ceph recovery研究(1)
当PG完成了Peering过程后,处于Active状态的PG就可以对外提供服务了。如果该PG的各个副本上有不一致的对象,就需要进行修复。Ceph的修复过程有两种:Recovery和Backfill。
void ReplicatedPG::do_request(
OpRequestRef& op,
ThreadPool::TPHandle &handle)
{
assert(!op_must_wait_for_map(get_osdmap()->get_epoch(), op));
if (can_discard_request(op)) {
return;
}
if (flushes_in_progress > 0) {
dout(20) << flushes_in_progress << " flushes_in_progress pending " << "waiting for active on " << op << dendl;
waiting_for_peered.push_back(op);
op->mark_delayed("waiting for peered");
return;
}
if (!is_peered()) {
// Delay unless PGBackend says it's ok
if (pgbackend->can_handle_while_inactive(op)) {
bool handled = pgbackend->handle_message(op);
assert(handled);
return;
} else {
waiting_for_peered.push_back(op);
op->mark_delayed("waiting for peered");
return;
}
}
...
}注:此外,根据ceph数据读写流程,OSD::dispatch_session_waiting()等阶段均有可能阻塞请求
Recovery是仅依据PG日志中的缺失记录来修复不一致的对象。Backfill是PG通过重新扫描所有的对象,对比发现缺失的对象,通过整体拷贝来修复。当一个OSD失效时间过长导致无法根据PG日志来修复,或者新加入的OSD导致数据迁移时,就会启动Backfill过程。
从第10章可知,PG完成Peering过程后,就处于activate状态,如果需要Recovery,就产生DoRecovery事件,触发修复操作。如果需要Backfill,机会产生RequestBackfill事件来触发Backfill操作。在PG的修复过程中,如果既有需要Recovery过程的OSD,又有需要Backfill过程的OSD,那么处理过程需要先进行Recovery过程的修复,再完成Backfill过程的修复。
void ReplicatedPG::on_activate()
{
// all clean?
if (needs_recovery()) {
dout(10) << "activate not all replicas are up-to-date, queueing recovery" << dendl;
queue_peering_event(
CephPeeringEvtRef(
std::make_shared<CephPeeringEvt>(
get_osdmap()->get_epoch(),
get_osdmap()->get_epoch(),
DoRecovery())));
} else if (needs_backfill()) {
dout(10) << "activate queueing backfill" << dendl;
queue_peering_event(
CephPeeringEvtRef(
std::make_shared<CephPeeringEvt>(
get_osdmap()->get_epoch(),
get_osdmap()->get_epoch(),
RequestBackfill())));
} else {
dout(10) << "activate all replicas clean, no recovery" << dendl;
queue_peering_event(
CephPeeringEvtRef(
std::make_shared<CephPeeringEvt>(
get_osdmap()->get_epoch(),
get_osdmap()->get_epoch(),
AllReplicasRecovered())));
}
publish_stats_to_osd();
if (!backfill_targets.empty()) {
last_backfill_started = earliest_backfill();
new_backfill = true;
assert(!last_backfill_started.is_max());
dout(5) << "on activate: bft=" << backfill_targets << " from " << last_backfill_started << dendl;
for (set<pg_shard_t>::iterator i = backfill_targets.begin(); i != backfill_targets.end(); ++i) {
dout(5) << "target shard " << *i << " from " << peer_info[*i].last_backfill << dendl;
}
}
hit_set_setup();
agent_setup();
}本章介绍Ceph的数据修复的实现过程。首先介绍数据修复的资源预约的知识,然后通过介绍修复的状态转换图,大概了解整个数据修复的过程。最后分别详细介绍Recovery过程和Backfill过程的具体实现。
1. 资源预约
在数据修复的过程中,为了控制一个OSD上正在修复的PG最大数目,需要资源预约,在主OSD上和从OSD上都需要预约。如果没有预约成功,需要阻塞等待。一个OSD能同时修复的最大PG数在配置选项osd_max_backfills中设置,默认值为1。
类AsyncReserver用来管理资源预约,其模板参数<T>为要预约的资源类型。该类实现了异步的资源预约。当成功完成资源预约后,就调用注册的回调函数通知调用方预约成功(src/common/AsyncReserver.h):
template <typename T>
class AsyncReserver {
Finisher *f; //当预约成功,用来执行的回调函数
unsigned max_allowed; //定义允许的最大资源数量,在这里指允许修复的PG的数量
unsigned min_priority; //最小的优先级
Mutex lock;
//优先级到待预约资源链表的映射,pair<T, Context *>定义预约的资源和注册的回调函数(注:值越大,优先级越高)
map<unsigned, list<pair<T, Context*> > > queues;
//资源在queues链表中的位置指针
map<T, pair<unsigned, typename list<pair<T, Context*> >::iterator > > queue_pointers;
//预约成功,正在使用的资源
set<T> in_progress;
};在OSDService中,我们看到执行如下操作时需要资源预约:
class OSDService {
public:
// -- backfill_reservation --
Finisher reserver_finisher;
AsyncReserver<spg_t> local_reserver;
AsyncReserver<spg_t> remote_reserver;
public:
AsyncReserver<spg_t> snap_reserver;
};
OSDService::OSDService(OSD *osd) :
reserver_finisher(cct),
local_reserver(&reserver_finisher, cct->_conf->osd_max_backfills, cct->_conf->osd_min_recovery_priority),
remote_reserver(&reserver_finisher, cct->_conf->osd_max_backfills, cct->_conf->osd_min_recovery_priority),
snap_reserver(&reserver_finisher,cct->_conf->osd_max_trimming_pgs),
{
}1.1 资源预约
函数request_reservation()用于预约资源:
/**
* Requests a reservation
*
* Note, on_reserved may be called following cancel_reservation. Thus,
* the callback must be safe in that case. Callback will be called
* with no locks held. cancel_reservation must be called to release the
* reservation slot.
*/
void request_reservation(
T item, ///< [in] reservation key
Context *on_reserved, ///< [in] callback to be called on reservation
unsigned prio
) {
Mutex::Locker l(lock);
assert(!queue_pointers.count(item) &&
!in_progress.count(item));
queues[prio].push_back(make_pair(item, on_reserved));
queue_pointers.insert(make_pair(item, make_pair(prio,--(queues[prio]).end())));
do_queues();
}
void do_queues() {
typename map<unsigned, list<pair<T, Context*> > >::reverse_iterator it;
for (it = queues.rbegin();it != queues.rend() &&in_progress.size() < max_allowed && it->first >= min_priority;
++it) {
while (in_progress.size() < max_allowed &&!it->second.empty()) {
pair<T, Context*> p = it->second.front();
queue_pointers.erase(p.first);
it->second.pop_front();
f->queue(p.second);
in_progress.insert(p.first);
}
}
}具体处理过程如下:
1) 把要请求的资源根据优先级添加到queue队列中,并在queue_pointers中添加其对应的位置指针:
queues[prio].push_back(make_pair(item, on_reserved));
queue_pointers.insert(make_pair(item, make_pair(prio,--(queues[prio]).end())));2) 调用函数do_queues()用来检查queue中的所有资源预约申请:从优先级高的请求开始检查,如果还有配额并且其请求的优先级至少不小于最小优先级,就把资源授权给它。
3) 在queue队列中删除该资源预约请求,并在queue_ponters删除该资源的位置信息。把该资源添加到in_progress队列中,并把请求相应的回调函数添加到Finisher类中,使其执行该回调函数。最后通知预约成功。
1.2 取消预约
函数cancle_reservation()用于释放拥有的不再使用的资源:
/**
* Cancels reservation
*
* Frees the reservation under key for use.
* Note, after cancel_reservation, the reservation_callback may or
* may not still be called.
*/
void cancel_reservation(
T item ///< [in] key for reservation to cancel
) {
Mutex::Locker l(lock);
if (queue_pointers.count(item)) {
unsigned prio = queue_pointers[item].first;
delete queue_pointers[item].second->second;
queues[prio].erase(queue_pointers[item].second);
queue_pointers.erase(item);
} else {
in_progress.erase(item);
}
do_queues();
}具体处理过程如下:
1) 如果该资源还在queue队列中,就删除(这属于异常情况的处理);否则在in_progress队列中删除该资源
2) 调用do_queues()函数把该资源重新授权给其他等待的请求。
2. 数据修复状态转换图
如下图11-1所示的是修复过程状态转换图。当PG进入Active状态后,就进入默认的子状态Activating:
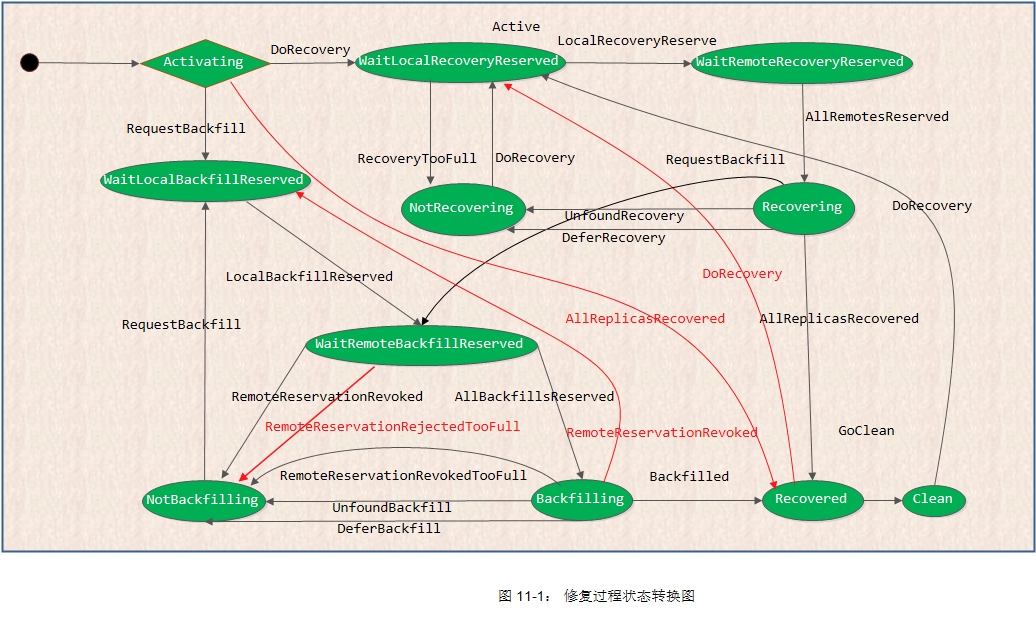
数据修复的状态转换过程如下所示:
情况1:当进入Activating状态后,如果此时所有的副本都完整,不需要修复,其状态转移过程如下:
1) Activating状态接收到AllReplicasRecovered事件,直接转换到Recovered状态
2) Recovered状态接收到GoClean事件,整个PG转入Clean状态
代码参考如下:
void ReplicatedPG::on_activate()
{
...
else {
dout(10) << "activate all replicas clean, no recovery" << dendl;
queue_peering_event(
CephPeeringEvtRef(
std::make_shared<CephPeeringEvt>(
get_osdmap()->get_epoch(),
get_osdmap()->get_epoch(),
AllReplicasRecovered())));
}
...
}
struct Activating : boost::statechart::state< Activating, Active >, NamedState {
typedef boost::mpl::list <
boost::statechart::transition< AllReplicasRecovered, Recovered >,
boost::statechart::transition< DoRecovery, WaitLocalRecoveryReserved >,
boost::statechart::transition< RequestBackfill, WaitLocalBackfillReserved >
> reactions;
explicit Activating(my_context ctx);
void exit();
};
struct Recovered : boost::statechart::state< Recovered, Active >, NamedState {
typedef boost::mpl::list<
boost::statechart::transition< GoClean, Clean >,
boost::statechart::custom_reaction< AllReplicasActivated >
> reactions;
explicit Recovered(my_context ctx);
void exit();
boost::statechart::result react(const AllReplicasActivated&) {
post_event(GoClean());
return forward_event();
}
};情况2: 当进入Activating状态后,没有Recovery过程,只需要Backfill过程的情况:
1) Activating状态直接接收到RequestBackfill事件,进入WaitLocalBackfillReserved状态;
2) 当WaitLocalBackfillReserved状态接收到LocalBackfillReserved事件后,意味着本地资源预约成功,转入WaitRemoteBackfillReserved;
3) 所有副本资源预约成功后,主PG就会接收到AllBackfillsReserved事件,进入Backfilling状态,开始实际数据Backfill操作过程;
4) Backfilling状态接收到Backfilled事件,标志Backfill过程完成,进入Recovered状态;
5) 异常处理:当在状态WaitRemoteBackfillReserved和Backfilling接收到RemoteReservationRejected事件,表明资源预约失败,进入NotBackfilling状态,再次等待RequestBackfilling事件来重新发起Backfill过程;
注:此情况的代码分析过程,我们会在后面详细讲解
情况3:当PG既需要Recovery过程,也可能需要Backfill过程时,PG先完成Recovery过程,再完成Backfill过程,特别强调这里的先后顺序。其具体过程如下:
1) Activating状态:在接收到DoRecovery事件后,转移到WaitLocalRecoveryReserved状态;
2) WaitLocalRecoveryReserved状态:在这个状态中完成本地资源的预约。当收到LocalRecoveryReserved事件后,标志着本地资源预约的完成,转移到WaitRemoteRecoveryReserved状态;
3) WaitRemoteRecoveryReserved状态:在这个状态中完成远程资源的预约。当接收到AllRemotesReserved事件,标志着该PG在所有参与数据修复的从OSD上完成资源预约,进入Recoverying状态;
4) Recoverying状态:在这个状态完成实际的数据修复工作。完成后把PG设置为PG_STATE_RECOVERING状态,并把PG添加到recovery_wq工作队列中,开始启动数据修复:
PG::RecoveryState::Recovering::Recovering(my_context ctx)
: my_base(ctx),
NamedState(context< RecoveryMachine >().pg->cct, "Started/Primary/Active/Recovering")
{
context< RecoveryMachine >().log_enter(state_name);
PG *pg = context< RecoveryMachine >().pg;
pg->state_clear(PG_STATE_RECOVERY_WAIT);
pg->state_set(PG_STATE_RECOVERING);
pg->publish_stats_to_osd();
pg->osd->queue_for_recovery(pg);
}5) 在Recoverying状态完成Recovery工作后,如果需要Backfill工作,就接收RequestBackfill事件,转入Backfill流程;
6) 如果没有Backfill工作流程,直接接收AllReplicasRecovered事件,转入Recovered状态;
7) Recovered状态:到达本状态,意味着已经完成数据修复工作。当收到事件GoClean后,PG就进入clean状态。
3. Recovery过程
数据修复的依据是在Peering过程中产生的如下信息:
-
主副本上的缺失对象的信息保存在pg_log类的pg_missing_t结构中;
-
各从副本上的缺失对象信息保存在OSD对应的peer_missing中的pg_missing_t结构中;
-
缺失对象的位置信息保存在类MissingLoc中
根据以上信息,就可以知道该PG里各个OSD缺失的对象信息,以及该缺失的对象目前在哪些OSD上有完整的信息。基于上面的信息,数据修复过程就相对比较清晰:
-
对于主OSD缺失的对象,随机选择一个拥有该对象的OSD,把数据拉取过来;
-
对于replica缺失的对象,从主副本上把缺失的对象数据推送到从副本上来完成数据的修复;
-
对于比较特殊的快照对象,在修复时加入了一些优化的方法;
3.1 触发修复
Recovery过程由PG的主OSD来触发并控制整个修复的过程。在修复的过程中,先修复主OSD上缺失(或者不一致)的对象,然后修复从OSD上缺失的对象。
3.1.1 Recovery触发流程
下面我们给出PG从Activating状态进入Recovering状态的调用流程:
1) Active/Activating产生DoRecovery()事件
void ReplicatedPG::on_activate()
{
// all clean?
if (needs_recovery()) {
dout(10) << "activate not all replicas are up-to-date, queueing recovery" << dendl;
queue_peering_event(
CephPeeringEvtRef(
std::make_shared<CephPeeringEvt>(
get_osdmap()->get_epoch(),
get_osdmap()->get_epoch(),
DoRecovery())));
}
...
}2) 进入WaitLocalRecoveryReserved状态
struct Activating : boost::statechart::state< Activating, Active >, NamedState {
typedef boost::mpl::list <
boost::statechart::transition< AllReplicasRecovered, Recovered >,
boost::statechart::transition< DoRecovery, WaitLocalRecoveryReserved >,
boost::statechart::transition< RequestBackfill, WaitLocalBackfillReserved >
> reactions;
explicit Activating(my_context ctx);
void exit();
};上面我们看到Activating状态下接收到DoRecovery事件后直接进入WaitLocalRecoveryReserved状态。
WaitLocalRecoveryReserved状态进行本地资源预约,过程如下:
struct WaitLocalRecoveryReserved : boost::statechart::state< WaitLocalRecoveryReserved, Active >, NamedState {
typedef boost::mpl::list <
boost::statechart::transition< LocalRecoveryReserved, WaitRemoteRecoveryReserved >
> reactions;
explicit WaitLocalRecoveryReserved(my_context ctx);
void exit();
};
PG::RecoveryState::WaitLocalRecoveryReserved::WaitLocalRecoveryReserved(my_context ctx)
: my_base(ctx),
NamedState(context< RecoveryMachine >().pg->cct, "Started/Primary/Active/WaitLocalRecoveryReserved")
{
context< RecoveryMachine >().log_enter(state_name);
PG *pg = context< RecoveryMachine >().pg;
pg->state_set(PG_STATE_RECOVERY_WAIT);
pg->osd->local_reserver.request_reservation(
pg->info.pgid,
new QueuePeeringEvt<LocalRecoveryReserved>(
pg, pg->get_osdmap()->get_epoch(),
LocalRecoveryReserved()),
pg->get_recovery_priority());
pg->publish_stats_to_osd();
}上面我们看到,当本地资源预约成功,就会产生一个LocalRecoveryReserved事件,并投递到PG的消息队列中。WaitLocalRecoveryReserved状态收到LocalRecoveryReserved事件后,直接跳转到WaitRemoteRecoveryReserved状态
3)WaitRemoteRecoveryReserved状态进行远程资源预约
struct WaitRemoteRecoveryReserved : boost::statechart::state< WaitRemoteRecoveryReserved, Active >, NamedState {
typedef boost::mpl::list <
boost::statechart::custom_reaction< RemoteRecoveryReserved >,
boost::statechart::transition< AllRemotesReserved, Recovering >
> reactions;
set<pg_shard_t>::const_iterator remote_recovery_reservation_it;
explicit WaitRemoteRecoveryReserved(my_context ctx);
boost::statechart::result react(const RemoteRecoveryReserved &evt);
void exit();
};
PG::RecoveryState::WaitRemoteRecoveryReserved::WaitRemoteRecoveryReserved(my_context ctx)
: my_base(ctx),
NamedState(context< RecoveryMachine >().pg->cct, "Started/Primary/Active/WaitRemoteRecoveryReserved"),
remote_recovery_reservation_it(context< Active >().remote_shards_to_reserve_recovery.begin())
{
context< RecoveryMachine >().log_enter(state_name);
post_event(RemoteRecoveryReserved());
}
boost::statechart::result
PG::RecoveryState::WaitRemoteRecoveryReserved::react(const RemoteRecoveryReserved &evt) {
PG *pg = context< RecoveryMachine >().pg;
if (remote_recovery_reservation_it != context< Active >().remote_shards_to_reserve_recovery.end()) {
assert(*remote_recovery_reservation_it != pg->pg_whoami);
ConnectionRef con = pg->osd->get_con_osd_cluster(
remote_recovery_reservation_it->osd, pg->get_osdmap()->get_epoch());
if (con) {
pg->osd->send_message_osd_cluster(
new MRecoveryReserve(
MRecoveryReserve::REQUEST,
spg_t(pg->info.pgid.pgid, remote_recovery_reservation_it->shard),
pg->get_osdmap()->get_epoch()),
con.get());
}
++remote_recovery_reservation_it;
} else {
post_event(AllRemotesReserved());
}
return discard_event();
}
PG::RecoveryState::Active::Active(my_context ctx)
: my_base(ctx),
NamedState(context< RecoveryMachine >().pg->cct, "Started/Primary/Active"),
remote_shards_to_reserve_recovery(
unique_osd_shard_set(
context< RecoveryMachine >().pg->pg_whoami,
context< RecoveryMachine >().pg->actingbackfill)),
remote_shards_to_reserve_backfill(
unique_osd_shard_set(
context< RecoveryMachine >().pg->pg_whoami,
context< RecoveryMachine >().pg->backfill_targets)),
all_replicas_activated(false)
{
...
}在WaitRemoteRecoveryReserved构造函数中直接抛出RemoteRecoveryReserved事件,之后在WaitRemoteRecoveryReserved::react(const RemoteRecoveryReserved &)函数中,逐个的向remote_shards_to_reserve_recovery中的每一个OSD副本发送MRecoveryReserve消息,进行远程资源预约。
注:如下是远程副本的处理
远程副本OSD接收到MRecoveryReserve::REQUEST消息后,调用OSD::handle_pg_recovery_reserve()函数进行处理:
void OSD::handle_pg_recovery_reserve(OpRequestRef op)
{
MRecoveryReserve *m = static_cast<MRecoveryReserve*>(op->get_req());
assert(m->get_type() == MSG_OSD_RECOVERY_RESERVE);
if (!require_osd_peer(op->get_req()))
return;
if (!require_same_or_newer_map(op, m->query_epoch, false))
return;
PG::CephPeeringEvtRef evt;
if (m->type == MRecoveryReserve::REQUEST) {
evt = PG::CephPeeringEvtRef(
new PG::CephPeeringEvt(
m->query_epoch,
m->query_epoch,
PG::RequestRecovery()));
}
...
}在handle_pg_recovery_reserve()函数中,产生PG::RequestRecovery()事件。由RepNotRecovering对该事件进行处理,直接进入RepWaitRecoveryReserved。在RepWaitRecoveryReserved状态下,进行远程资源预约,预约成功产生RemoteRecoveryReserved事件,向PG Primary报告远程资源预约成功,且该PG Replica自身进入RepRecovering状态:
struct RepNotRecovering : boost::statechart::state< RepNotRecovering, ReplicaActive>, NamedState {
typedef boost::mpl::list<
boost::statechart::custom_reaction< RequestBackfillPrio >,
boost::statechart::transition< RequestRecovery, RepWaitRecoveryReserved >,
boost::statechart::transition< RecoveryDone, RepNotRecovering > // for compat with pre-reservation peers
> reactions;
explicit RepNotRecovering(my_context ctx);
boost::statechart::result react(const RequestBackfillPrio &evt);
void exit();
};
struct RepWaitRecoveryReserved : boost::statechart::state< RepWaitRecoveryReserved, ReplicaActive >, NamedState {
typedef boost::mpl::list<
boost::statechart::custom_reaction< RemoteRecoveryReserved >
> reactions;
explicit RepWaitRecoveryReserved(my_context ctx);
void exit();
boost::statechart::result react(const RemoteRecoveryReserved &evt);
};注:ReplicaActive状态的默认初始子状态为RepNotRecovering。
4)进入Recovering状态
当所有的远程资源都预约成功之后,就会进入Recovering状态。
struct Recovering : boost::statechart::state< Recovering, Active >, NamedState {
typedef boost::mpl::list <
boost::statechart::custom_reaction< AllReplicasRecovered >,
boost::statechart::custom_reaction< RequestBackfill >
> reactions;
explicit Recovering(my_context ctx);
void exit();
void release_reservations();
boost::statechart::result react(const AllReplicasRecovered &evt);
boost::statechart::result react(const RequestBackfill &evt);
};
PG::RecoveryState::Recovering::Recovering(my_context ctx)
: my_base(ctx),
NamedState(context< RecoveryMachine >().pg->cct, "Started/Primary/Active/Recovering")
{
context< RecoveryMachine >().log_enter(state_name);
PG *pg = context< RecoveryMachine >().pg;
pg->state_clear(PG_STATE_RECOVERY_WAIT);
pg->state_set(PG_STATE_RECOVERING);
pg->publish_stats_to_osd();
pg->osd->queue_for_recovery(pg);
}在Recovering的构造函数中,清除PG的PG_STATE_RECOVERY_WAIT状态,设置PG状态为PG_STATE_RECOVERING状态,然后将PG加入到recovery队列:
bool OSDService::queue_for_recovery(PG *pg)
{
bool b = recovery_wq.queue(pg);
if (b)
dout(10) << "queue_for_recovery queued " << *pg << dendl;
else
dout(10) << "queue_for_recovery already queued " << *pg << dendl;
return b;
}3.1.2 OSD::do_recovery()
由数据修复状态转换过程可知,当PG处于Active/Recoverying状态后,该PG被加入到OSD的RecoveryWQ工作队列中。在recovery_wq里,其工作队列的线程池的处理函数调用do_recovery()函数来执行实际的数据修复操作:
struct RecoveryWQ : public ThreadPool::WorkQueue<PG> {
void _process(PG *pg, ThreadPool::TPHandle &handle) override {
osd->do_recovery(pg, handle);
pg->put("RecoveryWQ");
}
}recovery_wq;
void OSD::do_recovery(PG *pg, ThreadPool::TPHandle &handle){
if (g_conf->osd_recovery_sleep > 0) {
handle.suspend_tp_timeout();
utime_t t;
t.set_from_double(g_conf->osd_recovery_sleep);
t.sleep();
handle.reset_tp_timeout();
dout(20) << __func__ << " slept for " << t << dendl;
}
// see how many we should try to start. note that this is a bit racy.
recovery_wq.lock();
int max = MIN(cct->_conf->osd_recovery_max_active - recovery_ops_active,
cct->_conf->osd_recovery_max_single_start);
if (max > 0) {
dout(10) << "do_recovery can start " << max << " (" << recovery_ops_active << "/" << cct->_conf>osd_recovery_max_active
<< " rops)" << dendl;
recovery_ops_active += max; // take them now, return them if we don't use them.
} else {
dout(10) << "do_recovery can start 0 (" << recovery_ops_active << "/" << cct->_conf->osd_recovery_max_active
<< " rops)" << dendl;
}
recovery_wq.unlock();
if (max <= 0) {
dout(10) << "do_recovery raced and failed to start anything; requeuing " << *pg << dendl;
recovery_wq.queue(pg);
return;
} else {
pg->lock_suspend_timeout(handle);
if (pg->deleting || !(pg->is_peered() && pg->is_primary())) {
pg->unlock();
goto out;
}
dout(10) << "do_recovery starting " << max << " " << *pg << dendl;
#ifdef DEBUG_RECOVERY_OIDS
dout(20) << " active was " << recovery_oids[pg->info.pgid] << dendl;
#endif
int started = 0;
bool more = pg->start_recovery_ops(max, handle, &started);
dout(10) << "do_recovery started " << started << "/" << max << " on " << *pg << dendl;
// If no recovery op is started, don't bother to manipulate the RecoveryCtx
if (!started && (more || !pg->have_unfound())) {
pg->unlock();
goto out;
}
PG::RecoveryCtx rctx = create_context();
rctx.handle = &handle;
/*
* if we couldn't start any recovery ops and things are still
* unfound, see if we can discover more missing object locations.
* It may be that our initial locations were bad and we errored
* out while trying to pull.
*/
if (!more && pg->have_unfound()) {
pg->discover_all_missing(*rctx.query_map);
if (rctx.query_map->empty()) {
dout(10) << "do_recovery no luck, giving up on this pg for now" << dendl;
recovery_wq.lock();
recovery_wq._dequeue(pg);
recovery_wq.unlock();
}
}
pg->write_if_dirty(*rctx.transaction);
OSDMapRef curmap = pg->get_osdmap();
pg->unlock();
dispatch_context(rctx, pg, curmap);
}
out:
recovery_wq.lock();
if (max > 0) {
assert(recovery_ops_active >= max);
recovery_ops_active -= max;
}
recovery_wq._wake();
recovery_wq.unlock();
}函数do_recovery()由RecoveryWQ工作队列的线程池的线程执行。其输入的参数为要修复的PG,具体处理流程如下:
1) 配置选项osd_recovery_sleep设置了线程做一次修复后的休眠时间。如果设置了该值,每次线程开始先休眠相应的时间长度。该参数默认值为0,不需要休眠。
2) 加入recovery_wq.lock()锁,用来保护recovery_wq队列以及变量recovery_ops_active。计算可修复对象的max值,其值为允许修复的最大对象数osd_recovery_max_active减去正在修复的对象数recovery_ops_active,然后调用函数recovery_wq.unlock()解锁;
3) 如果max小于等于0,即没有修复对象的配额,就把PG重新加入工作队列recovery_wq中并返回;否则如果max大于0,调用pg->lock_suspend_timeout(handle)重新设置线程超时时间。检查PG的状态,如果该PG处于正在被删除的状态,或者既不处于peered状态,也不是主OSD,则直接退出;
4) 调用函数pg->start_recovery_ops()修复,返回值more为还需要修复的对象数目。输出参数started为已经开始修复的对象数。
5) 如果more为0,也就是没有修复的对象了。但是pg->have_unfound()不为0,还有unfound对象(即缺失的对象,目前不知道在哪个OSD上能找到完整的对象),调用函数PG::discover_all_missing()在might_have_unfound队列中的OSD上继续查找该对象,查找的方法就是给相关的OSD发送获取OSD的pg_log的消息。
注:对于unfound的对象,是放到最后来进行恢复
6) 如果rctx.query_map->empty()为空,也就是没有找到其他OSD去获取pg_log来查找unfound对象,就结束该PG的recover操作,调用函数从recovery_wq._dequeue(pg)删除PG;
7) 函数dispatch_context()做收尾工作,在这里发送query_map的请求,把ctx.transaction的事务提交到本地对象存储中。
由上过程分析可知,do_recovery()函数的核心功能是计算要修复对象的max值,然后调用函数start_recovery_ops()来启动修复。
注:当本次recovery完成会回调ReplicatedPG::on_global_recover(),如果该PG仍然还有数据要recovery,则在on_global_recover()中会调用PG::finish_recovery_op()将该PG重新加回recovery_wq中
3.2 ReplicatedPG
类ReplicatedPG用于处理Replicate类型PG的相关修复操作。下面分析它用于修复的start_recovery_ops()函数及其相关函数的具体实现。
3.2.1 函数start_recovery_ops()
函数start_recovery_ops()调用recovery_primary()和recovery_replicas()来修复该PG上对象的主副本和从副本。修复完成后,如果仍需要Backfill过程,则抛出相应事件触发PG状态机,开始Backfill的修复进程。
注:这里ReplicatedPG::start_recovery_ops()操作包括recovery和backfill两者,优先进行recovery操作。函数的返回结果为是否成功启动recovery/backfill操作
class PG : DoutPrefixProvider {
protected:
BackfillInterval backfill_info;
map<pg_shard_t, BackfillInterval> peer_backfill_info;
bool backfill_reserved; //当前backfill操作是否预约成功,在进入Backfilling状态时会设置为true
bool backfill_reserving; //当前是否开始了backfill操作的预约(注:从"开始预约"到"预约成功"是有一段过程的)
};
bool ReplicatedPG::start_recovery_ops(int max, ThreadPool::TPHandle &handle,int *ops_started)
{
int& started = *ops_started;
started = 0;
bool work_in_progress = false;
assert(is_primary());
if (!state_test(PG_STATE_RECOVERING) && !state_test(PG_STATE_BACKFILL)) {
/* TODO: I think this case is broken and will make do_recovery()
* unhappy since we're returning false */
dout(10) << "recovery raced and were queued twice, ignoring!" << dendl;
return false;
}
const pg_missing_t &missing = pg_log.get_missing();
int num_missing = missing.num_missing();
int num_unfound = get_num_unfound();
if (num_missing == 0) {
info.last_complete = info.last_update;
}
if (num_missing == num_unfound) {
// All of the missing objects we have are unfound.
// Recover the replicas.
started = recover_replicas(max, handle);
}
if (!started) {
// We still have missing objects that we should grab from replicas.
started += recover_primary(max, handle);
}
if (!started && num_unfound != get_num_unfound()) {
// second chance to recovery replicas
started = recover_replicas(max, handle);
}
if (started)
work_in_progress = true;
bool deferred_backfill = false;
if (recovering.empty() && state_test(PG_STATE_BACKFILL) && !backfill_targets.empty() && started < max &&
missing.num_missing() == 0 && waiting_on_backfill.empty()) {
if (get_osdmap()->test_flag(CEPH_OSDMAP_NOBACKFILL)) {
dout(10) << "deferring backfill due to NOBACKFILL" << dendl;
deferred_backfill = true;
} else if (get_osdmap()->test_flag(CEPH_OSDMAP_NOREBALANCE) && !is_degraded()) {
dout(10) << "deferring backfill due to NOREBALANCE" << dendl;
deferred_backfill = true;
} else if (!backfill_reserved) {
dout(10) << "deferring backfill due to !backfill_reserved" << dendl;
if (!backfill_reserving) {
dout(10) << "queueing RequestBackfill" << dendl;
backfill_reserving = true;
queue_peering_event(
CephPeeringEvtRef(
std::make_shared<CephPeeringEvt>(
get_osdmap()->get_epoch(),
get_osdmap()->get_epoch(),
RequestBackfill())));
}
deferred_backfill = true;
} else {
started += recover_backfill(max - started, handle, &work_in_progress);
}
}
dout(10) << " started " << started << dendl;
osd->logger->inc(l_osd_rop, started);
if (!recovering.empty() || work_in_progress || recovery_ops_active > 0 || deferred_backfill)
return work_in_progress;
assert(recovering.empty());
assert(recovery_ops_active == 0);
dout(10) << __func__ << " needs_recovery: " << missing_loc.get_needs_recovery() << dendl;
dout(10) << __func__ << " missing_loc: " << missing_loc.get_missing_locs() << dendl;
int unfound = get_num_unfound();
if (unfound) {
dout(10) << " still have " << unfound << " unfound" << dendl;
return work_in_progress;
}
if (missing.num_missing() > 0) {
// this shouldn't happen!
osd->clog->error() << info.pgid << " recovery ending with " << missing.num_missing() << ": " << missing.missing << "\n";
return work_in_progress;
}
if (needs_recovery()) {
// this shouldn't happen!
// We already checked num_missing() so we must have missing replicas
osd->clog->error() << info.pgid << " recovery ending with missing replicas\n";
return work_in_progress;
}
if (state_test(PG_STATE_RECOVERING)) {
state_clear(PG_STATE_RECOVERING);
if (needs_backfill()) {
dout(10) << "recovery done, queuing backfill" << dendl;
queue_peering_event(
CephPeeringEvtRef(
std::make_shared<CephPeeringEvt>(
get_osdmap()->get_epoch(),
get_osdmap()->get_epoch(),
RequestBackfill())));
} else {
dout(10) << "recovery done, no backfill" << dendl;
queue_peering_event(
CephPeeringEvtRef(
std::make_shared<CephPeeringEvt>(
get_osdmap()->get_epoch(),
get_osdmap()->get_epoch(),
AllReplicasRecovered())));
}
} else { // backfilling
state_clear(PG_STATE_BACKFILL);
dout(10) << "recovery done, backfill done" << dendl;
queue_peering_event(
CephPeeringEvtRef(
std::make_shared<CephPeeringEvt>(
get_osdmap()->get_epoch(),
get_osdmap()->get_epoch(),
Backfilled())));
}
return false;
}该函数具体处理过程如下:
1) 首先检查OSD,确保该OSD是PG的主OSD。如果PG不处于PG_STATE_RECOVERING或者PG_STATE_BACKFILL的状态则退出;
2) 从pg_log获取missing对象,它保存了主OSD缺失的对象。参数num_missing为主OSD缺失的对象数目;num_unfound为该PG上缺失的对象却没有找到该对象其他正确副本所在的OSD;如果num_missing为0,说明主OSD不缺失对象,直接设置info.last_complete为最新版本info.last_update的值;
注:unfound对象是missing对象的一个子集
3) 如果num_missing等于num_unfound,说明主OSD所缺失对象都为unfound类型的对象,先调用函数ReplicatedPG::recover_replicas()启动修复replica上的对象;
4) 如果started为0,也就是已经启动修复的对象数量为0,调用函数ReplicatedPG::recover_primary()修复主OSD上的对象;
5) 如果started仍然为0,且num_unfound有变化,再次启动ReplicatedPG::recover_replicas()修复副本;
6) 如果started不为0,设置work_in_progress的值为true;
7) 如果recovering队列为空,也就是没有正在进行Recovery操作的对象,状态为PG_STATE_BACKFILL,并且backfill_targets不为空,started小于max,missing.num_missing()为0的情况下:
a) 如果标志get_osdmap()->test_flag(CEPH_OSDMAP_NOBACKFILL)设置了,就推迟Backfill过程;
b) 如果标志CEPH_OSDMAP_NOREBALANCE设置了,且不是degrade的状态,推迟Backfill过程;
c) 如果backfill_reserved没有设置,就抛出RequestBackfill事件给状态机,启动Backfill过程;
d) 否则,调用函数ReplicatedPG::recover_backfill()开始Backfill过程
8) 最后PG如果处于PG_STATE_RECOVERING状态,并且对象修复成功,就检查:如果需要Backfill过程,就向PG的状态机发送RequestBackfill事件;如果不需要Backfill过程,就抛出AllReplicasRecovered事件;
9) 否则,PG的状态就是PG_STATE_BACKFILL状态,清除该状态,抛出Backfilled事件;
接下来,我们会讲述:
-
recover_primary()修复PG主OSD上缺失的对象
-
recover_replicas()修复PG副本OSD上缺失的对象
-
recover_backfill()执行backfill过程
3.2.2 函数recover_primary()
函数recover_primary()用来修复一个PG的主OSD上缺失的对象:
class ReplicatedBackend : public PGBackend {
struct RPGHandle : public PGBackend::RecoveryHandle {
map<pg_shard_t, vector<PushOp> > pushes;
map<pg_shard_t, vector<PullOp> > pulls;
};
/// @see PGBackend::open_recovery_op
RPGHandle *_open_recovery_op() {
return new RPGHandle();
}
PGBackend::RecoveryHandle *open_recovery_op() {
return _open_recovery_op();
}
};
/**
* do one recovery op.
* return true if done, false if nothing left to do.
*/
int ReplicatedPG::recover_primary(int max, ThreadPool::TPHandle &handle)
{
assert(is_primary());
const pg_missing_t &missing = pg_log.get_missing();
dout(10) << "recover_primary recovering " << recovering.size()<< " in pg" << dendl;
dout(10) << "recover_primary " << missing << dendl;
dout(25) << "recover_primary " << missing.missing << dendl;
// look at log!
pg_log_entry_t *latest = 0;
int started = 0;
int skipped = 0;
PGBackend::RecoveryHandle *h = pgbackend->open_recovery_op();
map<version_t, hobject_t>::const_iterator p = missing.rmissing.lower_bound(pg_log.get_log().last_requested);
while (p != missing.rmissing.end()) {
handle.reset_tp_timeout();
hobject_t soid;
version_t v = p->first;
if (pg_log.get_log().objects.count(p->second)) {
latest = pg_log.get_log().objects.find(p->second)->second;
assert(latest->is_update());
soid = latest->soid;
} else {
latest = 0;
soid = p->second;
}
const pg_missing_t::item& item = missing.missing.find(p->second)->second;
++p;
hobject_t head = soid;
head.snap = CEPH_NOSNAP;
eversion_t need = item.need;
dout(10) << "recover_primary " << soid << " " << item.need << (missing.is_missing(soid) ? " (missing)":"")
<< (missing.is_missing(head) ? " (missing head)":"") << (recovering.count(soid) ? " (recovering)":"")
<< (recovering.count(head) ? " (recovering head)":"") << dendl;
if (latest) {
switch (latest->op) {
case pg_log_entry_t::CLONE:
/*
* Handling for this special case removed for now, until we
* can correctly construct an accurate SnapSet from the old
* one.
*/
break;
case pg_log_entry_t::LOST_REVERT:
{
if (item.have == latest->reverting_to) {
ObjectContextRef obc = get_object_context(soid, true);
if (obc->obs.oi.version == latest->version) {
// I'm already reverting
dout(10) << " already reverting " << soid << dendl;
} else {
dout(10) << " reverting " << soid << " to " << latest->prior_version << dendl;
obc->ondisk_write_lock();
obc->obs.oi.version = latest->version;
ObjectStore::Transaction t;
bufferlist b2;
obc->obs.oi.encode(b2);
assert(!pool.info.require_rollback());
t.setattr(coll, ghobject_t(soid), OI_ATTR, b2);
recover_got(soid, latest->version);
missing_loc.add_location(soid, pg_whoami);
++active_pushes;
osd->store->queue_transaction(osr.get(), std::move(t),
new C_OSD_AppliedRecoveredObject(this, obc),
new C_OSD_CommittedPushedObject(
this,
get_osdmap()->get_epoch(),
info.last_complete),
new C_OSD_OndiskWriteUnlock(obc));
continue;
}
} else {
/*
* Pull the old version of the object. Update missing_loc here to have the location
* of the version we want.
*
* This doesn't use the usual missing_loc paths, but that's okay:
* - if we have it locally, we hit the case above, and go from there.
* - if we don't, we always pass through this case during recovery and set up the location
* properly.
* - this way we don't need to mangle the missing code to be general about needing an old
* version...
*/
eversion_t alternate_need = latest->reverting_to;
dout(10) << " need to pull prior_version " << alternate_need << " for revert " << item << dendl;
for (map<pg_shard_t, pg_missing_t>::iterator p = peer_missing.begin();p != peer_missing.end(); ++p)
if (p->second.is_missing(soid, need) && p->second.missing[soid].have == alternate_need) {
missing_loc.add_location(soid, p->first);
}
dout(10) << " will pull " << alternate_need << " or " << need << " from one of " << missing_loc.get_locations(soid) << dendl;
}
}
break;
}
}
if (!recovering.count(soid)) {
if (recovering.count(head)) {
++skipped;
} else {
int r = recover_missing(soid, need, get_recovery_op_priority(), h);
switch (r) {
case PULL_YES:
++started;
break;
case PULL_OTHER:
++started;
case PULL_NONE:
++skipped;
break;
default:
assert(0);
}
if (started >= max)
break;
}
}
// only advance last_requested if we haven't skipped anything
if (!skipped)
pg_log.set_last_requested(v);
}
pgbackend->run_recovery_op(h, get_recovery_op_priority());
return started;
}其处理过程如下:
1) 调用pgbackend->open_recovery_op()返回一个PG类型相关的PGBackend::RecoveryHandle。对于ReplicatedPG其对应的RecoveryHandle为RPGHandle,内部有两个map,保存了Push和Pull操作的封装PushOp和PullOp:
struct RPGHandle : public PGBackend::RecoveryHandle {
map<pg_shard_t, vector<PushOp> > pushes;
map<pg_shard_t, vector<PullOp> > pulls;
};
//src/osd/osd_types.h
struct PushOp {
hobject_t soid;
eversion_t version;
bufferlist data;
interval_set<uint64_t> data_included;
bufferlist omap_header;
map<string, bufferlist> omap_entries;
map<string, bufferlist> attrset;
ObjectRecoveryInfo recovery_info;
ObjectRecoveryProgress before_progress;
ObjectRecoveryProgress after_progress;
static void generate_test_instances(list<PushOp*>& o);
void encode(bufferlist &bl) const;
void decode(bufferlist::iterator &bl);
ostream &print(ostream &out) const;
void dump(Formatter *f) const;
uint64_t cost(CephContext *cct) const;
};
struct PullOp {
hobject_t soid;
ObjectRecoveryInfo recovery_info;
ObjectRecoveryProgress recovery_progress;
static void generate_test_instances(list<PullOp*>& o);
void encode(bufferlist &bl) const;
void decode(bufferlist::iterator &bl);
ostream &print(ostream &out) const;
void dump(Formatter *f) const;
uint64_t cost(CephContext *cct) const;
};2) last_requested为上次修复的指针,通过调用lower_bound()函数来获取还没有修复的对象;
3) 遍历每一个未被修复的对象:latest为日志记录中保存的该缺失对象的最后一条日志,soid为缺失的对象。如果latest不为空:
关于pg_log_entry_t相关操作的说明请参看如下:
/**
* pg_log_entry_t - single entry/event in pg log
*
*/
struct pg_log_entry_t {
enum {
MODIFY = 1, // some unspecified modification (but not *all* modifications)
CLONE = 2, // cloned object from head
DELETE = 3, // deleted object
BACKLOG = 4, // event invented by generate_backlog [deprecated]
LOST_REVERT = 5, // lost new version, revert to an older version.
LOST_DELETE = 6, // lost new version, revert to no object (deleted).
LOST_MARK = 7, // lost new version, now EIO
PROMOTE = 8, // promoted object from another tier
CLEAN = 9, // mark an object clean
};
};a) 如果该日志记录是pg_log_entry_t::CLONE类型,这里不做任何的特殊处理,直到成功获取snapshot相关的信息SnapSet后再处理;
b) 如果该日志记录类型为pg_log_entry_t::LOST_REVERT类型:该revert操作为数据不一致时,管理员通过命令行强行回退到指定版本,reverting_to记录了回退的版本:
-
如果item.have等于latest->reverting_to版本,也就是通过日志记录显示当前已经拥有回退的版本,那么就获取对象的ObjectContext,如果检查对象当前的版本obc->obs.io.version等于latest->version,说明该回退操作完成;
-
如果item.have等于latest->reverting_to,但是对象当前的版本obc->obs.io.version不等于latest->version,说明没有执行回退操作,直接修改对象的版本号为latest->version即可。
-
否则,需要拉取该reverting_to版本的对象,这里不做特殊的处理,只是检查所有OSD是否拥有该版本的对象,如果有就加入到missing_loc记录该版本的位置信息,由后续修复继续来完成。(注:因为早期已经检查了各个副本OSD,因此这里只检查peering_missing即可)
c) 如果该对象在recovering过程中,表明正在修复,或者其head对象正在修复,跳过,并计数增加skipped;否则调用函数ReplicatedPG::recover_missing()来修复。
4) 调用函数pgbackend->run_recovery_op(),把PullOp或者PushOp封装的消息发送出去;
注:关于PullOp或PushOp的构造是在ReplicatedPG::recover_missing()中完成的,我们后面会详细介绍。
下面举例说明,当最后的日志记录类型为LOST_REVERT时的修复过程:
例11-1 日志修复过程
PG日志的记录如下: 每个单元代表一条日志记录,分别为对象的名字和版本以及操作,版本的格式为(epoch, version)。灰色的部分代表本OSD上缺失的日志记录,该日志记录是从权威日志记录中拷贝过来的,所以当前该日志记录是连续完整的。

情况1: 正常情况的修复
缺失的对象列表为[obj1,obj2]。当前修复对象为obj1。由日志记录可知,对象obj1被修改过三次,分别为版本6,7,8。当前拥有的obj1对象的版本have值为4,修复时只修复到最后修改的版本8即可。
情况2: 最后一个操作为LOST_REVERT类型的操作
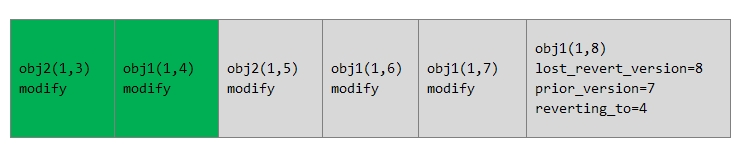
对于要修复的对象obj1,最后一次操作为LOST_REVERT类型的操作,该操作当前版本version为8,修改前的版本prior_version为7,回退版本reverting_to为4。
在这种情况下,日志显示当前已经有版本4,检查对象obj1的实际版本,也就是object_info里保存的版本号:
1) 如果该值是8,说明最后一次revert操作成功,不需要做任何修复动作;
2) 如果该值是4,说明LOST_REVERT操作就没有执行。当然数据内容已经是版本4了,只需要修改object_info的版本为8即可。
如果回退的版本reverting_to不是版本4,而是版本6,那么最终还是需要把obj1的数据修复到版本6的数据。Ceph在这里的处理,仅仅是检查其他OSD缺失的对象中是否有版本6,如果有,就加入到missing_loc中,记录拥有该版本的OSD位置,待后续继续修复。
3.2.3 函数recover_missing()
函数ReplicatedPG::recover_missing()用于恢复missing对象。在修复snap对象时,必须首先修复head对象或者snapdir对象,获取SnapSet信息,然后才能修复快照对象自己。
/*
* Return values:
* NONE - didn't pull anything
* YES - pulled what the caller wanted
* OTHER - needed to pull something else first (_head or _snapdir)
*/
enum { PULL_NONE, PULL_OTHER, PULL_YES };
int ReplicatedPG::recover_missing(
const hobject_t &soid, eversion_t v,
int priority,
PGBackend::RecoveryHandle *h)
{
if (missing_loc.is_unfound(soid)) {
dout(7) << "pull " << soid << " v " << v << " but it is unfound" << dendl;
return PULL_NONE;
}
// is this a snapped object? if so, consult the snapset.. we may not need the entire object!
ObjectContextRef obc;
ObjectContextRef head_obc;
if (soid.snap && soid.snap < CEPH_NOSNAP) {
// do we have the head and/or snapdir?
hobject_t head = soid.get_head();
if (pg_log.get_missing().is_missing(head)) {
if (recovering.count(head)) {
dout(10) << " missing but already recovering head " << head << dendl;
return PULL_NONE;
} else {
int r = recover_missing(head, pg_log.get_missing().missing.find(head)->second.need, priority,h);
if (r != PULL_NONE)
return PULL_OTHER;
return PULL_NONE;
}
}
head = soid.get_snapdir();
if (pg_log.get_missing().is_missing(head)) {
if (recovering.count(head)) {
dout(10) << " missing but already recovering snapdir " << head << dendl;
return PULL_NONE;
} else {
int r = recover_missing(
head, pg_log.get_missing().missing.find(head)->second.need, priority,h);
if (r != PULL_NONE)
return PULL_OTHER;
return PULL_NONE;
}
}
// we must have one or the other
head_obc = get_object_context(soid.get_head(),false,0);
if (!head_obc)
head_obc = get_object_context(soid.get_snapdir(),false,0);
assert(head_obc);
}
start_recovery_op(soid);
assert(!recovering.count(soid));
recovering.insert(make_pair(soid, obc));
pgbackend->recover_object(soid,v,head_obc,obc,h);
return PULL_YES;
}具体实现如下:
1) 检查如果对象soid是unfound,直接返回PULL_NONE值。暂时无法修复处于unfound的对象;
2) 如果修复的是snap对象:
a) 查看如果对应的head对象处于missing,递归调用函数recover_missing()先修复head对象;
b) 查看如果snapdir对象处于missing,就递归调用函数recover_missing()先修复snapdir对象;
3) 从head对象或者snapdir对象中获取head_obc信息;
4) 调用函数pgbackend->recover_object()把要修复的操作信息封装到PullOp或者PushOp对象中,并添加到RecoveryHandle结构中。
[参看]

