体过程如下:
1. 设置argv[1]为NULL
2. 拷贝"nginx: "到ngx_os_argv[0]
3. 追加上title到ngx_os_argv上
4. 如果是NGX_SOLARIS操作系统,如果原先proctitle的长度大于当前strlen("nginx: "+title)值的话,则将原来的proctitle放在
括号中追加到ngx_os_argv上
5. 后续填充空格
3. ngx_setproctitle相关源文件
这里我们把整个ngx_setproctitle相关的源文件贴出,以做参考:
1) 头文件ngx_setproctitle.h
/*
* Copyright (C) Igor Sysoev
* Copyright (C) Nginx, Inc.
*/
#ifndef _NGX_SETPROCTITLE_H_INCLUDED_
#define _NGX_SETPROCTITLE_H_INCLUDED_
#if (NGX_HAVE_SETPROCTITLE)
/* FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD */
#define ngx_init_setproctitle(log) NGX_OK
#define ngx_setproctitle(title) setproctitle("%s", title)
#else /* !NGX_HAVE_SETPROCTITLE */
#if !defined NGX_SETPROCTITLE_USES_ENV
#if (NGX_SOLARIS)
#define NGX_SETPROCTITLE_USES_ENV 1
#define NGX_SETPROCTITLE_PAD ' '
ngx_int_t ngx_init_setproctitle(ngx_log_t *log);
void ngx_setproctitle(char *title);
#elif (NGX_LINUX) || (NGX_DARWIN)
#define NGX_SETPROCTITLE_USES_ENV 1
#define NGX_SETPROCTITLE_PAD '\0'
ngx_int_t ngx_init_setproctitle(ngx_log_t *log);
void ngx_setproctitle(char *title);
#else
#define ngx_init_setproctitle(log) NGX_OK
#define ngx_setproctitle(title)
#endif /* OSes */
#endif /* NGX_SETPROCTITLE_USES_ENV */
#endif /* NGX_HAVE_SETPROCTITLE */
#endif /* _NGX_SETPROCTITLE_H_INCLUDED_ */此处NGX_HAVE_SETPROCTITLE并没有定义.
2) 源文件ngx_setproctitle.c
/*
* Copyright (C) Igor Sysoev
* Copyright (C) Nginx, Inc.
*/
#include <ngx_config.h>
#include <ngx_core.h>
#if (NGX_SETPROCTITLE_USES_ENV)
/*
* To change the process title in Linux and Solaris we have to set argv[1]
* to NULL and to copy the title to the same place where the argv[0] points to.
* However, argv[0] may be too small to hold a new title. Fortunately, Linux
* and Solaris store argv[] and environ[] one after another. So we should
* ensure that is the continuous memory and then we allocate the new memory
* for environ[] and copy it. After this we could use the memory starting
* from argv[0] for our process title.
*
* The Solaris's standard /bin/ps does not show the changed process title.
* You have to use "/usr/ucb/ps -w" instead. Besides, the UCB ps does not
* show a new title if its length less than the origin command line length.
* To avoid it we append to a new title the origin command line in the
* parenthesis.
*/
extern char **environ;
static char *ngx_os_argv_last;
ngx_int_t
ngx_init_setproctitle(ngx_log_t *log)
{
u_char *p;
size_t size;
ngx_uint_t i;
size = 0;
for (i = 0; environ[i]; i++) {
size += ngx_strlen(environ[i]) + 1;
}
p = ngx_alloc(size, log);
if (p == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
ngx_os_argv_last = ngx_os_argv[0];
for (i = 0; ngx_os_argv[i]; i++) {
if (ngx_os_argv_last == ngx_os_argv[i]) {
ngx_os_argv_last = ngx_os_argv[i] + ngx_strlen(ngx_os_argv[i]) + 1;
}
}
for (i = 0; environ[i]; i++) {
if (ngx_os_argv_last == environ[i]) {
size = ngx_strlen(environ[i]) + 1;
ngx_os_argv_last = environ[i] + size;
ngx_cpystrn(p, (u_char *) environ[i], size);
environ[i] = (char *) p;
p += size;
}
}
ngx_os_argv_last--;
return NGX_OK;
}
void
ngx_setproctitle(char *title)
{
u_char *p;
#if (NGX_SOLARIS)
ngx_int_t i;
size_t size;
#endif
ngx_os_argv[1] = NULL;
p = ngx_cpystrn((u_char *) ngx_os_argv[0], (u_char *) "nginx: ",
ngx_os_argv_last - ngx_os_argv[0]);
p = ngx_cpystrn(p, (u_char *) title, ngx_os_argv_last - (char *) p);
#if (NGX_SOLARIS)
size = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ngx_argc; i++) {
size += ngx_strlen(ngx_argv[i]) + 1;
}
if (size > (size_t) ((char *) p - ngx_os_argv[0])) {
/*
* ngx_setproctitle() is too rare operation so we use
* the non-optimized copies
*/
p = ngx_cpystrn(p, (u_char *) " (", ngx_os_argv_last - (char *) p);
for (i = 0; i < ngx_argc; i++) {
p = ngx_cpystrn(p, (u_char *) ngx_argv[i],
ngx_os_argv_last - (char *) p);
p = ngx_cpystrn(p, (u_char *) " ", ngx_os_argv_last - (char *) p);
}
if (*(p - 1) == ' ') {
*(p - 1) = ')';
}
}
#endif
if (ngx_os_argv_last - (char *) p) {
ngx_memset(p, NGX_SETPROCTITLE_PAD, ngx_os_argv_last - (char *) p);
}
ngx_log_debug1(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_CORE, ngx_cycle->log, 0,
"setproctitle: \"%s\"", ngx_os_argv[0]);
}
#endif /* NGX_SETPROCTITLE_USES_ENV */
[参看]:

